Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The progressive destruction of osteoarthritic articular cartilage has been attributed to multifactorial cellular events, including increased oxidative modifications in proteins, abnormal inflammatory and catabolic gene expressions and early apoptosis. A plant alkaloid colchicine (Col), leads to down regulation of multiple inflammatory pathways and modulation of innate immunity. A polyphenolic antioxidant luteolin (Lut) has also been reported to have potential chondroprotective effects through inhibition of degradative enzymes and increased gene expression of collagen in animal articular chondrocytes [Kang et al., Biomol Ther, 22:239-45, 2014]. We aimed to study the comparative anti-glyco-lipo-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects of Col and Lut on human osteoarthritic articular chondrocytes (OAC).
Methods: Chondrocytes were isolated from joint cartilage of KL grade 4 OA patients, during total knee arthroplasty as described previously [Naranda et al.,PeerJ. 5:e3079, 2017]. The alterations in cell counts, viability (MTT (3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium bromide), the levels of lipid hydroperoxides (LPO), 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-(HNE)-protein adduct and advanced glycoxidation end product (AGE)-protein adduct, osteopontin and proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α) were studied (ELISA).
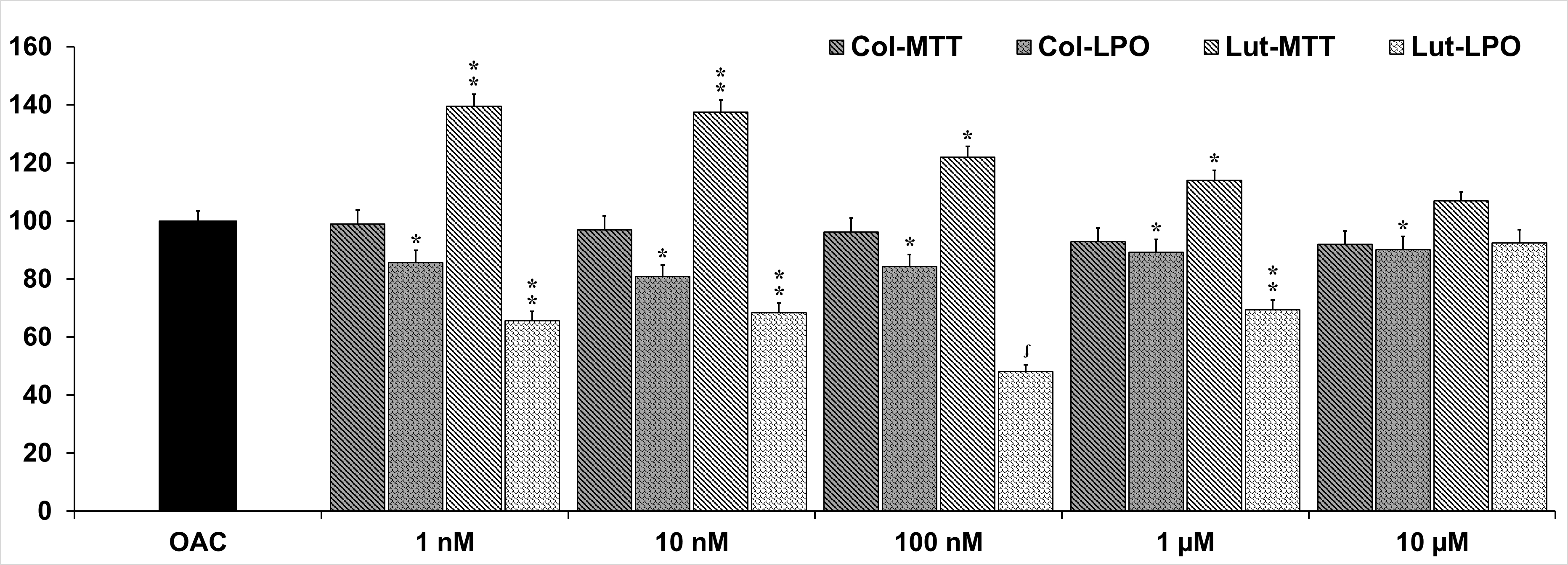
Results: Cell viability (MTT) (n=6) and LPO levels (n=3) of primary chondrocytes (30th day after isolation) treated with Col or Lut for 24 h are given in Figure. Lut increased viability at relatively lower concentrations (1 nM-1 μM). At higher concentrations (50-100μM), Lut and Col decreased the viability. Both inhibited LPO levels at 1 nM-1 μM concentrations, whereas, Lut demonstrated better inhibition compared to Col. Lut diminished HNE-protein adduct levels at concentrations of 1 nM-10 μM and Col at only 1 μM concentration. Both compounds also inhibited AGE-protein adduct levels in similar degrees at concentrations of 10 nM-1μM. Col strongly blocked the production of IL-1β in a concentration-dependent manner (1 nM-10μM), but not the levels of osteopontin, IL-6 and TNF-α. Lut also significantly attenuated IL-1β and IL-6 levels in a concentration-dependent manner (1 nM-10μM), but had no effect on osteopontin and TNF-α.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that both Col and Lut might have beneficial effects in OA, mediated at least partly through reduction of oxidative protein degeneration and cytokine release. Although the cytokine inhibition was achieved with both compounds, Lut exhibited more antioxidative efficacy than Col, and probably thus increased viability. (Supported by TUBITAK; The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey, No: 315S012).
Figure. OAC: Osteoarthritic chondrocytes. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ʄp< 0.001 versus OAC (ANOVA with HolmSidak post hoc test).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Goker B, Elmazoglu Z, Bitik B, Aytekin CN, Karasu C. Luteolin Modulates Glyco-Lipo-Oxidative Protein Modifications and Inhibits Inflammatory Cytokine Release in Human Osteoarthritic Articular Chondrocytes: Comparison with Colchicine [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/luteolin-modulates-glyco-lipo-oxidative-protein-modifications-and-inhibits-inflammatory-cytokine-release-in-human-osteoarthritic-articular-chondrocytes-comparison-with-colchicine/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/luteolin-modulates-glyco-lipo-oxidative-protein-modifications-and-inhibits-inflammatory-cytokine-release-in-human-osteoarthritic-articular-chondrocytes-comparison-with-colchicine/