Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The high prevalence of microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) and myeloperoxidase (MPO)-ANCA positive patients as well as frequent occurrence of interstitial lung disease (ILD) constitute unique epidemiological features of ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) in the Japanese population. Recent genome-wide association studies in European populations indicated that HLA-class II region was most strongly associated with AAV. In the Japanese population, we reported that HLA-DRB1*09:01 was associated with susceptibility to, and DRB1*13:02 with protection against, MPA and MPO-ANCA positive AAV (MPO-AAV) in Japan. In this study, we examined whether HLA-class II are associated with relapse of MPO-AAV, as well as occurrence of ILD in MPO-AAV, in a Japanese population.
Methods: Relapse rate and time to first relapse were analyzed in 206 MPO-AAV patients, who entered prospective cohort studies of remission maintenance therapy (RemIT-JAV and RemIT-JAV-RPGN) and achieved remission during the observation period. Association of HLA-DRB1 alleles with relapse rate was tested by chi-square analysis or Fisher exact test, and relapse-free interval was analyzed by log-rank test. Association study with ILD was performed in 297 MPO-AAV patients (126 with ILD and 171 without ILD) and 596 healthy controls. Statistical analyses were conducted using logistic regression analysis under the additive model.
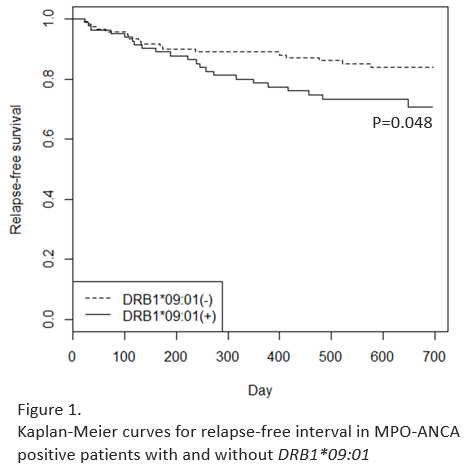
Results: Relapse occurred more frequently in the patients with DRB1*09:01 (DRB1*09:01 positive: 22/85, 25.9% vs DRB1*09:01 negative 18/121, 14.9%) (P=0.049, odds ratio [OR] 2.00), and time to relapse was significantly shorter in the patients with DRB1*09:01 than those without (P=0.048) (Figure 1). Although patients with DRB1*13:02 showed a tendency towards decreased relapse rate (DRB1*13:02 positive: 1/16 6.3% vs DRB1*13:02 negative: 39/190, 20.5%), the difference did not reach statistical significance (P=0.32, OR 0.26), nor did the time to first relapse (P=0.19). When the association of HLA alleles was tested between MPO-AAV with ILD and healthy individuals, DPB1*05:01 and DRB1*04:05 alleles were significantly decreased in MPO-AAV with ILD (Table 1). Case-case analysis between MPO-AAV patients with and without ILD also showed significant decrease of DPB1*05:01 in MPO-AAV with ILD (Table 1).
Conclusion: Association of DRB1*09:01 with relapse in MPO-AAV was observed in a Japanese population. In addition, HLA-DPB1*05:01 was significantly decreased in MPO-AAV with ILD.
|
Table 1. Association of HLA-class II alleles with interstitial lung disease in MPO-ANCA positive vasculitis |
|||||||
|
|
allele frequency |
vs HC |
vs MPO-AAV without ILD |
||||
|
|
MPO-AAV with ILD |
MPO-AAV without ILD |
HC |
P |
OR |
P |
OR |
|
DRB1*01:01 |
0.099 |
0.070 |
0.059 |
0.020 |
1.77 |
0.20 |
1.49 |
|
DRB1*04:05 |
0.079 |
0.126 |
0.127 |
0.036 |
0.59 |
0.071 |
0.59 |
|
DRB1*08:02 |
0.060 |
0.038 |
0.028 |
0.013 |
2.21 |
0.23 |
1.59 |
|
DRB1*09:01 |
0.210 |
0.249 |
0.153 |
0.027 |
1.47 |
0.26 |
0.79 |
|
DPB1*04:02 |
0.147 |
0.126 |
0.093 |
0.0089 |
1.75 |
0.45 |
1.20 |
|
DPB1*05:01 |
0.290 |
0.386 |
0.381 |
0.0072 |
0.67 |
0.020 |
0.67 |
|
HC: healthy controls, OR: odds ratio, MPO-AAV: MPO-ANCA positive vasculitis, ILD: interstitial lung disease. |
|||||||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kawasaki A, Sada KE, Hirano F, Kobayashi S, Yamada H, Furukawa H, Nagasaka K, Sugihara T, Yamagata K, Sumida T, Tohma S, Ozaki S, Hashimoto H, Makino H, Arimura Y, Harigai M, Tsuchiya N. Association of HLA Class II Alleles with Relapse and Interstitial Lung Disease in Myeloperoxidsae (MPO) -ANCA Positive Vasculitis in a Japanese Population [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-hla-class-ii-alleles-with-relapse-and-interstitial-lung-disease-in-myeloperoxidsae-mpo-anca-positive-vasculitis-in-a-japanese-population/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-hla-class-ii-alleles-with-relapse-and-interstitial-lung-disease-in-myeloperoxidsae-mpo-anca-positive-vasculitis-in-a-japanese-population/