Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster I: Strategy and Epidemiology
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (bari), an oral selective Janus kinase 1/2 inhibitor, has shown clinical efficacy in patients (pts) with RA and an inadequate response to conventional synthetic DMARDs.1 Baricitinib is approved for treating moderate-severe RA in over 40 countries. The two objectives of these analyses were to evaluate the percentage of pts, originally randomized to 2 mg or 4 mg in the Phase 3 RA-BUILD study, and rescued in the study and/or in RA-BEYOND (the long-term extension study); and to assess the clinical benefits post-rescue.
Methods: RA-BUILD was a 24-week study evaluating once daily bari 4 mg (N=227) and 2 mg (N=229) compared to placebo (N=228). Pts with <20% improvement in tender joint count or swollen joint count (SJC) at Weeks 14 and 16 compared to baseline were rescued to bari 4 mg at Week 16; at Week 20, rescue was based on investigators’ decision. Pts not rescued continued blinded treatment in RA-BEYOND and those with Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI)>10 at or after 3 months in RE-BEYOND were eligible for rescue to bari 4 mg, but not required. Once rescued, change in background medications was allowed. In RA-BEYOND, unrescued pts achieving sustained CDAI ≤10 were randomized to bari 2 mg or maintained at 4 mg. Descriptive longitudinal data analysis was based on observed data from pts randomized to bari 2- or 4-mg in RA-BUILD, including data up to 1 April 2017 in RA-BEYOND. Percent rescued and overall response rates in achieving CDAI ≤10, and pain (visual analogue scale ≤10, 20 or 40 mm), were evaluated from time of original randomization to bari 4 mg and 2 mg in RA-BUILD. Median change over time in CDAI, HAQ, SJC28 and pain after rescue from 2 to 4 mg was evaluated using pt data at time of rescue (reset as Week 0).
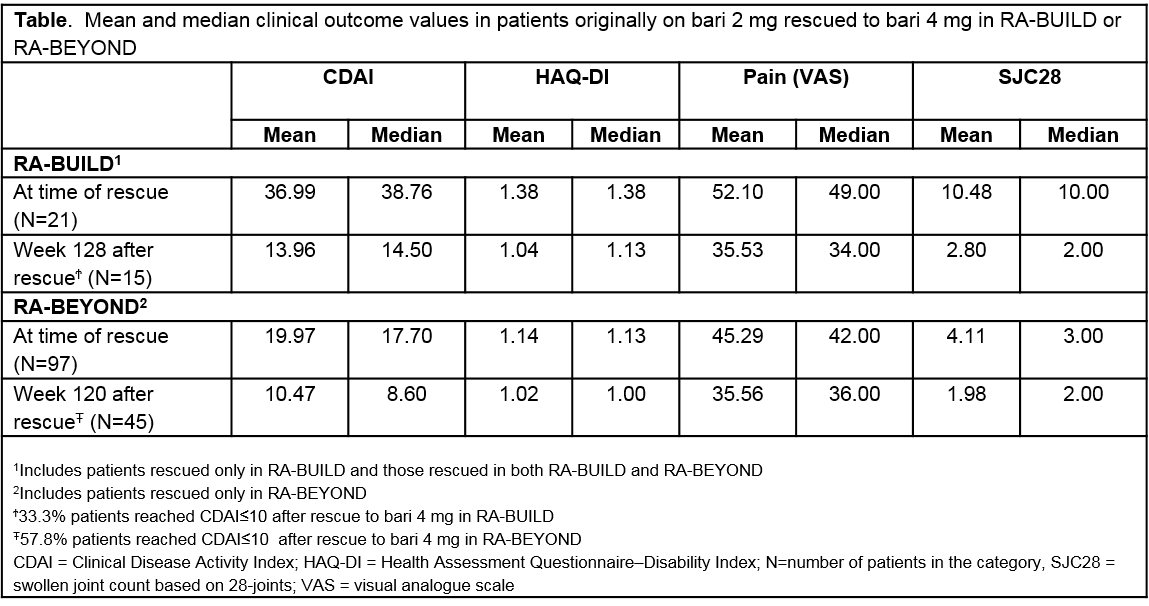
Results: The percentage of pts on bari 4 mg “rescued” in RA-BUILD was 36% compared to 52% in pts originally assigned to bari 2 mg. In RA-BEYOND, 7% of pts originally randomized to 4 mg were rescued after dose tapering to 2 mg. Clinically meaningful response rates in CDAI (≤10) and pain improvement increased and stabilized over time in the bari-treated population. Pts rescued in RA-BEYOND, after being treated with bari in RA-BUILD had less disease activity compared to pts rescued in RA-BUILD at the time of rescue (Table). Pts on 2 mg rescued to bari 4 mg in RA-BEYOND demonstrated improved disease control with the majority achieving CDAI≤10 and pain reduction (Figure).
Conclusion: Fewer pts originally assigned to bari 4 mg in RA-BUILD required rescue compared to pts assigned to 2 mg. Disease activity assessed by CDAI and patient-reported pain improved in many pts after rescue from 2 to 4 mg of bari.
References: 1.Dougados, M et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:88
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fleischmann R, Genovese MC, Cardoso A, Sun L, Chen YF, Walls CD, Schlichting DE, Takeuchi T, Dougados M, Smolen JS, Curtis JR. Longitudinal Efficacy Analysis of Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis and Inadequate Response to Conventional Synthetic Dmards: Response Following Rescue from Baricitinib 2mg to 4mg Once-Daily [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/longitudinal-efficacy-analysis-of-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-inadequate-response-to-conventional-synthetic-dmards-response-following-rescue-from-baricitinib-2mg-to-4mg-once-daily/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/longitudinal-efficacy-analysis-of-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-inadequate-response-to-conventional-synthetic-dmards-response-following-rescue-from-baricitinib-2mg-to-4mg-once-daily/