Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Individuals with an interleukin 6 receptor (IL6R) genetic variant not on IL6R blocking therapy have biomarker profiles similar to those treated with IL6R blockers. Individuals with the IL6 variant have impaired IL6 signaling due to reduced IL6Rs; the goal of IL6R blockade is also to impair IL6 signaling by binding to IL6R. This gene-drug pair may therefore facilitate whether the IL6R variant has an association with a reduced risk for a phenotype, which in turn can inform which diseases may benefit from treatment with IL6R blockade. To test this hypothesis, we performed a Phenome-Wide Association Study (PheWAS) to screen for associations between an IL6R genetic variant and a broad range of phenotypes in the electronic health records (EHR).
Methods: We studied veteran participants in the Veteran’s Affairs Million Veteran’s Project using genomic data linked to EHR. We extracted all diagnoses codes and mapped them to phenotype groups using published PheWAS methods. Routine laboratory measurements, e.g. complete blood count, were also extracted. A PheWAS was performed by constructing logistic regression models testing associations between the IL6R variant (Asp358Ala, rs2228145) and 1,342 phenotype groups; linear regression models were constructed to screen for associations between IL6R and 26 routine laboratory measurements. All models were adjusted for age, sex, population stratification, and healthcare utilization. Significance was reported using false discovery rate ≤0.05; data for Bonferroni adjustments also provided. We replicated findings using freely available online data from the Vanderbilt University Biobank (BioVU) and the UK Biobank, two biobanks with linked genetic and EHR data.
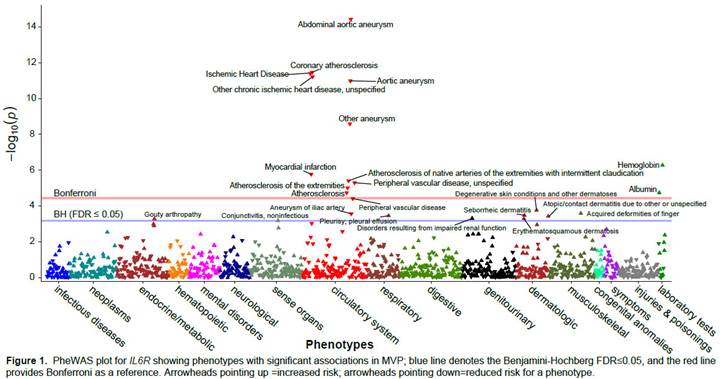
Results: We studied 330,374 participants; the minor allele frequency of the IL6R variant was 35.3%. IL6R was most strongly associated with a reduced risk of aortic aneurysm phenotypes (OR 0.87-0.90, 95% CI 0.84, 0.93) (Figure). We observed the expected association between IL6R and reduced C-reactive protein. We also observed known effects of IL6R blockade from clinical trials, increased hemoglobin. The protective effect of the IL6R variant for aortic aneurysm and coronary heart disease was replicated in BioVU and the UK Biobank, respectively.
Conclusion: In this proof of concept study, we demonstrated the application of the PheWAS using large EHR biobanks to potentially inform drug effects. The findings of a protective effect of a single IL6R variant with aortic aneurysms corresponded with the newest indication for IL6R blockade for giant cell arteritis, where clinical manifestation is aortic aneurysm.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cai T, Zhang Y, Ho YL, Link N, Sun J, Huang J, Cai T, Damrauer S, Ahuja Y, Honerlaw J, Huang J, Costa L, Schubert P, Hong C, Gagnon D, Sun Y, Gaziano M, Wilson P, Cho K, Tsao P, O'Donnell CJ, Liao KP. Phenome Wide Association Study of IL6R Variant Identifies Drug Target for Cardiovascular Disease and Inflammation [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/phenome-wide-association-study-of-il6r-variant-identifies-drug-target-for-cardiovascular-disease-and-inflammation/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/phenome-wide-association-study-of-il6r-variant-identifies-drug-target-for-cardiovascular-disease-and-inflammation/