Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We examined high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) levels in relation to structural progression in patients with RA receiving tofacitinib or methotrexate (MTX).
Methods: This was a post-hoc analysis of data from a Phase 3, randomized, double-blind controlled trial of tofacitinib monotherapy vs MTX (ORAL Start [NCT01039688]) in patients with early RA who were naïve to therapeutic doses of MTX. Patients were randomized to tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID), tofacitinib 10 mg BID, or MTX titrated up to 20 mg/week. hsCRP levels through Month (M) 24 were analyzed descriptively for patients with structural progression at M12 (change from baseline in modified Total Sharp Score [mTSS] >0.5; mTSS progressors) and those without structural progression at M12 (mTSS non‑progressors). The proportions of patients who were mTSS non-progressors at M6, M12, and M24 were summarized for patients with baseline hsCRP level ≤7 mg/L and >7 mg/L.
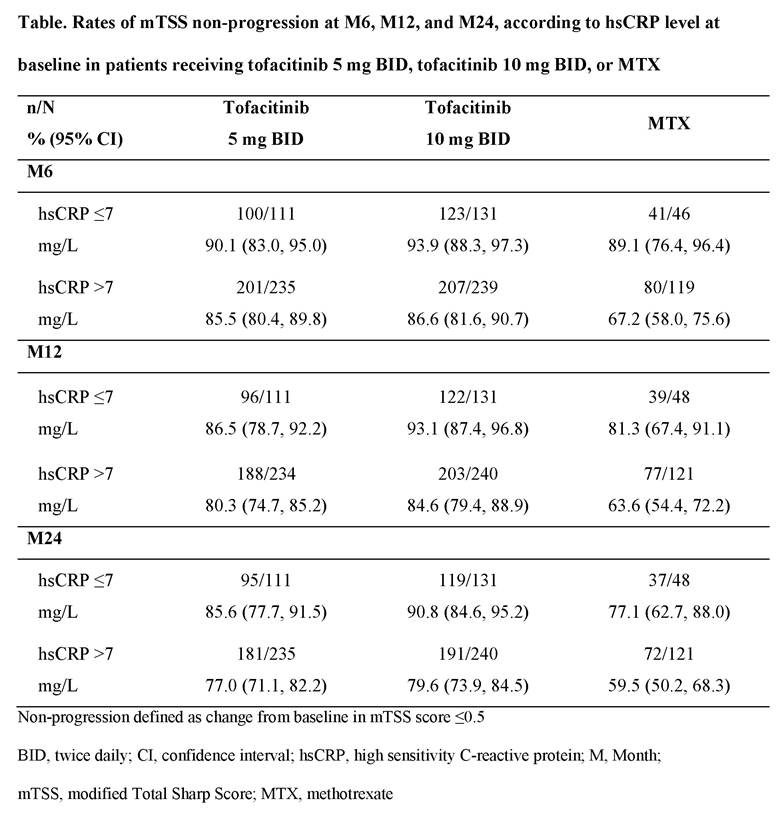
Results: A total of 885 patients who had mTSS assessments at M12 were included in this analysis, of whom 345 received tofacitinib 5 mg BID, 371 received tofacitinib 10 mg BID and 169 received MTX. Mean baseline hsCRP levels were similar across treatment groups, but M12 mTSS progressors appeared to have a higher mean baseline hsCRP vs non-progressors in all treatment groups (Figure). On a group level, patients who were mTSS progressors at M12 generally had numerically higher mean hsCRP levels vs mTSS non-progressors over 24 months (Figure); effect was generally greater with MTX vs tofacitinib groups. At M24, mean changes from baseline in hsCRP appeared higher for M12 progressors (-21.5 to -27.8 mg/L across groups) vs non‑progressors (-12.6 to -16.7 mg/L across groups). Rates of mTSS non-progression appeared to be numerically higher at M6, M12, and M24 in patients with baseline hsCRP ≤7 mg/L vs those with baseline hsCRP >7 mg/L (Table). At M24, among patients with baseline hsCRP >7 mg/L, 59.5% of patients treated with MTX and 77.0% and 79.6% treated with tofacitinib 5 mg and 10 mg BID, respectively, were mTSS non-progressors, compared with 77.1%, 85.6% and 90.8%, respectively, among patients with baseline CRP ≤7 mg/L (Table).
Conclusion: Patients with RA receiving tofacitinib 5 mg or 10 mg BID or MTX who showed structural progression at M12 generally had numerically higher mean hsCRP levels through M24. Numerically higher rates of non‑progression were observed over time in patients with baseline hsCRP ≤7 mg/L vs >7 mg/L. At M24, structural progression was lower with tofacitinib vs MTX, regardless of baseline hsCRP level.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fleischmann R, Connell CA, Fan H, Strengholt S. C-Reactive Protein Levels in Patients with or without Structural Progression: A Post-Hoc Analysis from a Phase 3 Tofacitinib Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/c-reactive-protein-levels-in-patients-with-or-without-structural-progression-a-post-hoc-analysis-from-a-phase-3-tofacitinib-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/c-reactive-protein-levels-in-patients-with-or-without-structural-progression-a-post-hoc-analysis-from-a-phase-3-tofacitinib-trial/