Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. Lymphopenia is a frequent feature of RA,1 and RA medications may also affect absolute lymphocyte count (ALC). Previous analyses showed an increased rate of serious infection (SI) in tofacitinib-treated patients (pts) whose ALCs were <500 cells/mm3, which was the basis for the recommendation to adopt the ALC <500 cells/mm3 threshold for treatment discontinuation. Here we describe the association between ALC and infection events in the tofacitinib RA clinical development program.
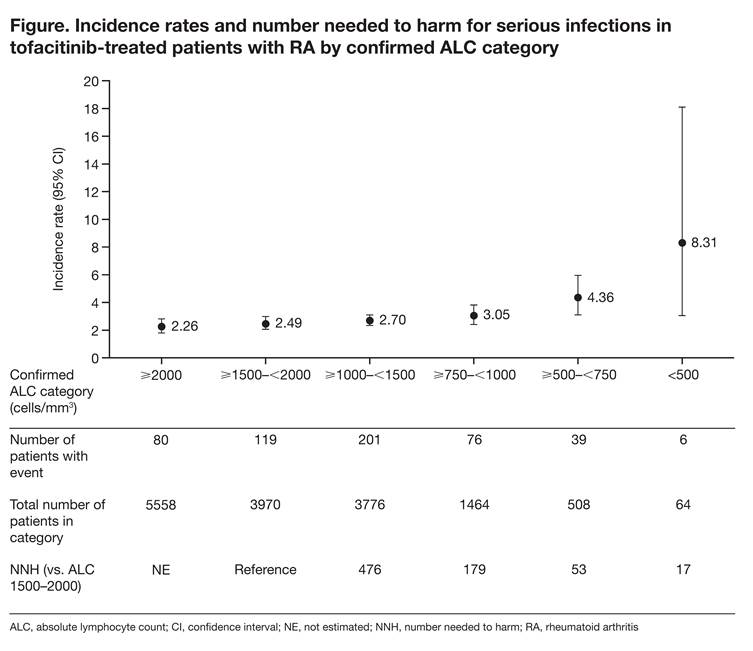
Methods: Data were pooled from pts in 19 RA studies (2 Phase [P] 1; 9 P2; 6 P3; 2 long-term extension [LTE] studies [1 LTE ongoing at time of analysis; database not locked at March 2015 cut-off]) across all tofacitinib doses (1, 3, 5, 10, 15, 30 mg twice daily and 20 mg once daily). Exposure-adjusted incidence rates (IRs; pts with event/100 pt-years) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for SIs, opportunistic infections (OIs), and herpes zoster (HZ; all reported cases, both serious and non-serious) were calculated for ALC categories: ≥2000, ≥1500–<2000 (normal reference range), ≥1000–<1500, ≥750–<1000, ≥500–<750, and <500 cells/mm3. Numbers needed to harm (NNH) were calculated as reciprocals of the differences in IRs relative to the ALC ≥1500–<2000 category.
Results: Of the 6194 pts (tofacitinib exposure: 19,229 pt-years) in this analysis, 527 (8.5%) reported SIs (IR 2.74 [95% CI: 2.51, 2.98]). The IR for SI in pts with normal ALC (≥1500–<2000 cells/mm3) was 2.49 (2.06, 2.98). IRs were similar in pts with ALC ≥750–<1500 cells/mm3, but increased by 75% to 4.36 (3.10, 5.96) and by 234% to 8.31 (3.05, 18.10) for ALCs ≥500–<750 and <500 cells/mm3, respectively, relative to pts with normal ALC (Figure); however, CIs were wider in the ≥500–<750 and <500 cells/mm3 ALC categories due to smaller pt numbers. For all ALC categories except <500 cells/mm3, IRs for SI with tofacitinib were within the range of published rates for biologic DMARDs (3.04–5.45).2 For NNH, 179 and 53 more pts in the ≥750–<1000 and ≥500–<750 cells/mm3 categories, respectively, would need to be treated to experience 1 additional SI event compared with pts with ALC ≥1500 cells/mm3. A similar pattern was observed with IRs for OI (0.21 [0.10, 0.38] for normal ALC vs 0.89 [0.38, 1.76] and 1.39 [0.04, 7.75] for ALCs ≥500–<750 and <500 cells/mm3, respectively). There was a trend for increased HZ risk with decreased ALC; IR differences between ALC categories were <2-fold with overlapping CIs and did not inform the selection of an appropriate ALC threshold.
Conclusion: These findings support the recommendation to discontinue tofacitinib in pts with ALC <500 cells/mm3 to decrease the risk of SI. Discontinuation at higher thresholds results in further decreases in SI incidence but also excludes a larger number of pts who will not develop a SI.
References:
1. Symmons et al. J R Soc Med. 1989; 82: 462–3
2. Strand et al. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015; 17: 362
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Burmester GR, Szekanecz Z, Biswas P, Krishnaswami S, Mojcik CF, Valdez H, Geier J, Strengholt S. Monitoring of Absolute Lymphocyte Count in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Tofacitinib [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/monitoring-of-absolute-lymphocyte-count-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-tofacitinib/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/monitoring-of-absolute-lymphocyte-count-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-tofacitinib/