Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients are at increased risk of heart failure (HF). The chronic inflammatory state in RA is associated with increased levels of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), a biomarker for HF. Recently, a study demonstrated that NT-proBNP levels in RA patients decreased under TNF-blocking therapy. It is unknown whether this is also observed in biologics with other mode of actions. We evaluated the effects of abatacept and tocilizumab therapy on NT-proBNP levels.
Methods: In 34 RA consecutive patients starting with abatacept (10 mg/kg every 4 weeks) and 14 RA consecutive patients starting with tocilizumab (8 mg/kg every 4 weeks), disease activity parameters and serum samples were collected at baseline and after 12 weeks of therapy. Clinical response was assessed using EULAR response criteria. Responding patients comprised both good and moderate EULAR responders. NT-proBNP levels were measured by the Elecsys 2010 electrochemiluminescence method (Roche diagnostics). For statistical analyses t-tests, Mann-Whitney U tests and linear regression were used.
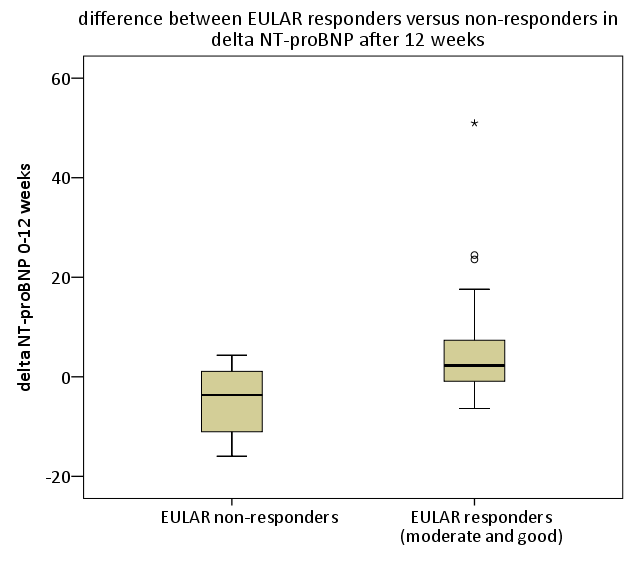
Results: NT-proBNP levels did not change significantly after 12 weeks (p=0.6) and there were no significant differences in NT-proBNP levels at baseline or after 12 weeks of treatment between the tocilizumab and abatacept group (p=0.16 and p=0.3, respectively). 34 patients (71%) were EULAR responders, (6=12% good, 28=88% moderate) and 14 patients (29%) were non-responders. Baseline DAS28, CRP and BSE were higher, though not significantly, in responders compared to non-responders (table). Baseline NT-proBNP levels were higher in responders versus non-responders (p=0.044). Change in NT-proBNP levels after 12 weeks of treatment was significantly different between responders and non-responders (p=0.002), with decreasing NT-proBNP levels in responders and increasing levels in non-responders.
Conclusion: There was a remarkable difference in the course of NT-proBNP levels between EULAR responders and non-responders, as responders started with higher baseline levels which decreased significantly under both abatacept and tocilizumab treatment, while in contrast the NT-proBNP levels of non-responding patients increased. These findings indicate favourable effects of abatacept and tocilizumab on cardiac function in RA patients responding to treatment and underscore the importance of tight control of systemic inflammation in order to decrease CV risk.
Disclosure:
I. A. M. van den Oever,
BMS,
8;
M. T. Nurmohamed,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reduction-of-inflammation-with-abatacept-and-tocilizumab-results-in-lower-n-terminal-pro-brain-natriuretic-peptide-levels-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-prospective-cohort-studies/