Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
We are currently witnessing a diversification of the available biotherapies (bDMARDs) for psoriatic arthritis (PsA), with the arrival of new classes of medication. Those treatment options are new, and there is no consensual hierarchy in the use of those medications, and no head-to-head comparative study. The present meta-analysis aims to evaluate the respective efficacy of TNF inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitor (ustekinumab), IL-12/23 inhibitor (secukinumab), and CTLA4-Ig (abatacept), on ACR response criteria, PASI response criteria, HAQ-DI, enthesitis and dactylitis outcomes in PsA.
Methods:
Randomised controlled trials assessing TNF inhibitors, ustekinumab, secukinumab or abatacept in psoriatic arthritis were selected through the MedLine database, ACR and EULAR scientific meeting archives. ACR20, ACR50, ACR70, PASI75 and PASI90 response rates and the proportion of patients with residual dactylitis or enthesitis were collected at the time of evaluation of the primary endpoint. The pooled response risk ratios (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (95%CI) were quantified for the standard dose of anti-TNF (golimumab 50 mg), ustekinumab (45 mg), secukinumab (150 mg) or abatacept (125 mg) in comparison with placebo. A meta-analysis was performed using the inverse variance approach and statistical heterogeneity was assessed with the Cochran Q-test and I2 values.
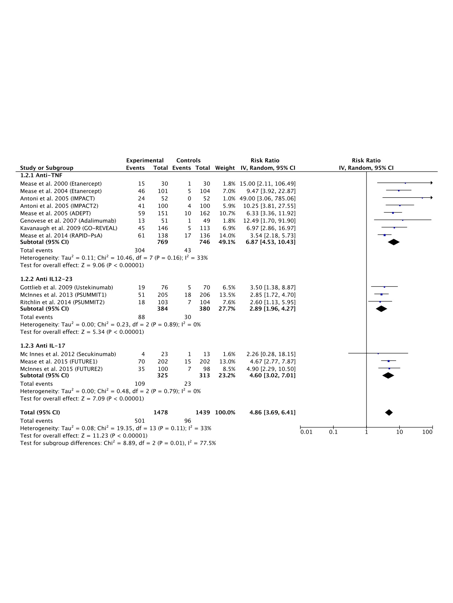
Results:
15 RCTs were selected for the meta-analysis. Anti-TNF, secukinumab, ustekinumab and abatacept showed higher ACR20 response rates, with RRs (95%CIs) ranging from 3.51 (2.92, 4.22) to 1.77 (1.31, 2.39), in comparison with placebo. Anti-TNF, secukinumab and ustekinumab showed higher ACR50 (see table) and ACR70 response rates, with RRs (95%CIs) ranging from 6.87 (4.53, 10.43) to 2.89 (1.96, 4.27) and 10.80 (6.25, 18.66) to 4.29 (2.04, 8.99), respectively, in comparison with placebo. Anti-TNF, secukinumab and ustekinumab showed higher PASI75 response rates, with RRs (95% CIs) ranging from 16.61 (6.38, 43.26) to 5.54 (3.01, 10.21), in comparison with placebo. Anti-TNF, secukinumab and ustekinumab showed a lower proportion of residual enthesitis, with RRs (95% CIs) ranging from 0.65 (0.50, 0.84) to 0.83 (0.71, 0.97), while only anti-TNF and secukinumab showed a lower proportion of residual dactylitis, with RRs (95%CI) ranging from 0.48 (0.31, 0.74) to 0.53 (0.43, 0.65), in comparison with placebo.
Conclusion:
In this meta-analysis, bDMARDs showed higher ACR20/50/70 and PASI75 response rates and a lower proportion of residual enthesitis and dactylitis, in comparison with placebo. However, the respective efficacy of bDMARDs, quantified using ORs or NNTs (data not shown), is variable among the different outcomes measures, in particular for enthesitis and dactylitis. Head-to-head studies are needed to draw definitive conclusions on potential efficacy differences between bDMARDs in PsA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Simons N, Degboé Y, Barnetche T, Cantagrel A, Ruyssen-Witrand A, Constantin A. Biological DMARD Efficacy in Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on ACR Response Criteria, PASI Response Criteria, HAQ-DI, Enthesitis and Dactylitis Outcomes [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biological-dmard-efficacy-in-psoriatic-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis-on-acr-response-criteria-pasi-response-criteria-haq-di-enthesitis-and-dactylitis-outcomes/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biological-dmard-efficacy-in-psoriatic-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis-on-acr-response-criteria-pasi-response-criteria-haq-di-enthesitis-and-dactylitis-outcomes/