Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Sirukumab (SIR), a human monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to the IL-6 cytokine with high affinity, is in development for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in the global SIRROUND Phase 3 trial program. SIR significantly reduced signs/symptoms of RA and inhibited radiographic progression. SIR has been well tolerated in RA patients (pts) with a safety profile similar to that of other drugs targeting the IL-6 pathway. Pooled safety data from SIRROUND trials are presented.
Methods: Safety data through July 29, 2016 from 5 Phase 3 trials of SIR were analyzed. These trials included pts with moderate to severe active RA who were refractory or intolerant to conventional DMARDs (SIRROUND-D, M, H) or anti-TNF therapy (SIRROUND-T). SIRROUND-LTE is a long-term extension study for pts completing SIRROUND-D or T. SIR was administered SC at 50mg q4w or 100mg q2w. Safety analyses are presented by SIR treatment group for adverse events (AEs), serious AEs (SAEs), mortality, and AEs of special interest (serious infections, gastrointestinal [GI] perforations, major adverse cardiovascular events [MACE], and malignancies).
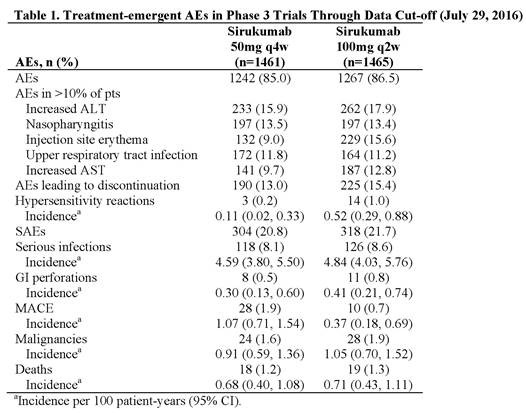
Results: In Phase 3 trials, 2926 pts received SIR. Pts were treated for up to 3.9 years (approximately 5300 patient-years of drug exposure), with a median exposure of 1.76 years. Similar proportions of pts had treatment-emergent AEs, discontinuations due to AEs, and SAEs in the 50mg and 100mg groups (Table). Incidences of common AEs were generally comparable across dose groups; however, injection site reactions (ISRs) occurred more frequently with more frequent dosing: 100-mg q2w (21.9%) versus 50-mg q4w (12.7%) dose, with erythema, pruritus, and swelling most frequently reported. Pneumonia (1.8%) and cellulitis (1.1%) were the only individual SAEs reported in ≥1% of all SIR-treated pts. No dose effect was observed for the incidence of serious infections. Rates of GI perforation and malignancies were low in both dose groups. MACE rates for SIR 50mg q4w were similar to those reported for other agents and RA in general and were numerically lower with SIR 100mg q2w. The overall mortality rates were similar for the 2 SIR doses and also consistent with those observed with other agents and RA.
Conclusion: In this pooled safety analysis of SIR in pts with active RA, no new safety signals were observed. Overall, no dose response was observed between SIR 50mg q4w and 100mg q2w for types and frequencies of AEs, with the exception of hypersensitivity and ISRs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aletaha D, Thorne C, Schiff M, Harigai M, Agarwal P, Rao R, Cohen C, Cheng B, Brown K, Hsu B. Integrated Phase 3 Safety Results of Sirukumab, an Anti–IL-6 Cytokine Monoclonal Antibody, in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrated-phase-3-safety-results-of-sirukumab-an-anti-il-6-cytokine-monoclonal-antibody-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrated-phase-3-safety-results-of-sirukumab-an-anti-il-6-cytokine-monoclonal-antibody-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis/