Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Safety concerns have been raised regarding the risk of serious infections (SI) with the different available biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs). Little is known about the risk of SI in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treated with non-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors (non-TNFi) bDMARDs. In RA patients treated in routine care with the three non-TNFi, abatacept, rituximab and tocilizumab, we aimed to estimate 1) crude and adjusted incidence rates (IR) and 2) relative risks (RR) of SI during the first year since treatment start.
Methods: Collaborative observational cohort study conducted in Denmark (DK) and Sweden (SE) in parallel. RA patients in DANBIO (DK) and ARTIS/SRQ (SE) who started a non-TNFi treatment between 2010-2015 were included and their clinical characteristics at baseline were identified. Baseline comorbidities, reimbursed/dispensed antibiotic prescriptions and incident SI (hospitalization listing infection as major cause of admission) were identified through linkage to National Patient Registries and Prescription Drug Registries. IR of SI/100 patient years (adjusted for age and sex) and rate ratios (as estimates of RR, adjusted for additional covariates) during the first year since treatment start were assessed by Poisson regression.
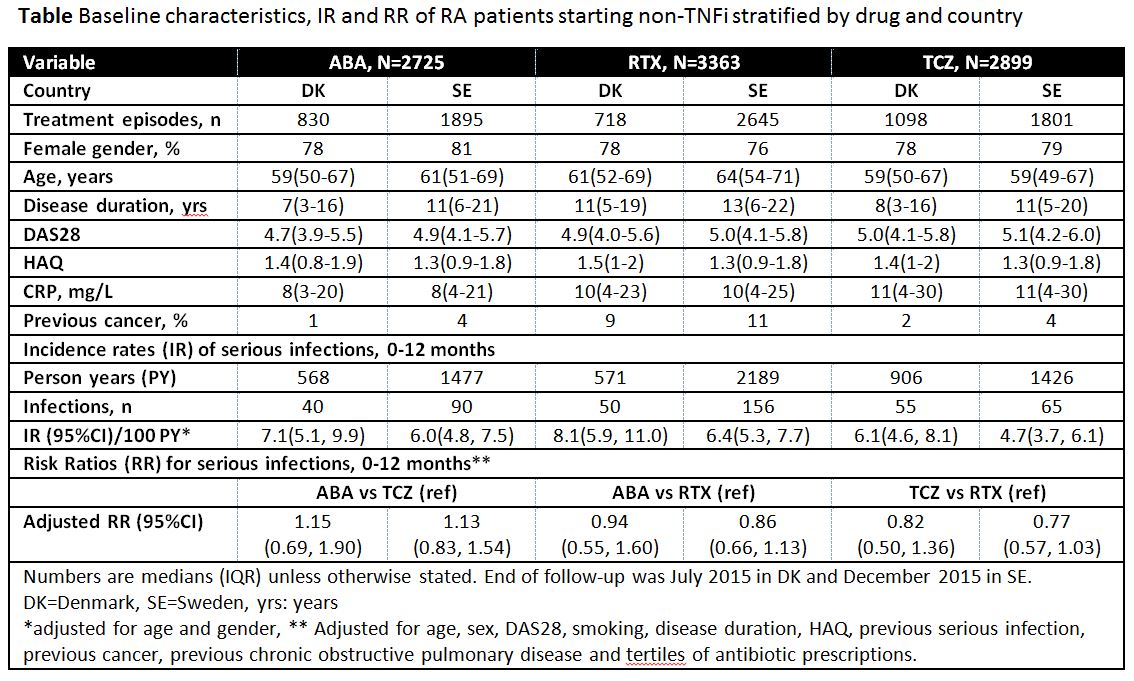
Results: 8,987 treatment episodes were identified (abatacept 2,725/rituximab 3,363/tocilizumab 2,899). Differences in baseline characteristics between the three drugs were observed (Table). During the first year since treatment start, 456 SI were identified. Age/sex-adjusted IRs for SI were numerically different across treatments in each country (abatacept/rituximab/tocilizumab for SE 6.0/6.4/4.7 and for DK 7.1/8.1/6.1, respectively), but the confidence intervals (CI) were wide. Differences in the 1-year adjusted between-drug comparisons (=RR) were observed, but with 1 included in the CIs(Table).
Conclusion: Differences in baseline characteristics were observed. Numerical differences in IR between the three drugs were seen, and the relative risk of SI seemed to vary with drug. However, the findings should be interpreted with caution due to few events and risk of residual confounding.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lederballe Grøn K, Arkema EV, Glintborg B, Mehnert F, Østergaard M, Dreyer L, Nørgaard M, Krogh NS, Askling J, Hetland ML. Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Treated with Abatacept, Rituximab and Tocilizumab in Denmark and Sweden: Risk of Serious Infections [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-abatacept-rituximab-and-tocilizumab-in-denmark-and-sweden-risk-of-serious-infections/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-abatacept-rituximab-and-tocilizumab-in-denmark-and-sweden-risk-of-serious-infections/