Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster I: Strategy and Epidemiology
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In Phase 3 trial (RA-BEGIN), baricitinib (BARI) monotherapy demonstrated superiority to MTX in pain reduction and HAQ-DI improvement in treatment of csDMARD-naïve active RA patients.1 No prospective head-to-head (H2H) trial data are available comparing BARI monotherapy vs. bDMARD monotherapy in csDMARD-naïve RA patients.
The objective was to assess pain and HAQ-DI for BARI monotherapy from a randomized, MTX-controlled trial vs adalimumab (ADA), tocilizumab (TCZ), and tofacitinib (TOFA) monotherapy from similar randomized, MTX-controlled trials in csDMARD/bDMARD naive RA patients using matching-adjusted indirect comparison (MAIC).
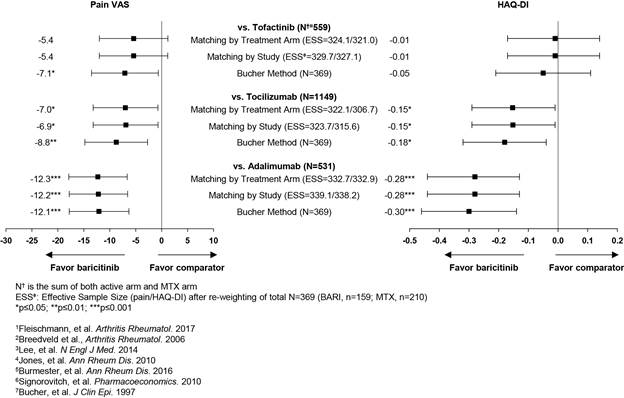
Methods: Individual patient data from the RA-BEGIN BARI 4 mg arm were weighted to match baseline characteristics of the ADA arm from PREMIER,2 TOFA 5 mg arm from ORAL-START,3 and TCZ 8 mg/kg arm from combination of AMBITION and FUNCTION,4,5 respectively; MTX arms were also matched between trials. Method of moments was used to determine weights for age, gender, baseline disease scores, and baseline values of the outcome variable. Mean change on pain VAS and HAQ-DI at Week 24 for BARI were adjusted for the above baseline characteristics with the weighted linear model, and then indirectly compared vs. respective published results for Week 24 TCZ and TOFA and for Week 26 ADA data. Statistical significance of the weighted treatment effect was assessed with the bootstrap method. Sensitivity analyses included MAIC with study level matching6, Bucher’s method without matching adjustment7, and inclusion of disease duration as an additional matching variable.
Results: Across trials, the mean baseline pain VAS ranged from 58.7 to 65.2 with a 6-month mean change in pain of -28.3 to -33.5 for the MTX arm, indicating comparability between trials. Similar HAQ-DI and changes in HAQ-DI for the MTX arm were observed. At Week 24, BARI showed numerically greater improvement over MTX in pain than that for TCZ, ADA, and TOFA; statistically significant pain improvement were observed for BARI vs ADA and TCZ with all 3 matching methods but only with the Bucher method for TOFA (Figure). BARI-treated patients showed significantly greater improvement in HAQ-DI at Week 24 than TCZ and ADA but not TOFA (Figure). Sensitivity analyses showed consistent results.
Conclusion: This indirect comparison of different studies in cs/bDMARD-naïve RA patients, after adjusting for differences in baseline characteristics, suggest a greater pain reduction and improved physical function for BARI monotherapy vs. TCZ and ADA monotherapy. There is suggestion of greater pain reduction for BARI monotherapy vs. TOFA monotherapy, but no differences in improved physical function between the JAK inhibitors. A H2H clinical trial would be needed to confirm these results.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fautrel B, Zhu B, Taylor PC, van de Laar M, Emery P, de Leonardis F, Gaich CL, Nicolay C, Kadziola Z, de la Torre I, Fleischmann R. Comparative Effectiveness in Pain and HAQ-DI Improvement for Baricitinib Versus Adalimumab, Tocilizumab, and Tofacitinib Monotherapies in Csdmard-Naïve Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Matching-Adjusted Indirect Comparison (MAIC) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-effectiveness-in-pain-and-haq-di-improvement-for-baricitinib-versus-adalimumab-tocilizumab-and-tofacitinib-monotherapies-in-csdmard-naive-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-a/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-effectiveness-in-pain-and-haq-di-improvement-for-baricitinib-versus-adalimumab-tocilizumab-and-tofacitinib-monotherapies-in-csdmard-naive-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-a/