Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: 4M090 ACR Abstract: Systemic Sclerosis & Rel D/O–Clinical II: Clinical Trials II (1875–1880)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Recent studies on large cohorts of patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) have shown that lowering the upper threshold of the modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS) as a study inclusion criterion leads to cohort enrichment with patients with progressive skin disease. Limitations of these studies were lack of racial diversity and low proportion of patients with anti-RNA-Polymerase III (Pol3) antibodies. As the Texas-based GENISOS cohort is an ethnically diverse cohort, including a large proportion of Pol3-positive patients, this study aimed to assess the effect of different mRSS cut-off values at baseline on progression of skin fibrosis after one year of follow-up.
Methods: We extracted data from GENISOS for patients fulfilling the 1980 ACR criteria for SSc and the Le Roy criteria for diffuse cutaneous SSc, who had a minimum mRSS of 7 at inclusion and a follow-up visit with documented mRSS at 12±2 months. Progressors were defined as having an increase in mRSS >5 points and ≥25% from the baseline to 2nd visit, while regressors were defined as having a decrease in mRSS of >5 points and ≥25%. To identify the optimal cut-off of baseline mRSS that yields the highest sensitivity for progressive skin fibrosis, we developed ROC curves and logistic regression models with “progression” as outcome variable and a binary variable of baseline mRSS cut-off point as predictor.
Results: 152 patients (age and disease duration [median, Q1-Q3, years] 49.5, 40.2-57.3 and 2.2, 1.1-3.3 respectively, 22.4% males) matched the inclusion criteria. The proportion of patients of African American ethnicity was 32/152 and 50/152 patients were Pol3-positive.
After one year of follow-up, 17 patients (11.2%) classified as progressors and 51 (33.6%) as regressors. Progressors were more frequently positive for anti-topoisomerase antibodies (37.5% vs. 15.3%, p=0.028), negative for anti-Pol3 antibodies (93.8% vs. 62.3 %, p=0.012), had a shorter disease duration (median, Q1-Q3: 1.3, 0.5-2.2 vs. 2.4, 1.1-3.5 years, p=0.005) and lower mRSS (median, Q1-Q3: 21, 11-25 vs. 24, 16-31, p=0.012) than the remainder of the patients.
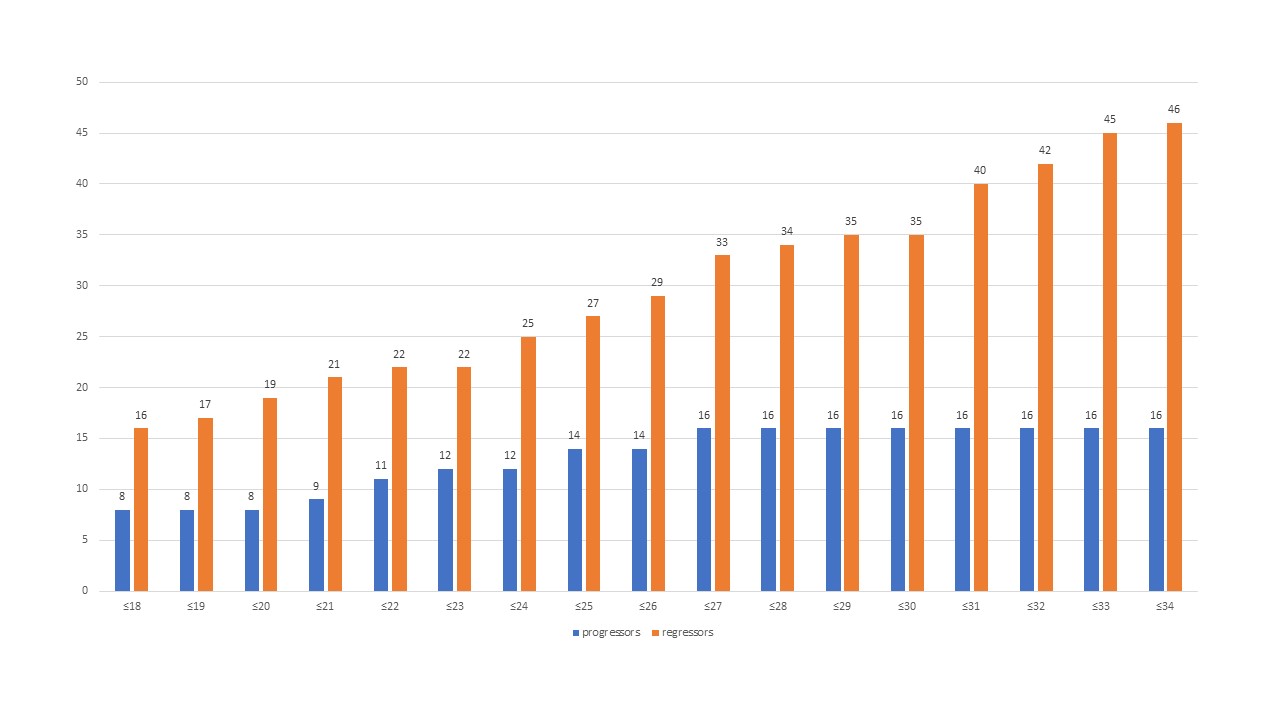
Sixteen of 17 progressors, but only 33 of 51 regressors had a baseline mRSS≤27. The mRSS cut-off of ≤27 had the highest probability of progression (odds ratio 9.1, 95% confidence interval 1.2-70.9, p=0.035, area under the curve 0.652). Using this cut-off as an inclusion criterion in a clinical trial (vs. no cut-off) would have included 94% of all progressors, but only 65% of all regressors and 67% of all patients. The figure displays absolute numbers of progressors and regressors at 1 year for each mRSS cut-off.
Conclusion: This analysis reconfirmed, in a population rich in patients of African American origin and with high prevalence of Pol3 antibodies, that setting a lower upper threshold of mRSS at study inclusion increases the proportion of progressors and reduces the absolute number of regressors.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mihai C, Dobrota R, Assassi S, Mayes MD, Distler O. Influence of Setting an Upper Limit of the Modified Rodnan Skin Score As an Inclusion Criterion in Systemic Sclerosis Clinical Trials on the Ratio of Skin Fibrosis Progression Vs. Improvement – an Analysis of the Genisos Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influence-of-setting-an-upper-limit-of-the-modified-rodnan-skin-score-as-an-inclusion-criterion-in-systemic-sclerosis-clinical-trials-on-the-ratio-of-skin-fibrosis-progression-vs-improvement/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influence-of-setting-an-upper-limit-of-the-modified-rodnan-skin-score-as-an-inclusion-criterion-in-systemic-sclerosis-clinical-trials-on-the-ratio-of-skin-fibrosis-progression-vs-improvement/