Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Safety and Comorbidity
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 has been found to play a critical role in mood disorders, with symptoms such as anxiety and depression having implications for RA disease activity. Studies have shown poorer disease outcomes in RA patients with depression.1 This study evaluated the effect of baseline depressive symptoms on the efficacy of sarilumab and improvements in health-related quality of life (HRQOL).
Methods: Post hoc statistical analyses of clinical and patient-reported outcomes (baseline; Week 24) were conducted in patients with moderately-to-severely active RA from 3 Phase 3 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing the efficacy and safety of subcutaneous (SC) sarilumab 200 mg every 2 weeks (q2w) plus methotrexate (MTX) in MOBILITY [NCT01061736], plus csDMARDs in TARGET [NCT01709578] and as monotherapy versus adalimumab SC 40 mg q2w in MONARCH [NCT02332590]. Patients were categorized with probable Major Depressive Disorder (PMDD)2 at baseline defined by a Mental Health (MH) domain score ≤56 on the Medical Outcomes Study 36-item short form (SF-36) questionnaire.
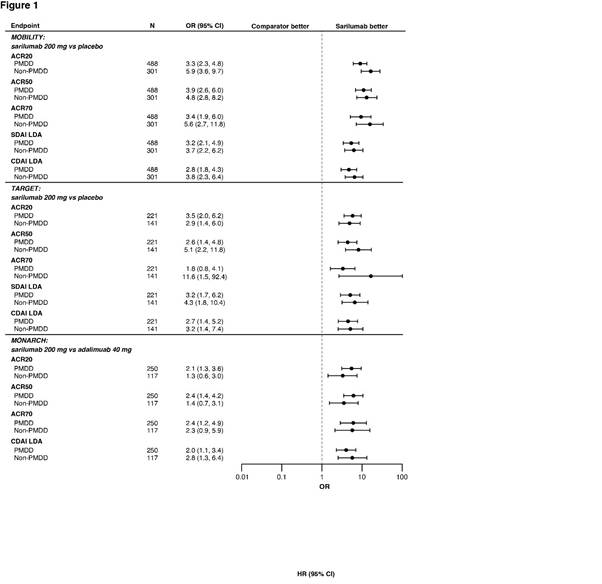
Results: Of 1197, 546 and 369 patients in MOBILITY, TARGET and MONARCH, respectively, 60.2%, 59.5% and 67.8%, were classified as PMDD. Disease duration, baseline DAS-28 CRP, tender and swollen joint counts and SF-36 MH scores were similar between sarilumab 200mg plus MTX in MOBILITY and sarilumab 200mg plus csDMARDs in TARGET versus placebo, and versus adalimumab in MONARCH in the PMDD subgroups. Interaction between PMDD and non-PMDD subgroups was non-significant for all endpoints except change from baseline in Patient Global Assessment of disease activity in MOBILITY (nominal P < 0.05). Odds ratios for responses by ACR20/50/70, SDAI ≤ 11 and CDAI ≤ 10 at Week 24 were nominally higher with sarilumab 200mg versus placebo in both PMDD and non-PMDD subgroups in MOBILITY (nominal P < 0.0001), TARGET (nominal P < 0.01), and in PMDD by ACR20/50/70 in MONARCH (nominal P < 0.05) (Figure 1). MH scores for PMDD subgroups were nominally higher (P < 0.05) in ACR20 responders with sarilumab 200mg versus placebo at Week 24 in MOBILITY (Figure 2). Sarilumab safety was consistent with IL-6R blockade.
Conclusion: These post-hoc analyses suggest that sarilumab treatment is equally efficacious irrespective of baseline PMDD status.
1. Matcham F et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2016;17:155.
2. Matcham F et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2016;17:224.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Mangan E, Hagino O, Sadeh J, Boklage S, Kimura T. Exploring the Effects of Depressive Symptoms on the Efficacy of Sarilumab and Improvements in Health-Related Quality of Life [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-the-effects-of-depressive-symptoms-on-the-efficacy-of-sarilumab-and-improvements-in-health-related-quality-of-life/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-the-effects-of-depressive-symptoms-on-the-efficacy-of-sarilumab-and-improvements-in-health-related-quality-of-life/