Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: A substantial amount of patients with chronic low back pain (CLBP) have axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), but early recognition of these patients is difficult for general practitioners (GPs). As a result, several referral strategies have been developed to help physicians identify patients at risk for axSpA within the large group of CLBP patients. Most referral strategies were developed in secondary care patients. The only referral strategy that was developed and validated in primary low back patients is the CaFaSpA strategy. After model development and validation it is important to perform an impact analysis before implementation in daily clinical practice. The purpose of this study is to assess the impact of using a referral strategy on patient outcomes in young primary care patients with CLBP at risk for axSPA.
Methods: A clustered randomized controlled trial was performed in a primary care setting (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01944163). Each cluster contained the general practices from a single primary care practice and their included patients. Clusters were randomized to either the intervention (use of CaFaSpA referral strategy) or the control group (usual care). Primary outcome was disability caused by CLBP, measured with the Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire (RMDQ) at baseline and 4 months. A linear mixed-effects model was used to analyze mean change in RMDQ score.
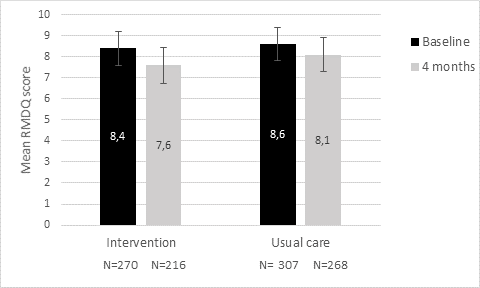
Results: In total 679 patients were included within 93 GP clusters. Sixty-four percent of our study population were female and mean age was 36 years. Median RMDQ score at baseline was 8 (IQR 4-12) in both groups. Compared to baseline, mean RMDQ score decreased by 0.74 points at 4 months (intervention) and by 0.46 points (control) (Figure 1). This decrease did not significantly differ between groups (p=0.50).
Conclusion: Although the CaFaSpA referral strategy can be used as a screening tool to identify axSpA patients but this strategy did not have an early impact on disability caused by CLBP.
Figure 1. Estimated mean RMDQ scores over time for the overall intervention and usual care group. Bars indicate 95% confidence intervals for the mean estimates.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jamal M, Korver A, Kuijper M, Lopes Barreto D, van den Hoogen F, Appels CWY, Spoorenberg A, Koes B, van Hoeven L, Hazes J, Weel AE. The IMPACT of a Referral Algorithm for Axial Spondyloarthritis: Four Month Follow-up in Patient Reported Outcomes [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-a-referral-algorithm-for-axial-spondyloarthritis-four-month-follow-up-in-patient-reported-outcomes/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-a-referral-algorithm-for-axial-spondyloarthritis-four-month-follow-up-in-patient-reported-outcomes/