Session Information
Session Type: ACR Late-breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
The need for drugs that achieve structure modification in OA is imminent but their development has been burdened by the need for large, long term studies. New imaging biomarkers using structured machine learning offer opportunity for shorter duration and smaller DMOAD trials. MIV-711, a potent and selective cathepsin K inhibitor reduced CTX-I and CTX-II after once-daily administration for up to 28 days in healthy volunteers. Our aim was to examine the efficacy (symptoms and structure) and safety of MIV-711 in knee OA patients.
Methods:
Patients with ACR knee OA, KL2-3 and pain ≥4 & <10 on 0-10 NRS were enrolled at one of 6 European sites and randomised to receive MIV-711 100mg or 200mg or matched placebo qd. Participants remained on usual analgesic medication. Clinical (pain, function, QoL) and safety data were recorded serially and MRI was performed at baseline and wk26. Primary outcome was change in NRS pain score with the key secondary endpoint of change in MRI bone area (medial femur). The main analyses were conducted using linear mixed models.
Results:
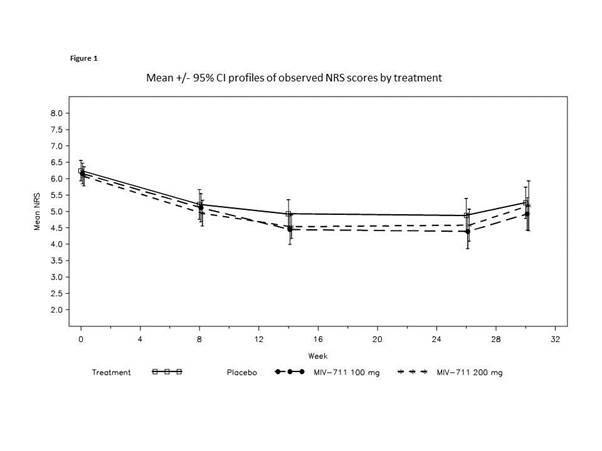
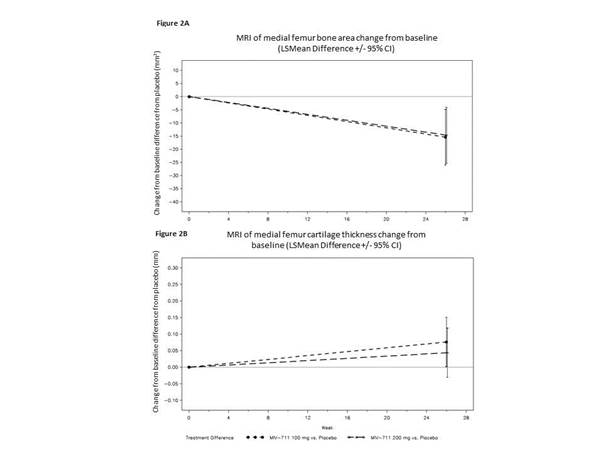
244 participants were enrolled (100mg n=82, 200mg n=82, placebo n=80), 69% women, mean age 62, mean BMI ~32. NRS pain scores; function and QoL measures were not statistically significantly reduced compared to placebo. However, there was a trend to reduction for MIV-711 on the NRS (Figure 1) and across the majority of patient-reported outcomes. Significant reduction in medial femur bone area change for both MIV-711 doses (unadjusted p-values =0.002 and 0.004) were observed at wk26, with no evident differences between the 2 doses (Figure 2A). MIV-711 treated participants demonstrated reduced loss of cartilage thickness on the medial femur versus placebo (unadjusted p=0.023 for 100mg dose, 0.125 for 200mg dose, Figure 2B); medial tibia cartilage loss was not significant. The reductions observed for the biomarkers CTX-I and –II were substantial and of a similar magnitude, indicating strong target engagement for both doses. There was generally good tolerability and safety, with infrequent musculoskeletal symptoms, infections and rashes.
Conclusion:
MIV-711 demonstrated significant reduction in OA bone disease progression, and also reduced cartilage progression, in the femur. Although there was no statistically significant reduction in pain, the study duration required to fully realize the symptom benefits expected from structure modification is unclear. Further evaluation of this novel agent is now warranted.
Disclosure: P. G. Conaghan, Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation, 5,Flexion Therapeutics, 5,AbbVie, 5,Infirst, 5,Medivir, 5,Merck Serono, 5,ONO Pharmaceutical Co., 5; M. A. Bowes, Imorphics Ltd, 3; S. R. Kingsbury, Medivir AB, 5; A. Brett, Imorphics Ltd, 3; G. Guillard, Imorphics Ltd, 3; Å. Jansson, Medivir AB, 3,Medivir AB, 1; C. Wadell, Medivir AB, 3; R. Bethell, Medivir AB, 3,Medivir AB, 1; J. Öhd, Medivir AB, 3,Medivir AB, 1.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Conaghan PG, Bowes MA, Kingsbury SR, Brett A, Guillard G, Jansson Å, Wadell C, Bethell R, Öhd J. Miv-711, a Novel Cathepsin K Inhibitor Demonstrates Evidence of Osteoarthritis Structure Modification: Results from a 6 Month Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Phase IIA Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/miv-711-a-novel-cathepsin-k-inhibitor-demonstrates-evidence-of-osteoarthritis-structure-modification-results-from-a-6-month-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-phase-iia-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/miv-711-a-novel-cathepsin-k-inhibitor-demonstrates-evidence-of-osteoarthritis-structure-modification-results-from-a-6-month-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-phase-iia-trial/