Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Metabolic and Crystal Arthropathies – Basic and Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: several metabolic disturbances that reduce the activity of pyrophosphatases have been associated with development of pyrophosphate arthritis (PPA), but there is scarce data on their influence of clinical manifestations, as such disease-specific variables are not recorded in most available databases. To evaluate factors associated to severity of clinical joint involvement in patients with definite PPA.
Methods: transversal study with prospective recruitment of cases (patients con a PPA diagnosis confirmed by microscopy plus presence of X-ray chondrocalcinosis in at least one joint) and controls (patients with synovial effusion shown to have no PP crystals and no chondrocalcinosis in hands and knee X-rays, paired by age and gender). Patients with hemochromatosis or primary hyperparathyroidsm were not included. [[Population general variables were included along with plausible metabolic variables (Ca, P, Mg, iPth, iron saturation [satFe%], ferritin, diuretics and type of diuretic, and HFE genotype), and joint involvement distribution (mono-oligo-polyarticular) and clinical manifestations (acute PPA [A-PPA] and chronic inflammatory PPA [CI-PPA]), as in EULAR recommendations.
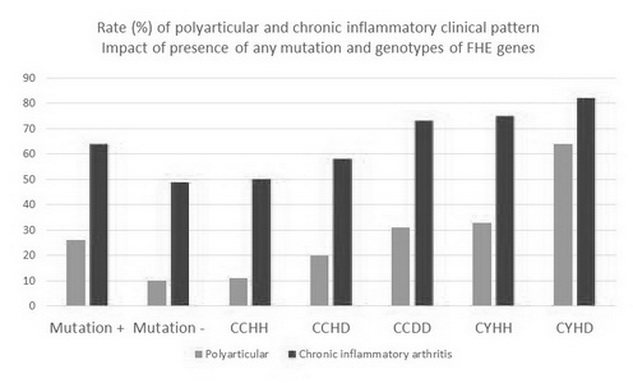
Results: 340 patients and 316 controls were recruited, 53% were men, age at inclusion was 67±10 yr (IQ range 62-75), time from onset of symptoms 5.2±5.3 yr (IQ range 1-8). Regarding cases, A-PPA was present in 147 (43.2%), CI-PPA in 193 (56.8%), monoarticular joint distribution in 102 (30.0%), oligoarticular in 176 (51.8%), and polyarticular in 62 (18.2%). Patients showed higher serum ferritin levels and lower Mg levels than controls (253mcg/dl and 2.00 mg/dl vs. 204 mcg/dl and 2.08 mg/dl, respectively), along with higher rate of any HFE gene mutations (Odds 2.30, 95% CI 1.66-3.20). Genotypes including heterozygotic mutations for C282Y allele (CY), homozygotic of H63D allele (DD), and double heterozygotic for C282Y and H63D (CYHD) were statistically associated with higher frequency of polyarticular involvement and with CI-PPA (Figure). Nonetheless, only CY genotypes were associated with the most severe phenotypes when time from onset of symptoms was considered in analysis, also showing the highest satFe%.
Conclusion: patients with definite PPA show differences in magnesium and iron parameters compared to controls, and may contribute, along with other factors, to development of PPA. Nevertheless, only presence of some HFE genotypes, especially CY, were associated with more severe pattern of clinical involvement.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Perez-Ruiz F, Atxotegi J. Association of HFE Genotypes with Clinical Severity in Patients with Definite Calcium Pyrophosphate Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-hfe-genotypes-with-clinical-severity-in-patients-with-definite-calcium-pyrophosphate-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-hfe-genotypes-with-clinical-severity-in-patients-with-definite-calcium-pyrophosphate-arthritis/