Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster I: Strategy and Epidemiology
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. ORAL Strategy (NCT02187055), a 12-month, global, Phase 3b/4 study, demonstrated that in patients with RA and an inadequate response to MTX, tofacitinib + MTX was non-inferior to adalimumab + MTX, while tofacitinib monotherapy was not non-inferior to either combination based on American College of Rheumatology (ACR)50 response rates at Month 6.1 This post hoc analysis aimed to assess the clinical and functional efficacy across treatments in the ORAL Strategy trial using cumulative probability plots.
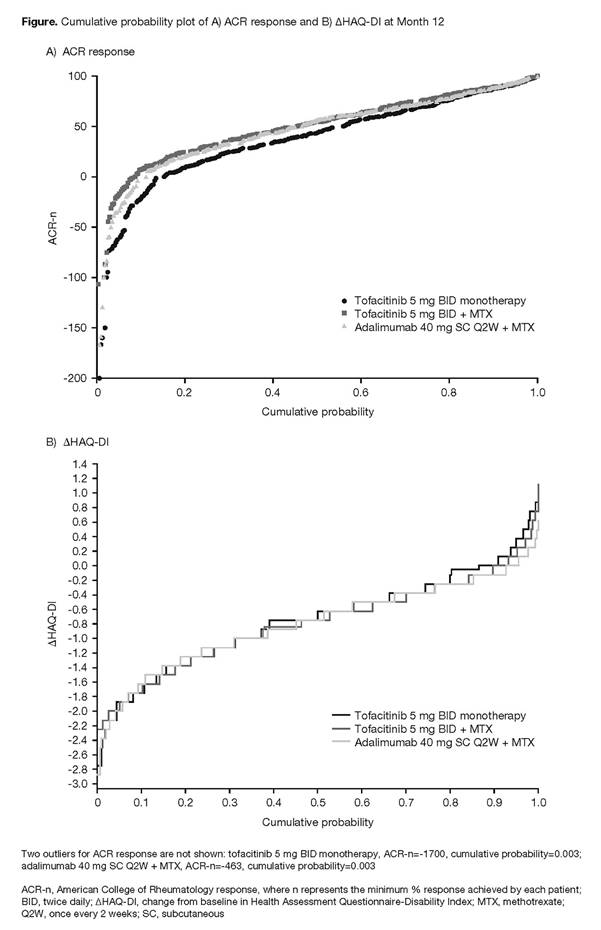
Methods: Efficacy was evaluated between patients who received tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID) as monotherapy (N=384), tofacitinib 5 mg BID + MTX (N=376), and adalimumab 40 mg subcutaneously once every 2 weeks + MTX (N=386) based on ACR responses and changes from baseline in Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (ΔHAQ-DI) at Month 12. Cumulative probability plots for ACR-n (where ACR is the % improvement from baseline in ACR components, and n represents the minimum % achieved by each patient) and ΔHAQ-DI are presented. The area under the curve (AUC) was calculated for ACR-n up to Month 12 (in months), and an analysis of covariance model was used to assess treatment effects in terms of the AUC of ACR-n at Month 12; there was no adjustment for multiplicity for this post hoc analysis.
Results: The cumulative probability plots of ACR responses at Month 12 indicated that the proportion of patients who achieved responses of ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70 was similar for tofacitinib + MTX and adalimumab + MTX, but was numerically smaller for tofacitinib monotherapy (Figure A). Responses of approximately ≥ACR80 were achieved by a similar proportion of patients in each treatment group. Least squares mean (standard error) AUC of ACR-n up to Month 12 (in months) was similar for tofacitinib + MTX (437 [35]) and adalimumab + MTX (402 [35]), but was smaller for tofacitinib monotherapy (319 [35]; p<0.05; data not shown). The cumulative probability plots of ΔHAQ-DI suggested that, in general, reductions from baseline in HAQ-DI were similar across treatment groups (Figure B), although a slightly higher proportion of patients who received tofacitinib monotherapy reported an increase in HAQ-DI vs other treatments.
Conclusion: These data support the primary ORAL Strategy findings,1 indicating that in patients with RA, clinical efficacy, based on ACR response, was generally similar for tofacitinib + MTX and adalimumab + MTX, while a smaller proportion of patients who received tofacitinib monotherapy achieved ACR response in general, and particularly for <ACR80. Functional efficacy, based on ΔHAQ-DI, was generally similar across all treatment groups. Cumulative probability analyses for CDAI will be further evaluated.
1. Fleischmann et al. Lancet 2017; 390: 457–68.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Takeuchi T, Smolen JS, Fleischmann R, Iikuni N, Fan H, Soma K, Akylbekova E, Hirose T. Clinical and Functional Response to Tofacitinib and Adalimumab in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Probability Plot Analysis of Results from the ORAL Strategy Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-functional-response-to-tofacitinib-and-adalimumab-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-probability-plot-analysis-of-results-from-the-oral-strategy-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-functional-response-to-tofacitinib-and-adalimumab-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-probability-plot-analysis-of-results-from-the-oral-strategy-trial/