Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
The clinical and mechanistic relevance of peripheral CD4+CXCR4+ T cells in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM)-associated interstitial lung disease (IIM-ILD) is not known.
Methods:
Patients with IIM-ILD (n=36), disease-related controls (n=30), and healthy persons (n=13) were recruited. CD4+CXCR4+ T cell percentages, stromal cell-derived factor-1(SDF-1), Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6), autoantibodies, lung function, HR-CT scores, and individual disease progress were analyzed. Cytokine expression of isolated CD4+CXCR4+ T cell and co-cultured fibroblast proliferation was measured.
Results:
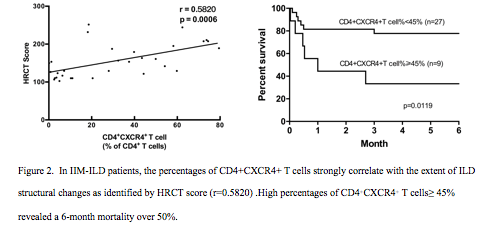
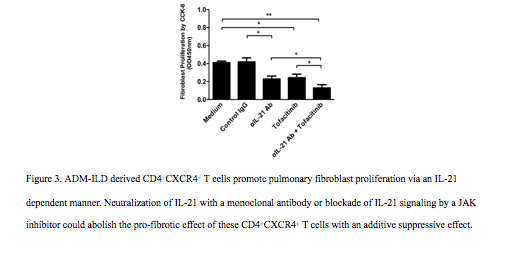
The percentages of peripheral CD4+CXCR4+ T cells are significantly elevated in IIM-ILD patients compared to controls (p<0.01 Figure 1), correlate with HRCT scores (r=0.5820) and pulmonary function impairments (FVC, DLCO/VA). They are associated with anti-MDA5 autoantibodies and the amyopathic dermatomyositis (ADM) phenotype. In IIM-ILD, percentages of CD4+CXCR4+ T cells ≥ 45% revealed a 6-month mortality over 50% (Figure 2). CD4+CXCR4+ T cells from ADM-ILD patients express high levels of IL-21. In vitro blockade of IL-21 signaling by neutralization of IL-21 or JAK inhibitor could abolish the fibroblast proliferation (Figure 3).
Conclusion:
CD4+CXCR4+ T cells appear to be a potentially valuable novel biomarker associated with the severity and prognosis of IIM-ILD. They promote pulmonary fibroblast proliferation via IL-21, which may herald future targeted treatments for this severe disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang K, Zhao J, Chen Z, Li T, Tan X, Zheng Y, Gu L, Guo L, Sun F, Wang H, Li J, Wang X, Riemekasten G, Ye S. CD4+CXCR4+t Cells in Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cd4cxcr4t-cells-in-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathy-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cd4cxcr4t-cells-in-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathy-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/
