Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 7, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster III: Comorbidities
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (BARI) is an oral selective inhibitor of Janus kinase (JAK)1 and JAK2 approved in the EU for the treatment of active RA. Patients (pts) with RA have increased cardiovascular risk, including for arterial and venous occlusive events.1-3 This abstract examines the effects of BARI on cardiovascular events in RA.
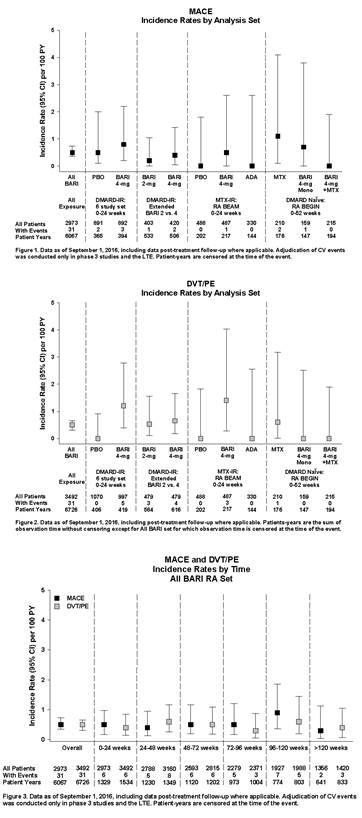
Methods: Data were pooled from 8 completed studies (1 Phase 1b, 3 Phase 2, 4 Phase 3) and 1 ongoing long term extension study (LTE) with data up to Sept. 1, 2016. The All BARI RA (All Exposure) analysis set included all pts exposed to any BARI dose. Comparisons with placebo (PBO) were based on 6 studies with BARI 4 mg once daily (QD) and PBO. Dose response was assessed based on 4 studies with BARI 2 and 4 mg QD, including data from the LTE (Extended 2 vs 4 mg set). Two studies contained active comparators (MTX and adalimumab [ADA]). Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) (composite of myocardial infarction, stroke and cardiovascular death) were blindly adjudicated by an independent panel for phase 3 studies and the LTE. Study database terms of “deep vein thrombosis” (DVT) / “pulmonary embolism” (PE) were analyzed without adjudication. Incidence rates (IR) per 100 pt-years [PY] of exposure were used.
Results: 3492 pts were exposed to BARI (6637 PY), 2723 pts (78.0%) for >1 year and 1867 (53.5%) for >2 years. In the 6-study PBO-controlled set (0-24 weeks), 2 cases of MACE were reported in the PBO group and 3 cases in the BARI 4 mg group (Figure 1). DVT/PE were reported for 0 pts in the PBO group and 5 in the BARI 4 mg group (Figure 2); 2 were serious, all had multiple risk factors, 1 occurred after discontinuing study drug, and 4 pts either continued or restarted BARI without worsening or occurrence of another event. In the Extended 2 vs. 4 mg set, IR for MACE and DVT/PE were comparable between doses. In the All BARI RA set, event rates were stable over time (Figure 3), with overall IR of 0.51 per 100 PY for MACE and 0.46 for DVT/PE (published RA DVT/PE rates 0.29 to 0.79 per 100 PY).
Conclusion: For MACE, IR were similar across analysis sets and did not increase with prolonged exposure. For DVT/PE, events were reported for BARI 4 mg but not PBO; IR were similar between doses, consistent over time, and comparable to published rates in RA.1-3
References: 1. Solomon DH et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(12):1608-12, 2. Romero-Diaz J et al. J Rheumatol. 2009;36(1)68-75, 3. Ogdie A et al. Eur Heart J. 2017. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehx145
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Weinblatt M, Taylor PC, Burmester GR, Witt S, Saifan C, Walls C, Rooney TP, Chen L, Takeuchi T. Cardiovascular Safety during Treatment with Baricitinib in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cardiovascular-safety-during-treatment-with-baricitinib-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cardiovascular-safety-during-treatment-with-baricitinib-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/