Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Benepali, the etanercept biosimilar, is licenced in the UK for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and costs less than Enbrel. This study aimed to evaluate the comparative effectiveness and tolerance of Benepali in RA patients that were switched from Enbrel.
Methods: A retrospective observational study design. Data collected from 38 patients with RA who had previously been established on Enbrel and were switched to Benepali with unchanged dosing regimens. Patient’s baseline characteristics, DAS-28, CRP, tender joints, swollen joints and global scores were collected before and after the switch from hospital records at a single centre.
Variables were analysed using the Bland-Altman 95% limits of agreement on the estimated mean bias between paired measurements ± 1.96SD. Student’s paired t-test was used to assess the significance of the mean difference.
Results: Patients had a mean age of 59.3 years, 69% were female and 88.5% were seropositive. There were 9/39 that had used a biologic prior to Enbrel.
|
Table 1: Markers of disease activity in Enbrel and Benepali |
||||
|
|
Enbrel average |
Benepali average |
Mean difference |
P-value |
|
DAS-28 (n=38) |
3.08 |
3.42 |
+0.35 |
0.06 |
|
CRP (n=38) |
7.00 |
6.95 |
-0.05 |
0.98 |
|
Tender joints (n=38) |
3.10 |
3.84 |
+0.74 |
0.15 |
|
Swollen joints (n=38) |
1.26 |
1.5 |
+0.24 |
0.54 |
|
Patient global health (n=38) |
38.6 |
49.6 |
+11 |
0.05 |
The mean difference in DAS-28, CRP, tender and swollen joints is not statistically significant (Table 1). There was an average increased global score of 11/100 (p=0.05) with Benepali. This suggests that the more objective scores were less likely to be affected by the switch to Benepali.
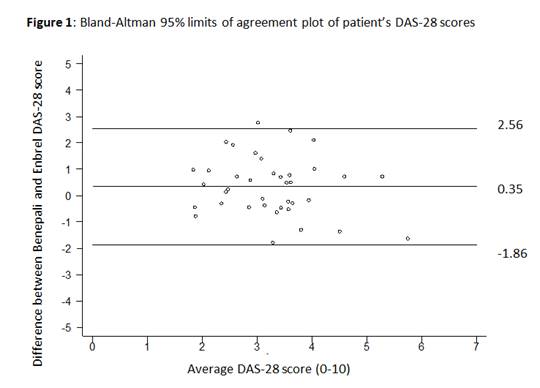
Bland-Altman analysis (Figure 1) shows wide limits of agreement (-1.86 to 2.56), with a small mean difference of 0.348 (95% CI -0.01, 0.71) in DAS-28 scores. This suggests that although majority of patients did not have a significant variation in their DAS-28, there were a number of patients that did significantly better or worse on the Benepali.
Benepali was discontinued 17% of patients (6/36); 4 stopped due to ineffectiveness (all of which were switched back to Enbrel) and 2 stopped due to adverse drug reactions (1 patient developed injection site reactions and switched back to Enbrel, and the other patient developed a rash and had a significant fall in neutrophils and was re-challenged with Benepali).
Conclusion: In this RA clinical cohort, objective measures of disease activity were not statistically different for Benepali compared with Enbrel. The switch to Benepali resulted in a drug cost saving of £26400 per annum.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dyball S, Hoskins V, Christy-Kilner S, Haque S. Effectiveness and Tolerability of Benepali in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Switched from Enbrel [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-and-tolerability-of-benepali-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-switched-from-enbrel/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-and-tolerability-of-benepali-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-switched-from-enbrel/