Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 7, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster III: Comorbidities
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Abstract
Background/Purpose: Rituximab-based chemotherapy can induce hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation (HBVr) in patients with hematological malignancies who have been exposed to HBV infection. However, informative data regarding the risk of Rituximab on HBVr among patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is unsettled.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed RA patients in Taipei Veterans General Hospital and patients with available HBV markers before rituximab administration were enrolled. HBVr was defined as either an increase in HBV DNA >1 Log10 IU/ml compared with baseline or threefold increase in serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level accompanied with HBV DNA > 20,000 IU/mL in cases without baseline HBV viral load, or hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) reverse seroconversion in HBsAg-negative cases.
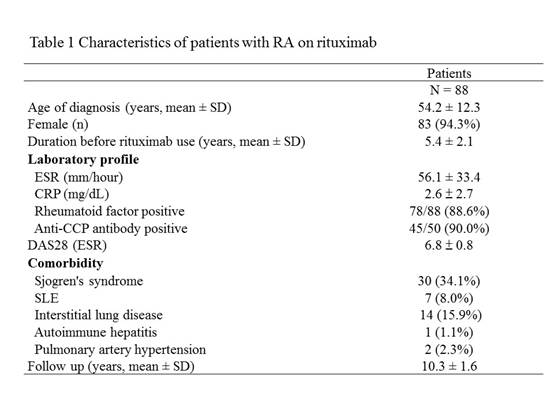
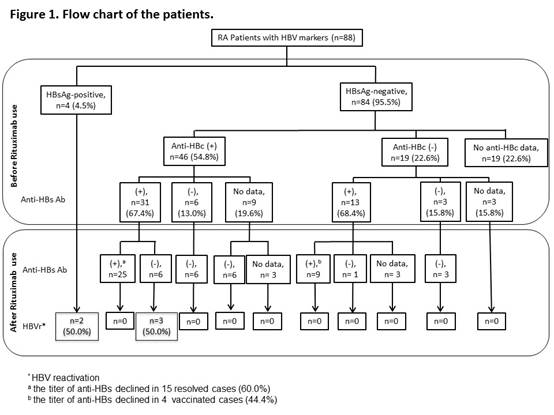
Results: Eighty-eight patients were enrolled; 83 (94.3%) were female and the mean age at diagnosis was 54.2 years (Table 1). They received a median of 9 cycles of RTX (range 1-20) without anti-HBV prophylaxis. Four patients were positive for hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) before rituximab administration (Figure 1). In 84 HBsAg-negative patients, 46 were positive for anti-hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HBc), 19 were negative for anti-HBc, and 19 did not have anti-HBc data. Among 46 HBsAg-negative/anti-HBc-positive patients, 31 were hepatitis B surface antibody (anti-HBs)-positive, 6 were anti-HBs-negative, and 9 did not have anti-HBs data. During 10,877 person-months of follow-up, 5 (5.7%) patients developed HBVr. HBVr occurred in 2 (50.0%) of 4 HBsAg-positive patients and the time to HBVr was 40 and 74 months after the start of rituximab, respectively. Among 31 HBsAg-negative/anti-HBc-positive/anti-HBs-positive patients, a decrease in anti-HBs levels was observed in 21 (67.7%) cases after rituximab treatment and anti-HBs disappeared in 6 (19.4%) patients. Three (50.0%) of anti-HBs-disappear patients seroreverted to HBsAg-positive and all of them developed HBVr later with the mean time from the start of rituximab to HBVr was 59.3 months (range 56-62months).
Conclusion: HBVr is common in HBsAg-positive RA patients under rituximab therapy. More importantly, rituximab may lead to high disappearance rate of anti-HBs in resolved HBV cases, resulting in high risk of HBVr. Monitor HBV status frequently is critical in RA patients who have been exposed to HBV infection during rituximab treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chen MH, Tsao YP, Huang YH, Chou CT, Tsai CY. High Incidence of Hepatitis Related to HBV Reactivation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Resolved Hepatitis B Infection during Rituximab Treatment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-incidence-of-hepatitis-related-to-hbv-reactivation-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-resolved-hepatitis-b-infection-during-rituximab-treatment/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-incidence-of-hepatitis-related-to-hbv-reactivation-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-resolved-hepatitis-b-infection-during-rituximab-treatment/