Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose :
pSS is characterized by a strong IFN signature, ectopic germinal centers formation and a chronic blood lymphopenia. IL-7 plays a central part in T cells homeostasis and in lymphoid structures organization. We aimed to assess the role of IL-7 in pSS pathogenesis.
Methods :
IL-7 serum level was assessed in 372 pSS patients and 73 paired controls. Primary cultures of salivary gland epithelial cells (SGEC) from patients and controls were stimulated by Poly I:C 30 ng/ml, IFN-α 600UI/ml, IFN-γ 5ng/ml and IFN-λ (IL-28) 25ng/ml for 72 hours. IL-7 secretion was tested in culture supernatant by ELISA. IL-7 expression after 24 hours stimulation was assessed by quantitative RT-PCR. IL-7 and its receptor’s expressions were evaluated in RNA-Seq analysis from cells form salivary glands biopsies (SGB) and PBMC.
Results :
pSS patients had higher serum IL-7 levels than controls: 7.56 ng/ml ± 8.52 (mean ± SD) versus 4.86 ng/ml ± 5.59; p<0.0001. A positive correlation with B cells activation markers, IFN-induced chemokines and disease activity markers was observed. In multivariate analysis, serum IL-7 level was associated with CXCL13, anti-SSA, RF, κ light-chain and low C4.
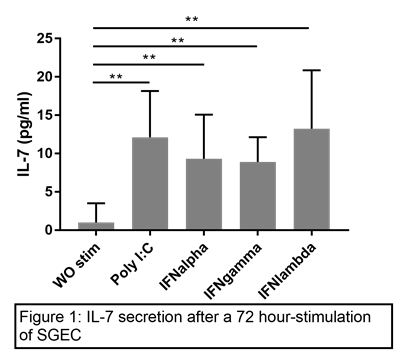
SGEC stimulation with Poly I:C, IFN-α, -γ and -λ induced IL-7 protein secretion in the supernatant (p=0.002, p=0.004, p=0.007, p=0.004 respectively) (Figure 1). A trend for a greater IL-7 production in pSS patients compared to controls was observed. IL-7 expression was confirmed by quantitative RT-PCR. Among cell subsets purified ex vivo from SGB and PBMC, RNA-Seq analysis showed a greater expression of IL-7 by epithelial cells of patients compared to controls (p=0.03). No difference was observed regarding T and B cells either from biopsies or PBMC. IL-7 receptor expression was equivalent between patients and controls. Analysis of T cells exhaustion profile and IL-7 intracellular signaling are on-going.
Conclusion :
Our data demonstrate that IL-7 is secreted within the target tissue of pSS by SGEC after stimulation by IFNs. This IFN/IL-7 pathway can be involved in the organization of ectopic germinal centers found in pSS. But more importantly, since Il-7 is one of the major controller of homeostasis of T cells, this IFN/IL-7 pathway could be involved in the persistent lymphopenia which is a hallmark of the disease, either by favoring exhaustion of T cells or by an impaired function of the IL-7 intracellular signaling. Both mechanisms are currently explored and will be presented.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Virone A, Pascaud J, Rivière E, Gottenberg JE, Le Guern V, Mariette X, Nocturne G. IL-7 in Primary Sjogren Syndrome (pSS) Is Secreted By Salivary Gland Epithelial Cells after IFN Stimulation and Is Associated with B-Cell Activation [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/il-7-in-primary-sjogren-syndrome-pss-is-secreted-by-salivary-gland-epithelial-cells-after-ifn-stimulation-and-is-associated-with-b-cell-activation/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/il-7-in-primary-sjogren-syndrome-pss-is-secreted-by-salivary-gland-epithelial-cells-after-ifn-stimulation-and-is-associated-with-b-cell-activation/