Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Current guidelines for RA treatment are focused on the importance of defining the duration of symptoms before diagnosis to achieve better outcomes. This concept allows the definition of Early (ERA) and established RA (RA). Evidence suggest that ERA patients achieve better outcomes in terms of disease activity, bone erosions and survival. This study shows the clinimetric and treatment differences between patients with ERA and RA in an excellence clinical care center in Colombia.
Methods:
The study used a cohort of Colombian patients with RA (Satisfying ACR/EULAR classification criteria). Data collected from clinical records were: RA classification, disease activity using DAS-28 ESR (DAS-28), number of synthetic and biological DMARDs used, and their respective dose. Data was obtained for 0, 3, 12, 24, and 36 months of follow-up. Patients were classified as ERA or RA. Mean DAS-28, synthetic DMARDs dose, number of synthetic and biologic DMARDs used from each period of time were calculated.
Results:
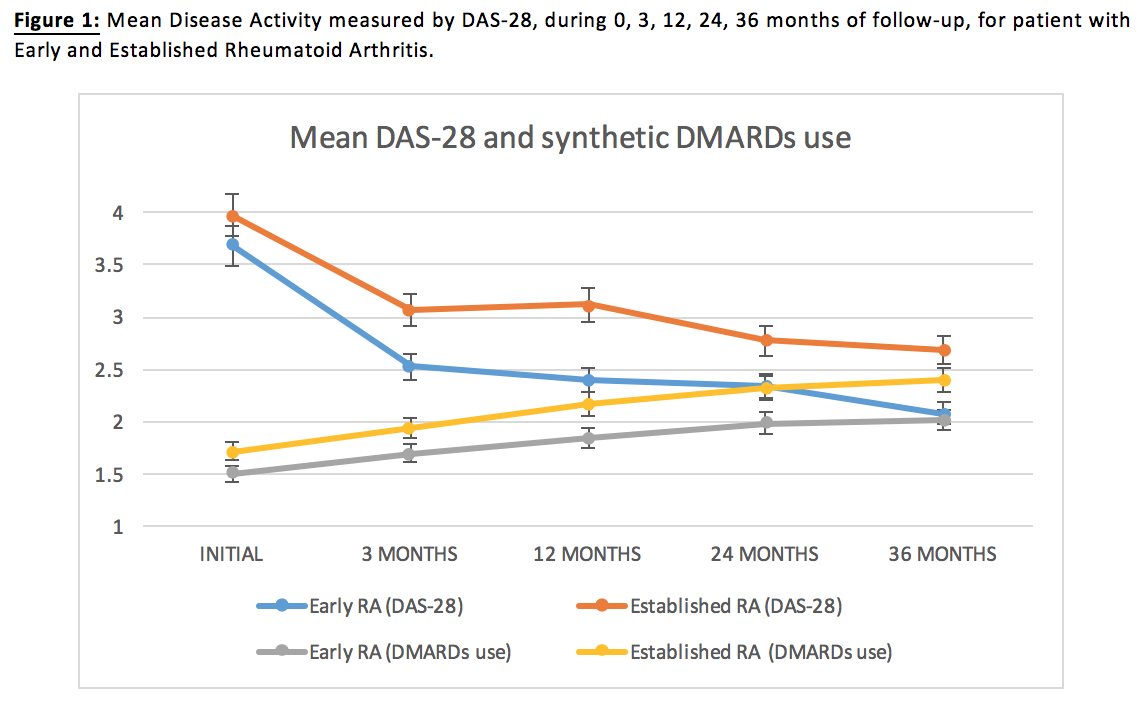
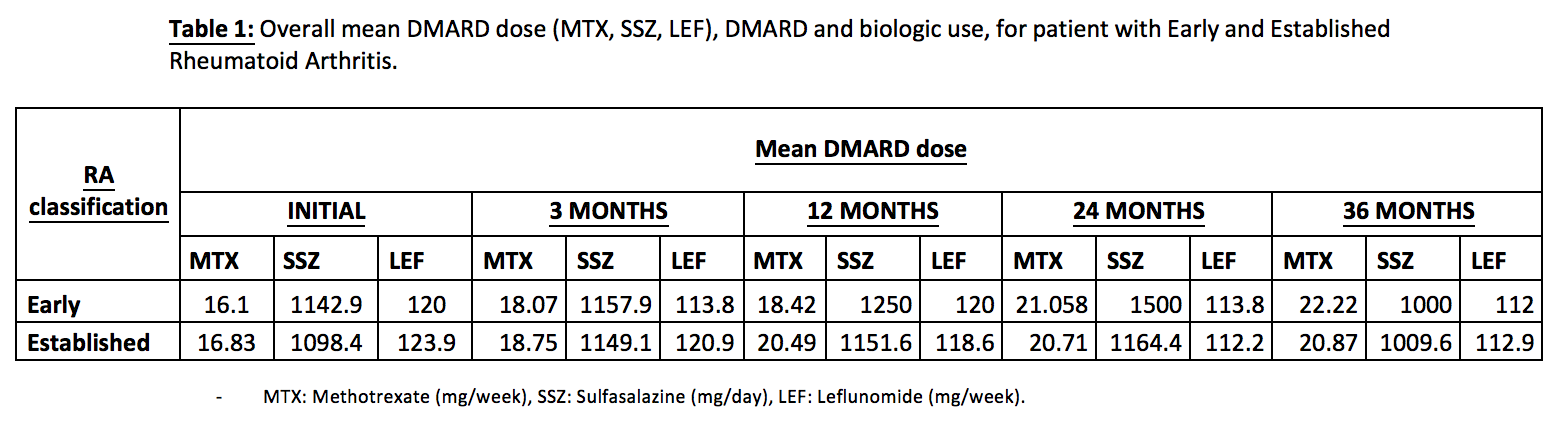
An overall of 805 patients were included; 147 patients with ERA and 658 patients with RA. 82% of patients are seropositive. Both group of patients began with mean DAS-28 corresponding to moderate activity (ERA: 3.67; RA: 3.87). Mean DAS-28 achieve remission since 3 months of follow-up for ERA group. Mean DAS-28 for RA did not achieve remission, but low activity was achieved since 3 months. Mean synthetic and biologic DMARDs use was constantly increasing in both groups, but the number was always greater in RA. About mean DMARD dose for specific drugs, weekly MTX dose stands as it was initially greater in RA, but it achieves an upper limit since 12 months of follow-up. ERA Mean weekly MTX dose constantly increase until 36 months, even surpassing RA mean dose.
Conclusion:
Results are consistent with existent evidence of disease behavior in other populations, by showing that Colombian patients with ERA achieve lower disease activity and even remission, and use less medication in comparison to RA patients. DMARD doses were greater in RA group, except for MTX.
Reference:
Casta–eda S, Navarro F, Fern‡ndez-Carballido C, Tornero C, Marced E, Corteguera M. Diferencias en el manejo de la artritis reumatoide precoz y establecida. Reumatolog’a Cl’nica. 2011;7(3):172-178.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Florez-Suarez J, Mendez P, Bermudez E, Coral P, Quintana-Lopez G. Clinimetric and Drug Use Differences in Colombian Patients with Early and Established Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinimetric-and-drug-use-differences-in-colombian-patients-with-early-and-established-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinimetric-and-drug-use-differences-in-colombian-patients-with-early-and-established-rheumatoid-arthritis/