Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Multiple studies have observed unfavorable changes in lipid profile associated with tocilizumab (TCZ, anti-IL6 receptor antagonists) and some other rheumatoid arthritis (RA) therapies. The real-world cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk associated with the first anti IL-6R medication for RA, TCZ, remains uncertain. Our objective was to assess the CVD risk associated with TCZ compared to individual tumor necrosis inhibitor (TNFi) therapies, as well as to other biologics used for RA (e.g. rituximab, abatacept).
Methods: Using 2006-2015 Medicare and MarketScan claims data, we conducted a retrospective cohort study among RA patients who initiated biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDS) after January 1, 2010 and had at least 365 days medical and pharmacy coverage before initiation. The primary outcome was a composite of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and fatal CVD assessed using a validated method. Subgroups analyses were done for RA patients experienced to other bDMARDs before initiation and by stratifying patients with respect to key CVD risk factors to identify both higher and lower CVD risk patients. Incidence rates and 95% confidence intervals were calculated using Poisson regression. COX regression was used to generate unadjusted and adjusted hazard ratio.
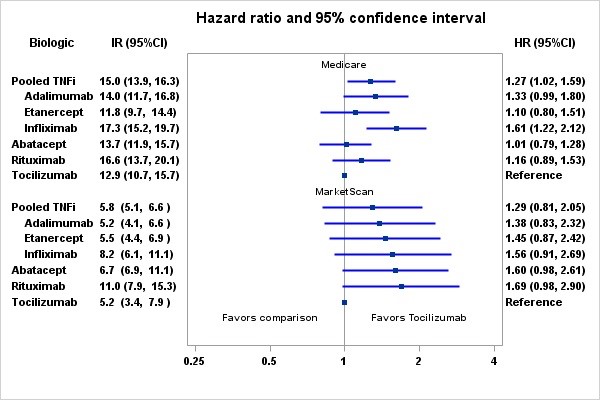
Results: We identified 354,486 RA patients and 463,446 initiations of bDMARDS. After applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, the final cohort contained 88,463 RA patients and 117,493 episodes. The mean (SD) age was 64.7 in Medicare and 52.2 in MarketScan. The majority were female (83.9% Medicare; 80.5% MarketScan), and 68.6% were non-Hispanic White in Medicare. TCZ users were similar to abatacept and rituximab users except that TCZ users were less likely to be naïve to bDMARDS. Compared to TNFi users, TCZ users were likely to be white, have a history of CVD (other than MI or stroke), heart failure, atrial fibrillation, hospitalization, and more physician visits in baseline. TCZ users were less likely to be diabetic, use methotrexate in baseline, and naïve to bDMARDS.
The crude incidence rate (IR) per 1000 patient-years for composite CVD among Medicare patients ranged from 13.3 (95%CI: 11.1-16.0) for etanercept to 19.4 (95%CI: 16.3-20.9) for rituximab users. The crude incidence rate for pooled TNFi users was 16.4 (15.2-17.7). Compared to TCZ, the adjusted hazard ratios were 1.03 (0. 82-1.29) for abatacept, 1.25 (0.96-1.61) for rituximab, 1.13 (0.84-1.52) for etanercept, 1.33 (0.99-1.80) for adalimumab, and 1.57 (1.21-2.05) for infliximab (Figure). There were no significant differences in CVD risk between tocilizumab and any other biologic using MarketScan data.
Conclusion: Consistent with findings of a recently completed safety trial in RA, tocilizumab was associated with a comparable CVD risk compared to etanercept, as well as a number of other RA biologics, in two large data sources.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Xie F, Yun H, Levitan E, Muntner PM, Curtis JR. Tocilizumab and the Risk for Cardiovascular Disease Events Among Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Direct Comparison in Real World Setting [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tocilizumab-and-the-risk-for-cardiovascular-disease-events-among-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-a-direct-comparison-in-real-world-setting/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tocilizumab-and-the-risk-for-cardiovascular-disease-events-among-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-a-direct-comparison-in-real-world-setting/