Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic, recurrent, inflammatory disease of the apocrine sweat glands. The purpose of the current study was to identify transcripts and upstream regulators that are differentially expressed in HS skin specimens compared to normal skin harvested at abdominoplasty.
Methods:
Surgical specimens from operative HS debridement (n=10, IRB 041408) and abdominoplasty (n=11, IRB 101419) were collected. Total RNA was extracted, amplified, biotin-labeled, purified and hybridized to Illumina HumanHT-12 v4 Expression BeadChips and scanned using a HiScanSQ system (Illumina Inc., CA). Low-level analysis of raw BeadChip data was performed using the limma and beadarray packages. Differentially expressed genes were detected by fitting gene-wise linear models to the normalized expression data at a false discovery rate (FDR) of <0.05 and an absolute log2-fold change greater than or equal to abs(logFC)≥1.00 (equivalent to 2.0 fold changes). Differentially expressed genes were modelled using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA, Ingenuity, Qiagen, CA) and upstream regulator analysis was performed.
Results:
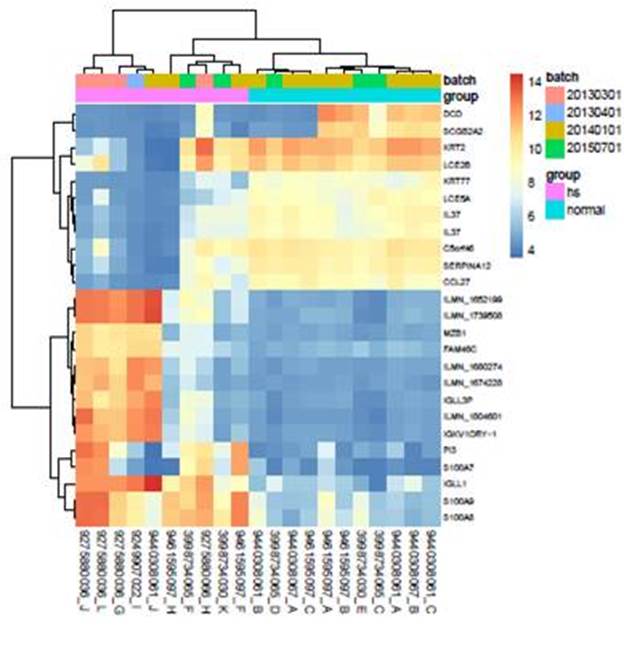
In the HS to normal control comparison, 436 genes were overexpressed and 363 genes were under-expressed. The top 25 differentially expressed genes are shown in Figure 1. Notably, Dermicidin an antimicrobial protein normally found in human sweat was significantly downregulated in the HS specimens. Significant differential expression was observed in 30 canonical pathways in the HS samples based on a –log(p-value) cut off of 1.3 and a Z -score activation prediction cut off of >2 or <-2, (Table 1). Upstream regulator analysis identified interferon alpha (IFN-α), IFN-γ, lipopolysaccharide, tumor necrosis factor and oncostatin-M as the top five upstream regulators in the HS dataset compared to normal skin (Table 2).
Conclusion:
Production of antimicrobial peptides is dysregulated in HS, and inflammatory pathways, particularly the interferon pathway and pathways of leukocyte activation are upregulated suggesting novel pathways that could be therapeutic targets for the management of this disease.
Figure 1. Differential gene expression in HS and normal tissue.
Table 1: Top 30 canonical pathways in HS
|
|
Ingenuity Canonical Pathways |
-log(p-value) |
Ratio |
z-score |
Down-regulated |
No change |
Upregulated |
|
1 |
Interferon Signaling |
7.87 |
0.528 |
4.24 |
2/36 (6%) |
0/36 (0%) |
17/36 (47%) |
|
2 |
Leukocyte Extravasation Signaling |
7.4 |
0.27 |
2.10 |
19/211 (9%) |
0/211 (0%) |
38/211 (18%) |
|
3 |
Th1 Pathway |
6.07 |
0.289 |
3.77 |
6/135 (4%) |
0/135 (0%) |
33/135 (24%) |
|
4 |
Th2 Pathway |
4.86 |
0.26 |
2.65 |
9/150 (6%) |
0/150 (0%) |
30/150 (20%) |
|
5 |
Role of NFAT in Regulation of the Immune Response |
4.29 |
0.237 |
3.68 |
11/186 (6%) |
0/186 (0%) |
33/186 (18%) |
|
6 |
Tec Kinase Signaling |
4.24 |
0.241 |
2.20 |
14/170 (8%) |
0/170 (0%) |
27/170 (16%) |
|
7 |
Dendritic Cell Maturation |
3.59 |
0.223 |
3.48 |
10/193 (5%) |
0/193 (0%) |
33/193 (17%) |
|
8 |
Neuroinflammation Signaling Pathway |
3.19 |
0.196 |
3.71 |
19/311 (6%) |
0/311 (0%) |
42/311 (14%) |
|
9 |
JAK/Stat Signaling |
3.13 |
0.265 |
2.13 |
5/83 (6%) |
0/83 (0%) |
17/83 (20%) |
|
10 |
Oncostatin M Signaling |
3.1 |
0.353 |
3.32 |
0/34 (0%) |
0/34 (0%) |
12/34 (35%) |
|
11 |
FcγRIIB Signaling in B Lymphocytes |
3.08 |
0.302 |
2.00 |
4/53 (8%) |
0/53 (0%) |
12/53 (23%) |
|
12 |
IL-6 Signaling |
3.06 |
0.234 |
2.04 |
8/128 (6%) |
0/128 (0%) |
22/128 (17%) |
|
13 |
Production of Nitric Oxide and Reactive Oxygen Species in Macrophages |
2.96 |
0.211 |
3.48 |
16/194 (8%) |
0/194 (0%) |
25/194 (13%) |
|
14 |
TREM1 Signaling |
2.54 |
0.253 |
3.44 |
1/75 (1%) |
0/75 (0%) |
18/75 (24%) |
|
15 |
p70S6K Signaling |
2.52 |
0.22 |
2.04 |
12/132 (9%) |
0/132 (0%) |
17/132 (13%) |
|
16 |
iCOS-iCOSL Signaling in T Helper Cells |
2.38 |
0.22 |
2.40 |
7/123 (6%) |
0/123 (0%) |
20/123 (16%) |
|
17 |
PKCθ Signaling in T Lymphocytes |
2.19 |
0.211 |
2.75 |
6/133 (5%) |
0/133 (0%) |
22/133 (17%) |
|
18 |
Role of Pattern Recognition Receptors in Recognition of Bacteria and Viruses |
1.76 |
0.197 |
2.84 |
5/137 (4%) |
0/137 (0%) |
22/137 (16%) |
|
19 |
Acute Phase Response Signaling |
1.7 |
0.188 |
3.27 |
5/170 (3%) |
0/170 (0%) |
27/170 (16%) |
|
20 |
LPS/IL-1 Mediated Inhibition of RXR Function |
1.69 |
0.18 |
2.14 |
20/222 (9%) |
0/222 (0%) |
20/222 (9%) |
|
21 |
GP6 Signaling Pathway |
1.63 |
0.194 |
2.75 |
6/134 (4%) |
0/134 (0%) |
20/134 (15%) |
|
22 |
Retinoic acid Mediated Apoptosis Signaling |
1.58 |
0.226 |
2.50 |
3/62 (5%) |
0/62 (0%) |
11/62 (18%) |
|
23 |
Tumoricidal Function of Hepatic Natural Killer Cells |
1.53 |
0.292 |
2.24 |
0/24 (0%) |
0/24 (0%) |
7/24 (29%) |
|
24 |
B Cell Receptor Signaling |
1.45 |
0.178 |
2.48 |
7/191 (4%) |
0/191 (0%) |
27/191 (14%) |
|
25 |
PPAR Signaling |
1.44 |
0.2 |
-2.52 |
7/95 (7%) |
0/95 (0%) |
12/95 (13%) |
|
26 |
Thrombopoietin Signaling |
1.42 |
0.215 |
2.14 |
3/65 (5%) |
0/65 (0%) |
11/65 (17%) |
|
27 |
Calcium-induced T Lymphocyte Apoptosis |
1.37 |
0.212 |
2.11 |
3/66 (5%) |
0/66 (0%) |
11/66 (17%) |
|
28 |
SAPK/JNK Signaling |
1.33 |
0.192 |
2.24 |
6/104 (6%) |
0/104 (0%) |
14/104 (13%) |
|
29 |
PI3K Signaling in B Lymphocytes |
1.32 |
0.185 |
2.13 |
8/130 (6%) |
0/130 (0%) |
16/130 (12%) |
|
30 |
Telomerase Signaling |
1.31 |
0.189 |
2.36 |
8/111 (7%) |
0/111 (0%) |
13/111 (12%) |
Table 2: Top upstream regulators in HS
|
Upstream Regulator |
Predicted Activation State |
Activation z-score |
p-value of overlap |
|
Interferon alpha |
Activated |
8.489 |
1.26E-26 |
|
IFNG |
Activated |
9.593 |
1.08E-20 |
|
lipopolysaccharide |
Activated |
9.683 |
2.63E-20 |
|
TNF |
Activated |
7.927 |
1.52E-19 |
|
OSM |
Activated |
7.511 |
6.33E-18 |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shanmugam V, Jones D, Bendall M, Crandall K. Transcriptomic Analysis of Hidradenitis Suppurativa Skin Demonstrates Dysregulation of Antimicrobial Proteins and Inflammatory Pathways [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/transcriptomic-analysis-of-hidradenitis-suppurativa-skin-demonstrates-dysregulation-of-antimicrobial-proteins-and-inflammatory-pathways/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/transcriptomic-analysis-of-hidradenitis-suppurativa-skin-demonstrates-dysregulation-of-antimicrobial-proteins-and-inflammatory-pathways/