Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Poster I: Clinical Manifestations and Comorbidity
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Demyelinating syndrome in NPSLE includes the wide range of lesions similar to multiple sclerosis (MS). Recently, the diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disease (NMOSD) has been established, independently of MS. Clinically, longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis (LETM) as is described in the definition of NMOSD can be observed even in patients with SLE. IL-6 in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) has been reported as one of biomarkers in NMOSD, but in lupus patients with LETM, the utility of CSF IL-6 for a diagnosis and as a surrogate maker after treatment has not been demonstrated. The aim of this study is to reveal the characteristic of lupus patients with NMOSD-like lesions, especially focusing on CSF IL-6.
Methods: SLE patients who had admitted to Kitasato University hospital due to a diagnosis and a treatment for NPSLE since 2004 to 2018 were exhaustively collected. Of collected NPSLE patients, patients who were classified as demyelinating syndrome were recruited for this analysis. To be compared with characteristics of patients with NMOSD not involving other autoimmune diseases, these patients were divided into two groups according to the lesions by magnetic resonance imaging: patients with LETM as is defined in international consensus diagnostic criteria for NMOSD and patients with brainstem and/or spinal cord lesions other than LETM. Clinical data including CSF IL-6 based on their medical charts were reviewed. The IL-6 levels in CSF were compared with non-parametric tests.
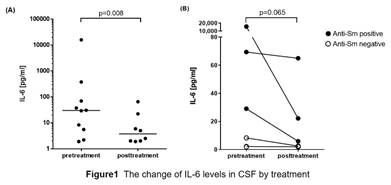
Results: Total 77 NPSLE patients admitted for 14 years. Of 77 patients, 12 patients (15.6%) had some brainstem and/or spinal cord lesions like demyelinating syndromes in NPSLE. 7 patients had LETM and of 7 patients with LETM, 2 patients were positive for anti-aquaporin 4 antibody. Of remined 5 patients, 1 patients had as small and punctuated lesion in brainstem and 4 patients had spinal cord lesion unlike LETM. The median level in CSF IL-6 in these 12 patients was 29.10pg/ml, which was significantly decreased to 3.75pg/ml (p=0.008) after treatment (Figure 1A). In patients with LETM, the median level of CSF IL-6 was 18.7pg/ml, which tended to be decreased (p=0.065) after treatment (Figure 1B). Interestingly, patients with LETM positive for anti-Sm antibody had higher CSF IL-6 level (Figure 1B).
Conclusion: IL-6 in CSF could be one of biomarkers in SLE patients with LETM, presumably depending on causes of LETM including autoantibodies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hasegawa Y, Arinuma Y, Ino K, Muramatsu T, Kondo J, Matsueda Y, Hoshiyama T, Tono T, Wada T, Nagai T, Tanaka S. Interkeukin-6 Level in Cerebrospinal Fluid As a Biomarker for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients with Longitudinally Extensive Transverse Myelitis like Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interkeukin-6-level-in-cerebrospinal-fluid-as-a-biomarker-for-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-with-longitudinally-extensive-transverse-myelitis-like-neuromyelitis-optica-spectrum-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interkeukin-6-level-in-cerebrospinal-fluid-as-a-biomarker-for-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-with-longitudinally-extensive-transverse-myelitis-like-neuromyelitis-optica-spectrum-disease/