Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis and Myopathies Poster II: Basic and Translational Science
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Anti-aminoacyl-tRNA-synthetase (ARS) antibodies are myositis specific autoantibodies and associated with common clinical characteristics called anti-synthetase syndrome (ASS). Recently anti-ARS detecting enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in which mixture of 5 ARS antigens are coated have been established and utilized in daily practice (MESACUPTM MBL, Japan). However, we sometimes encounter patients who are positive for anti-ARS by ELISA but negative by RNA-immunoprecipitation (IP). We verified the authenticity and clinical relevance of these anti-ARSs with discrepant results between different detection systems.
Methods: We examined medical records of 1628 samples that were screened for anti-ARS by ELISA between 2014 and 2017. There were 78 patients (134 samples) who were positive for anti-ARS by ELISA, and among these patient, we further analyzed 61 patients by RNA-IP. We found 16 patients who were positive for anti-ARS by ELISA but negative by RNA-IP. We examined clinical characteristics of these 16 patient sera. Statistical analysis was performed by using Fisher’s exact test. Furthermore, 7 of 16 patients were examined by protein-IP and individual ELISA methods to verify the authenticity of the discrepant results. The individual ELISA was also confirmed whether the serum autoantibody was absorbed to the antigen.
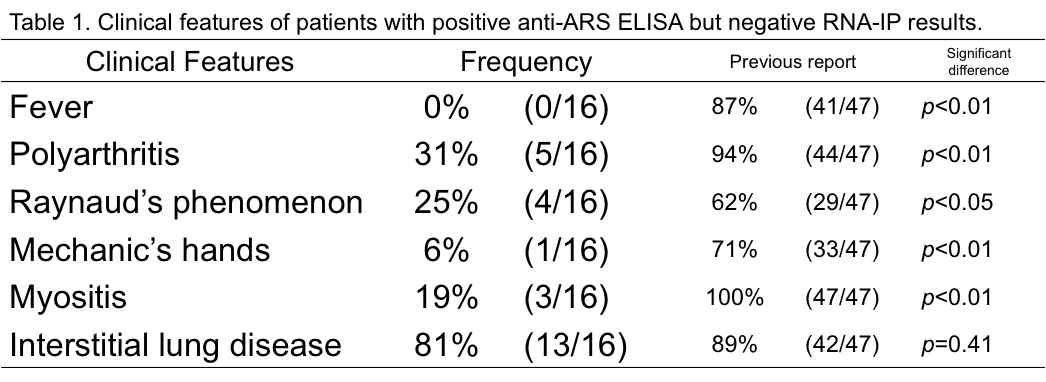
Results: Compared to the previous report (Love LA. et al. Medicine (Baltimore), 1991), the frequency of all symptoms of ASS other than interstitial lung disease (ILD) were significantly lower in 16 discrepant cases (Table 1). The radiological patterns of ILD frequently showed nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and/or organizing pneumonia (11/16 cases). Most cases showed good response to initial glucocorticoid therapy, but 46% of them had recurrence. The results of protein-IP showed that 5 of 7 patient sera reacted with either Jo-1 or KS but 2 did not immunoprecipitated any ARS proteins. The individual ELISA and absorption study showed all these samples reacted with some of the ARS antigens, of which Jo-1 was the most frequently recognized (Table 2).
Conclusion: There are some anti-ARS antibodies which are detected by ELISA but not RNA-IP. These antibodies might inhibit RNAs binding to ARS proteins or recognize denatured ARS antigens. Patients with such atypical anti-ARS showed significant association with ILD but less with the other characteristics of ASS. Furthermore, the ILD with atypical anti-ARS showed similar clinical response and course with that of ASS. Further investigation is needed to clarify whether such patients have distinct form of ASS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sasai T, Nakashima R, Ishikawa Y, Isayama T, Mimori T. Anti-Aminoacyl-tRNA-Synthetase Antibodies Which Are Positive By ELISA but Negative By RNA-Immunoprecipitation Suggest Different Antigen Recognition and Clinical Relevance Different from Typical Anti-Synthetase Syndrome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-aminoacyl-trna-synthetase-antibodies-which-are-positive-by-elisa-but-negative-by-rna-immunoprecipitation-suggest-different-antigen-recognition-and-clinical-relevance-different-from-typical-anti-s/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-aminoacyl-trna-synthetase-antibodies-which-are-positive-by-elisa-but-negative-by-rna-immunoprecipitation-suggest-different-antigen-recognition-and-clinical-relevance-different-from-typical-anti-s/