Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
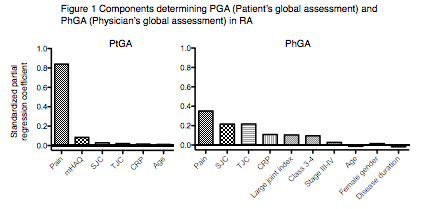
Results: Multivariate logistic regression identified age (OR: 1.01 [95% confidence interval: 1.01–1.02]), pain (2.15 [2.08–2.22]) and modified Health Assessment Questionnaire score (1.56 [1.39–1.75]) as significant predictors of positive discordance. On the other hand, TJC (0.93 [0.91–0.94]), SJC (0.92 [0.90–0.94]), CRP (0.88 [0.83–0.93]), class 3-4 (0.63 [0.53–0.76]), Z (0.72 [0.59–0.88]), and the large joint index (0.59 [0.47–0.74]) predicted significantly against positive discordance. Linear regression analysis demonstrated that PGA was mainly determined by pain, whereas PhGA was determined by various factors, including the large joint index (Figure 1) and Z.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sawada T, Tago M, Nishiyama S, Tahara K, Kato E, Mori H, Hayashi H, Nishino J, Matsui T, Tohma S. Influence of Large-Joint Involvement on Patient-Physician Discordance in Global Assessment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity Analyzed By Novel Joint Index [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influence-of-large-joint-involvement-on-patient-physician-discordance-in-global-assessment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-disease-activity-analyzed-by-novel-joint-index/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influence-of-large-joint-involvement-on-patient-physician-discordance-in-global-assessment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-disease-activity-analyzed-by-novel-joint-index/