Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose : SB4 is approved by the European Commission as a biosimilar of the reference etanercept (ETN). The phase III clinical study results have been reported previously.1,2 Data to date shows no correlation between the development of anti-drug antibody (ADA) and clinical response or adverse events with etanercept treatment. The objective of this study was to investigate the impact of the presence of ADA or injection site reaction (ISR) on efficacy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treated with SB4 or ETN up to week 24.
Methods : In this phase III randomized, double blind study, patients with moderate to severe RA received 50 mg/week of either SB4 or ETN with background methotrexate (MTX) for 52 weeks. Efficacy, safety and immunogenicity were assessed.
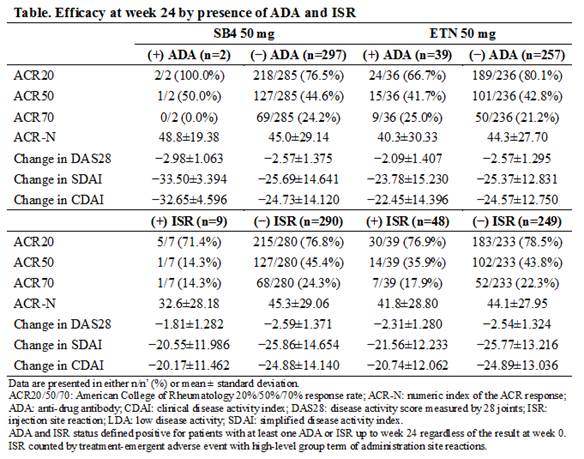
Results : Up to week 24, the incidence of ADA (2 patients [0.4%] in SB4 vs 39 patients [13.1%] in ETN, p < 0.001) and the incidence of ISR (9 patients [3.0%] in SB4 vs 48 patients [16.2%] in ETN, p < 0.001) were significantly lower in SB4 compared to ETN. Due to the low incidence of ADA in the SB4 treatment group, the impact of ADA on efficacy could not be evaluated. Within the ETN treatment group at week 24, there was a trend towards increased efficacy (ACR20, ACR-N, change in DAS28, remission and low disease activity based on DAS28, SDAI, or CDAI) in patients without detectable ADA compared to patients with ADA (Table). In regards to ISR, efficacy tended to be higher in patients who did not experience ISR compared to those who did within each treatment group.
There was no correlation between the presence of ADA and incidence of ISR. In patients without detectable ADA and patients with ADA, respectively, 3.0% (9/297) vs. 0.0% (0/2) of patients from SB4 group and 16.3% (42/248) vs. 15.4% (6/39) of patients from the ETN group experienced ISR.
Conclusion : Significantly fewer patients from SB4 developed ADA or experienced ISR compared to ETN, however the efficacy was still comparable between SB4 and ETN in patients without detectable ADA and in patients who did not experience ISR. Within the ETN group, there was a trend towards increased efficacy in patients without detectable ADA compared to patients with ADA. In both SB4 and ETN group, patients without ISR tended to have higher efficacy than patients with ISR. There was no correlation between the presence of ADA and ISR.
References
1. Emery P et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Jul 07.
2. Vencovsky J et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vencovsky J, Emery P, Keystone EC, Ghil J, Cheong SY, Hong E. Impact of Anti-Drug Antibody and Injection Site Reaction on Efficacy: 24-Week Results from a Phase III Study Comparing SB4 (etanercept biosimilar) with Reference Etanercept in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-anti-drug-antibody-and-injection-site-reaction-on-efficacy-24-week-results-from-a-phase-iii-study-comparing-sb4-etanercept-biosimilar-with-reference-etanercept-in-patients-with-rheumatoid/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-anti-drug-antibody-and-injection-site-reaction-on-efficacy-24-week-results-from-a-phase-iii-study-comparing-sb4-etanercept-biosimilar-with-reference-etanercept-in-patients-with-rheumatoid/