Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: High body mass index (BMI) is known to be associated with inadequate clinical response to anti-TNF agents in RA patients.1 However, there are limited data on how high BMI affects the response to rituximab in RA patients with an inadequate response or intolerance to anti-TNF agents. The objective is to investigate the impact of BMI on clinical response in the post-hoc analysis of Phase 3 randomized controlled trial comparing CT-P10 and reference rituximab, RTX2 (NCT02149121).
Methods: A total of 332 patients who received 2 cycles of either CT-P10 or RTX at weeks 0 and 24 were included in this analysis. Patients were classified into 3 groups; normal weight (<25kg/m2), overweight (25 kg/m2~30 kg/m2) and obesity (>=30 kg/m2) as per WHO BMI category. Improvement in disease activity by the DAS28-CRP, remission (<=2.6), low disease activity rate (LDA, <=3.2), ACR response at Week 24 and Week 48 and duration of sustained LDA (from the first LDA observed to the last LDA observed up to Week 48) were analysed by BMI categories in the each and combined group of CT-P10 and RTX.
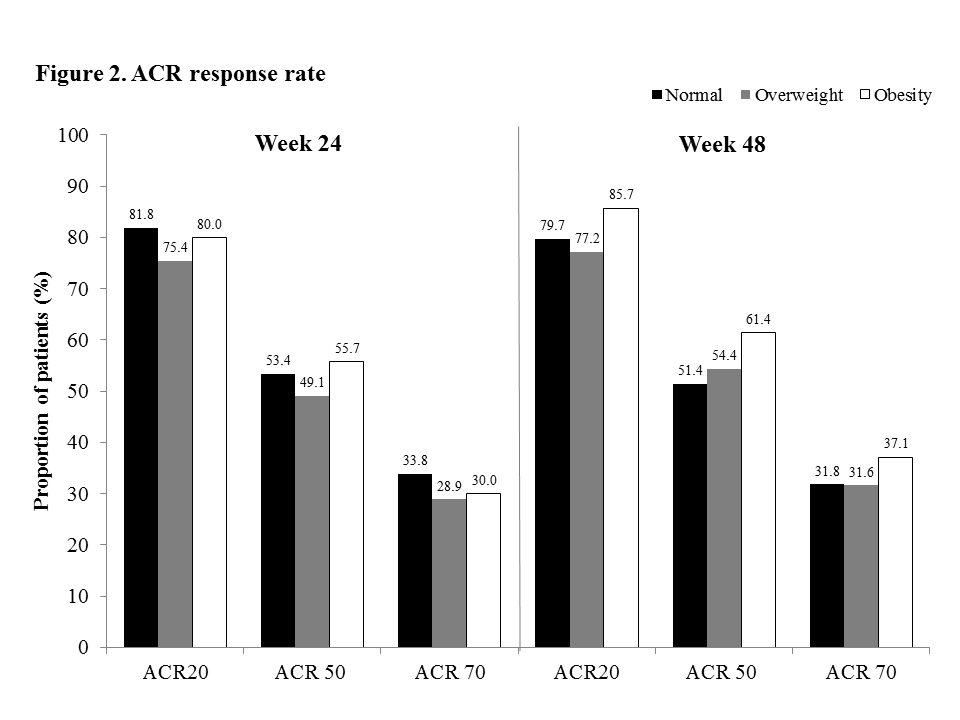
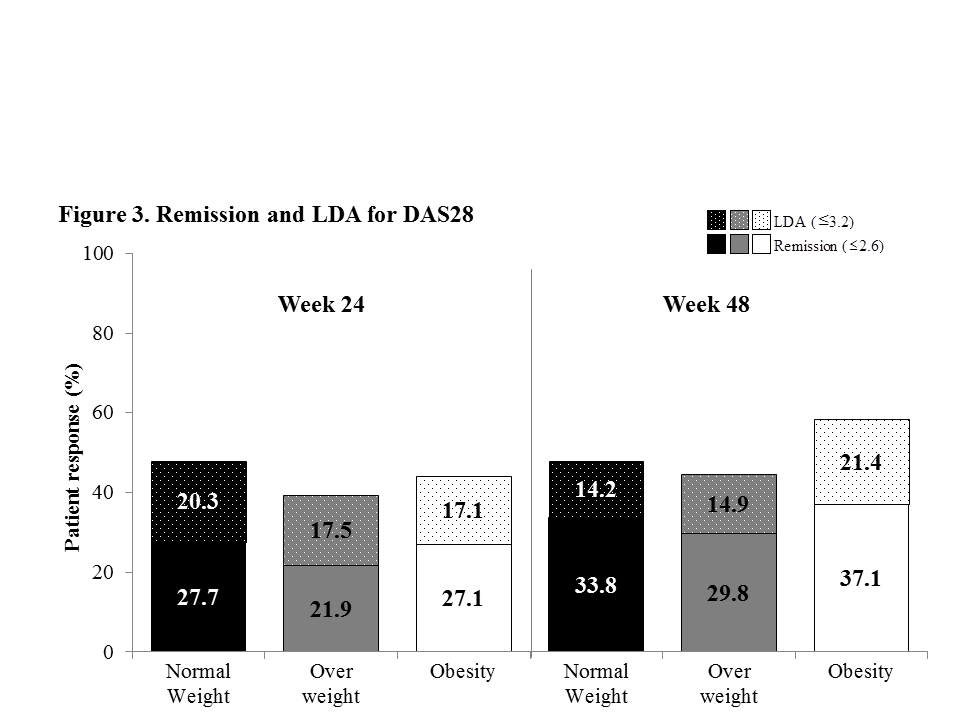
Results: In the pooled group of CT-P10 and RTX, the mean weights were 59kg in normal weight, 73kg in overweight and 91kg in obesity subgroups. All other baseline characteristics were comparable among BMI groups including baseline disease activity based on DAS28; Moderate, 22.3% vs. 22.8% vs. 25.7%, respectively; High, 77.7% vs. 77.2% vs. 74.3%, respectively. Mean change of DAS28 from baseline (Figure 1), ACR response rate (Figure 2) and rate of remission and LDA for DAS28 (Figure 3) were comparable among BMI groups and there were no statistical significant difference (p>0.05). No association was shown between DAS28 improvement and BMI (p>0.05). Mean duration of sustained LDA (months) for DAS28 were also comparable among the groups (5.1 vs. 5.2 vs. 5.6, respectively). Additionally, similar trends in all analyses were observed in each treatment group; CT-P10 and RTX.
Conclusion: The impact of BMI on the clinical response to rituximab treatment was not significant in RA patients. Therefore, these results support that rituximab could be a reasonable therapeutic option for obese RA patients with inadequate response to anti-TNF agents.
References
1. Gremese E, et al. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2013;65:94–100.
2. Yoo DH, et al. Arthritis Rheum 2016; 68 (Suppl 10):2039-41
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yoo DH, Park W, Suh CH, Shim SC, Lee SJ, Bae YJ, Park C, Han NR. Rituximab Is Effective in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Irrespective of Body Mass Index; Up to 48 Weeks Results from Phase 3 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-is-effective-in-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-irrespective-of-body-mass-index-up-to-48-weeks-results-from-phase-3-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-is-effective-in-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-irrespective-of-body-mass-index-up-to-48-weeks-results-from-phase-3-study/