Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, characterized by hepatic steatosis (HS), is a very common form of chronic liver disease in many countries. Limited data are available on liver enzyme elevation in patients (pts) with HS who are receiving medications for inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and psoriasis (PsO). Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA and PsA, and has also been studied in PsO. The objective of this study was to describe baseline characteristics and liver enzyme abnormalities in pts from the tofacitinib RA, PsA, and PsO clinical programs with/without HS at baseline.
Methods: Pts randomized to the tofacitinib (5 or 10 mg twice daily; doses pooled) and placebo arms of 25 studies in the RA, PsA, and PsO programs were included in this pooled post hoc analysis. Most studies allowed or mandated concomitant treatment with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. HS was determined by the investigator and captured per the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities term at baseline. Baseline characteristics, incidence of elevated total bilirubin, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) >1x and >3x the upper limit of normal (ULN) up to Month (M) 3, and change from baseline in C-reactive protein (CRP) at M3 – all by HS at baseline – are reported.
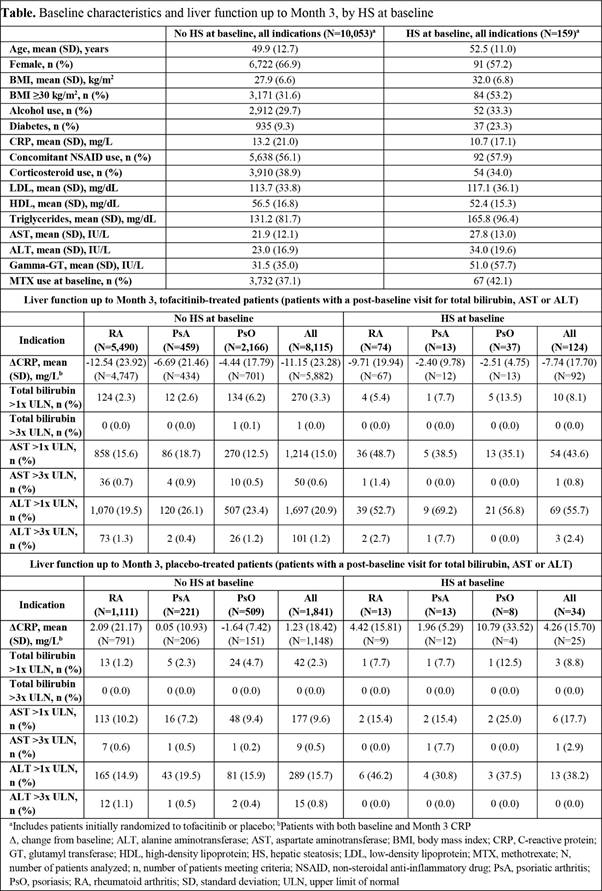
Results: A total of 10,212 pts were included in the analysis. The prevalence of HS was 1.6% across indications (RA: 87/6,729 [1.3%]; PsA: 27/710 [3.8%]; PsO: 45/2,773 [1.6%]). Baseline characteristics were generally similar in pts with or without HS (Table). However, baseline obesity, diabetes, triglycerides, and liver enzymes were numerically higher, and CRP was numerically lower, in pts with HS than in those without HS (Table). In both tofacitinib- and placebo-treated pts, incidence of elevated total bilirubin, AST and ALT >1x ULN up to M3 was higher in pts with HS than in those without HS, across indications (Table). Incidence of elevated total bilirubin, AST and ALT >3x ULN up to M3 was low across indications, irrespective of HS (Table). Among tofacitinib-treated pts, CRP was reduced at M3 in pts with or without HS, but to a lesser extent in those with HS, across indications. Among placebo-treated pts, changes in CRP were small, irrespective of HS (Table).
Conclusion: In this exploratory analysis, prevalence of HS at baseline was 1.6% across the tofacitinib RA, PsA, and PsO programs. After up to 3 months of tofacitinib treatment, incidence of mildly elevated liver enzymes was higher in pts with HS than in those without HS. Incidence of severely elevated liver enzymes was low overall, and similar in pts with or without HS. Further studies are needed to evaluate the effects of tofacitinib on CRP and liver enzymes, and the potential impact on clinical response, in pts with RA, PsA, or PsO who have comorbid HS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Soriano ER, Madariaga H, Castañeda O, Citera G, Schneeberger EE, Cardiel MH, Hendrikx T, Graham D, Shi H, Ponce de Leon D. Liver Enzyme Abnormalities after Tofacitinib Treatment in Patients with Hepatic Steatosis from the Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Psoriasis Clinical Programs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/liver-enzyme-abnormalities-after-tofacitinib-treatment-in-patients-with-hepatic-steatosis-from-the-rheumatoid-arthritis-psoriatic-arthritis-and-psoriasis-clinical-programs/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/liver-enzyme-abnormalities-after-tofacitinib-treatment-in-patients-with-hepatic-steatosis-from-the-rheumatoid-arthritis-psoriatic-arthritis-and-psoriasis-clinical-programs/