Session Information
Session Type: ACR Late-breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Effective treatment options are limited for refractory skin disease in dermatomyositis (DM). Anabasum is a non-immunosuppressive, synthetic, oral preferential CB2 agonist that triggers resolution of innate immune responses and reduces cytokine production by PBMC from DM patients. This purpose of this study was to test safety and efficacy of anabasum in DM subjects with refractory, moderate-to-severely active skin disease.
Methods: A double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled 16-week Phase 2 trial (JBT101-DM-001) enrolled adults with documented DM and a Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI) activity score ≥ 14, minimal active muscle involvement and failure or intolerance to hydroxychloroquine and stable DM medications including immunosuppressants. Subjects received 2 escalating doses of anabasum (20 mg QD X 4 weeks, then 20 mg BID X 8 weeks) or PBO X 12 weeks. Subjects were followed off study drug X 4 weeks. Safety and efficacy outcomes were assessed from Day 1 through end of study at Week 16. The primary efficacy objective was to assess efficacy of anabasum using CDASI activity score.
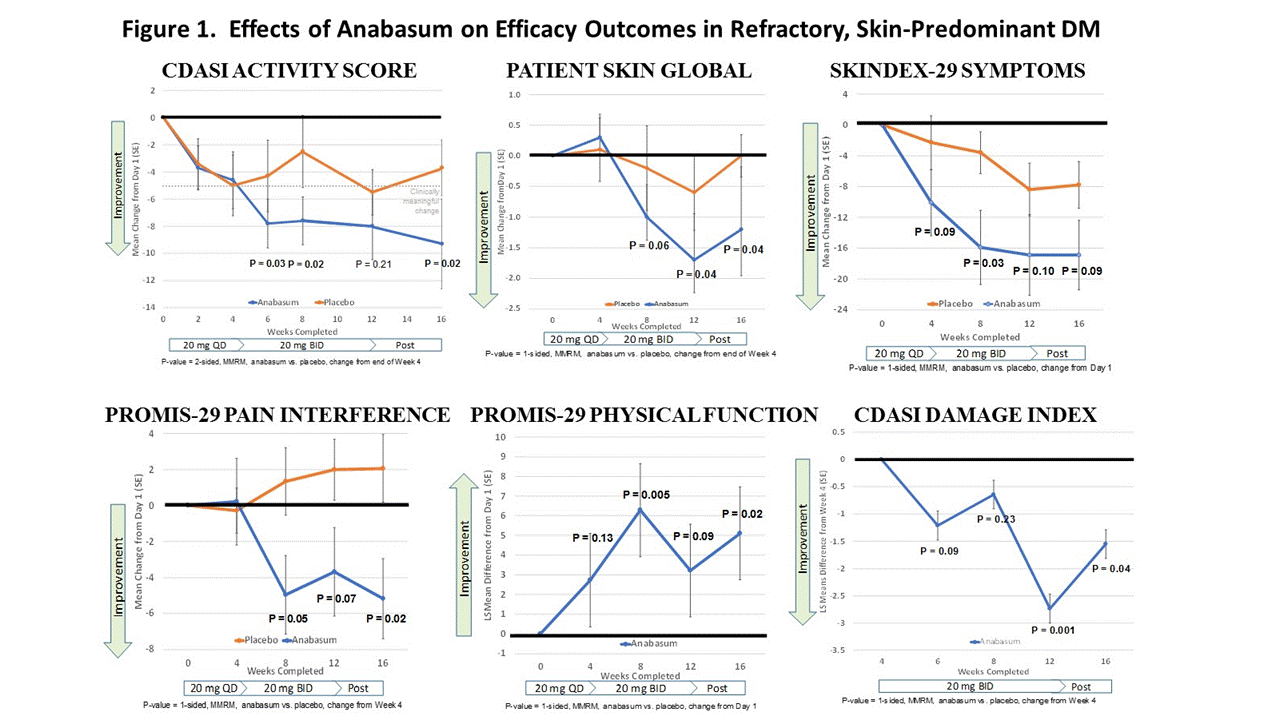
Results: 11 adults each received anabasum and PBO (N = 22). Demographic and disease characteristics were similar in both cohorts. Both cohorts had mean CDASI activity scores in the severe range (33-35) despite immunosuppressants (19/22 subjects). Anabasum subjects had clinically meaningful improvement in CDASI activity scores with mean reduction ≥ 5 points at all visits after 4 weeks. Improvement had statistical significance at end of study (Fig. 1, P = 0.02, 2-sided MMRM) that first became apparent after 4 weeks. Anabasum provided greater improvement than placebo in CDAI damage index, patient-reported global skin disease and overall disease assessments, skin symptoms including photosensitivity and itch, fatigue, sleep, pain interference with activities, pain, and physical function (examples in Fig. 1). Improvements in secondary efficacy outcomes reached statistical significance (P ≤ 0.1, 1-sided MMRM) at multiple visits after week 4 (Fig. 1). There were no serious, severe or unexpected adverse events (AEs) related to anabasum. Tolerability of anabasum was excellent with no study drop-outs. Subjects in the anabasum cohort had numerically more mild AEs than placebo subjects (29 vs. 19) and fewer moderate AEs (4 vs. 7). AEs in ≥ 3 subjects in any cohort were diarrhea, dizziness (lightheadedness), fatigue and dry mouth.
Conclusion: Anabasum demonstrated consistent evidence of clinical benefit across multiple efficacy outcomes and had acceptable safety and tolerability in this Phase 2 trial in refractory skin disease in DM. Further evaluation of anabasum in the treatment of DM is warranted.
Disclosure: V. P. Werth, None; E. Hejazi, None; S. M. Pena, None; J. S. Haber, None; J. Okawa, None; R. Feng, None; K. Gabre, None; J. Concha, None; C. Cornwall, Corbus Pharmaceuticals, Inc., 1,Corbus Pharmaceuticals, Inc., 3; N. Dgetluck, Corbus Pharmaceuticals, Inc., 1,Corbus Pharmaceuticals, Inc., 3; S. Constantine, Corbus Pharmaceuticals, Inc., 1,Corbus Pharmaceuticals, Inc., 3; B. White, Corbus Pharmaceuticals, 1,Corbus Pharmaceuticals, 3.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Werth VP, Hejazi E, Pena SM, Haber JS, Okawa J, Feng R, Gabre K, Concha J, Cornwall C, Dgetluck N, Constantine S, White B. A Phase 2 Study of Safety and Efficacy of Anabasum (JBT-101), a Cannabinoid Receptor Type 2 Agonist, in Refractory Skin-Predominant Dermatomyositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-2-study-of-safety-and-efficacy-of-anabasum-jbt-101-a-cannabinoid-receptor-type-2-agonist-in-refractory-skin-predominant-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-2-study-of-safety-and-efficacy-of-anabasum-jbt-101-a-cannabinoid-receptor-type-2-agonist-in-refractory-skin-predominant-dermatomyositis/