Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Safety and Comorbidity
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
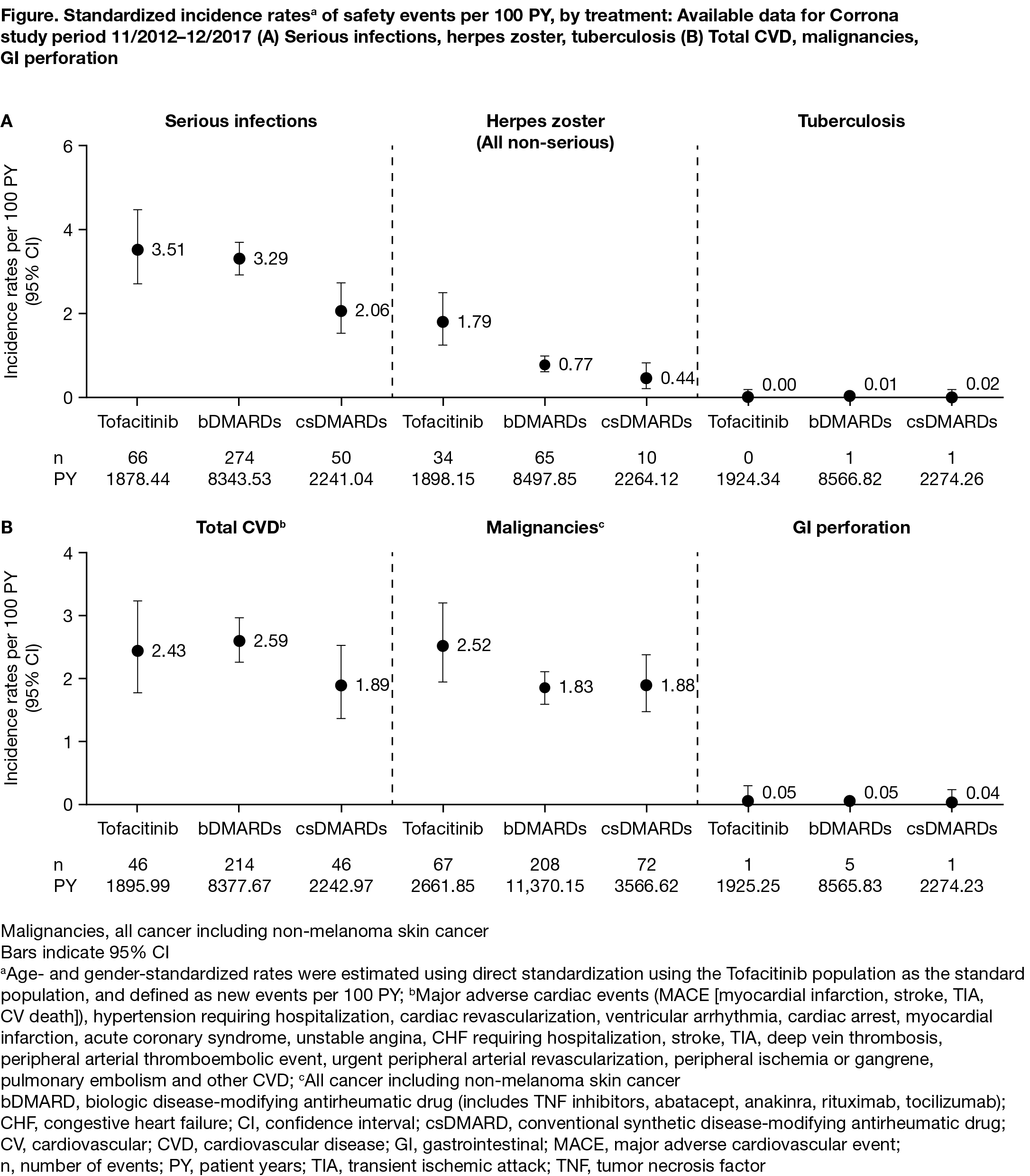
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. A prospective observational 5-year study, embedded within the US Corrona RA registry, was initiated to evaluate the safety of tofacitinib after US Food and Drug Administration approval on November 6, 2012. The study has now completed 5 years of data collection. The objective of the study was to assess the rates of adverse events (AEs) in patients initiating tofacitinib vs biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) and conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs). This analysis describes the age- and sex-standardized rates of AEs for the completed 5-year study period.
Methods: AEs were evaluated in three patient populations: 1) initiators of tofacitinib; 2) initiators of a bDMARD (with no prior/current tofacitinib exposure); and 3) initiators of a csDMARD (with no prior/current tofacitinib or bDMARD exposure). AE data were captured from prescribing physicians during follow-up. Patients who had at least one visit or AE at any time after initiation were included in the analysis. Standardized incidence rates and 95% confidence intervals were estimated across the 5-year period (November 6, 2012–December 31, 2017) using the age and gender distribution of tofacitinib initiators as the reference population.
Results: Age- and gender-standardized incidence rates of safety events per 100 patient-years [PY] were calculated for 1482 tofacitinib, 6881 bDMARD, and 2115 csDMARD initiators with 1925.34 PY, 8566.82 PY, and 2274.51 PY of follow-up, respectively. Patient characteristics are shown in the Table. Disease duration was longer, and both the number of prior bDMARDs and number of prior TNF inhibitors were higher, in tofacitinib initiators compared with bDMARD and csDMARD initiators. Standardized incidence rates for serious infections, cardiovascular events, malignancies, and gastrointestinal perforation were generally similar for the three groups (Figure). Non-serious herpes zoster incidence rates were higher for tofacitinib compared to bDMARDs and csDMARDs, consistent with the known safety profile.
Conclusion: In this analysis, despite patients in the tofacitinib group having longer disease duration and more prior biologic treatments, patients initiating tofacitinib, bDMARDs, and csDMARDs for the treatment of RA experienced comparable age- and gender-adjusted rates of serious infections, cardiovascular events, and malignancies. Tofacitinib initiators had a higher rate of non-serious herpes zoster than bDMARD and csDMARD initiators. A formal, propensity-matched analytic comparison of these data is planned.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kremer J, Cappelli LC, Etzel CJ, Greenberg J, Geier J, Madsen A, Chen C, Onofrei A, Barr CJ, Pappas DA, Dandreo KJ, Shapiro A, Connell CA, Kavanaugh A. Real-World Data from a Post-Approval Safety Surveillance Study of Tofacitinib Vs Biologic Dmards and Conventional Synthetic Dmards: Five-Year Results from a US-Based Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-data-from-a-post-approval-safety-surveillance-study-of-tofacitinib-vs-biologic-dmards-and-conventional-synthetic-dmards-five-year-results-from-a-us-based-rheumatoid-arthritis-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-data-from-a-post-approval-safety-surveillance-study-of-tofacitinib-vs-biologic-dmards-and-conventional-synthetic-dmards-five-year-results-from-a-us-based-rheumatoid-arthritis-registry/