Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Poster III: Treatment
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Disease activity is one of the major predictors of damage accrual and mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Glucocorticoid use, especially in high dose, could underestimate the inflammatory status in SLE patients. Based on that, a modification of the SLEDAI accounting for glucocorticoid dose has been proposed, the SLEDAI glucocorticoid index (SGI)1. The aim of this study is to evaluate the impact of SGI and Mex-SLEDAI GI (M-SGI) as predictors of damage and mortality.
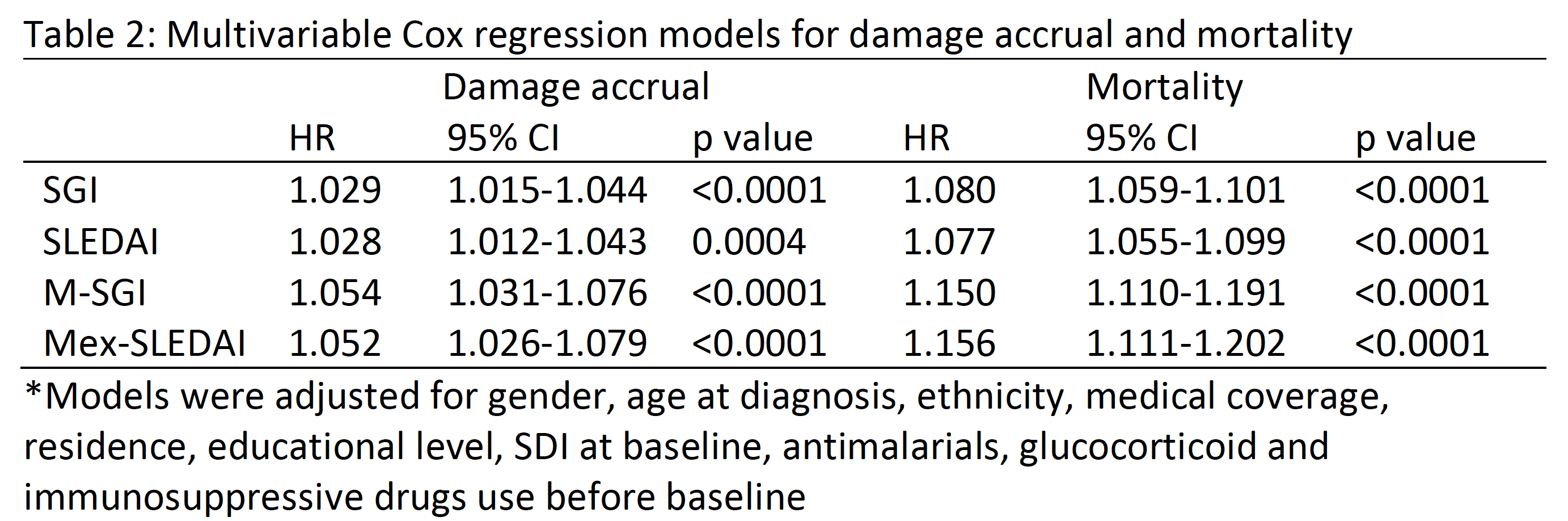
Methods: Patients from a multinational, multiethnic Latin American cohort were included in these analyses. SGI was calculated based on the impact of glucocorticoids proposed by the Toronto Cohort1. The same value for the impact of glucocorticoid was used for developing an M-SGI. Damage accrual was evaluated using the SLICC/ACR damage index (SDI). To evaluate the impact of SGI and M-SGI on the first increase on damage and on mortality, Cox regression models were performed, adjusting for gender, age at diagnosis, ethnicity, medical coverage, place of residence, educational level, SDI at baseline and antimalarial, glucocorticoid and immunosuppressive drugs use before baseline. Similar models were applied for the SLEDAI and the Mex-SLEDAI. All confounders were evaluated at or before baseline, and disease activity indices were evaluated as a time-dependent variable.
Results: One thousand three-hundred and twenty-one patients were included, median (25th-75th) age at diagnosis was 27.0 (20.0-37.0) years, 582 (44.1%) were Mestizo, 532 (40.3%) Caucasian, and 207 (15.7%) other. Median SLEDAI was 4 (0-12), Mex-SLEDAI was 3 (0-6), SGI was 7 (4-12) and M-SGI was 5 (2-9). Median follow-up was 4.3 (2.1-5.9) years. During follow up, sixty-nine patients (5.2%) died and 323 (24.5%) accrued new damage. The median values for the disease activity indices as a function of damage and mortality are depicted in Table 1. The corresponding hazard ratios are depicted in Table 2.
Conclusion: SGI and M-SGI predicted new damage and mortality in SLE patients independently of other well-known risk factors. However, their impact seems to be similar to those of the original versions of these instruments.
References
1. Touma Z, Gladman D, Su J, Urowitz M. 11 Development and initial validation of a novel lupus disease activity index to account for glucocorticoids: SLEDAI-2K glucocorticoids index (SGI). Lupus Sci Med 2017;4 :doi: 10.1136/lupus-2017-000215.11
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ugarte-Gil M, Segami I, Harvey G, Pons-Estel GJ, Quintana R, Reategui-Sokolova C, Cieza J, Catoggio LJ, Garcia M, Saurit V, Caeiro F, Drenkard C, Berbotto G, Sato E, Costallat L, Bonfa E, Tavares Brenol JC, Da Silva NA, Cavalcanti F, Iglesias-Gamarra A, Guibert-Toledano M, Reyes GA, Massardo L, Neira OJ, Cardiel MH, Barile L, Amigo MC, Silveira LH, Garcia de la Torre I, Acevedo-Vasquez E, Chacón-Díaz R, Esteva Spinetti MH, Alarcón GS, Pons-Estel BA. Sledai and Mex-Sledai Glucocorticoid Indices As Predictors of Damage and Mortality in Multinational Multiethnic Latin American Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sledai-and-mex-sledai-glucocorticoid-indices-as-predictors-of-damage-and-mortality-in-multinational-multiethnic-latin-american-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sledai-and-mex-sledai-glucocorticoid-indices-as-predictors-of-damage-and-mortality-in-multinational-multiethnic-latin-american-cohort/