Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients increasingly reach a state of absence of disease activity, or remission. However, the proportion of patients classified as in remission varies substantially between definitions and are often determined by disease activity score (DAS) of the joints. But, the importance of patients’ perspective is increasingly recognized, which often result in discordance between patients and physician assessment.
Objectives:
First, agreement between patient-perceived, physician-perceived remission and clinical response and remission definitions was determined in early RA patients. Second, the differences in clinical and patient-reported outcomes, in patients in physician-perceived remission, between patients in and not in self-perceived remission were assessed.
Methods:
In early RA patients receiving COBRA-light treatment, DAS44, ACR/EULAR Boolean-based remission, EULAR good and ACR70 response were determined after 12 weeks. Agreement percentages and kappa values between patient-perceived, physician-perceived remission and clinical response and remission definitions were calculated. In patients in physician-perceived remission, improvement in clinical and patient-reported outcomes (RAID) were compared between patients in and not in self-perceived remission.
Results:
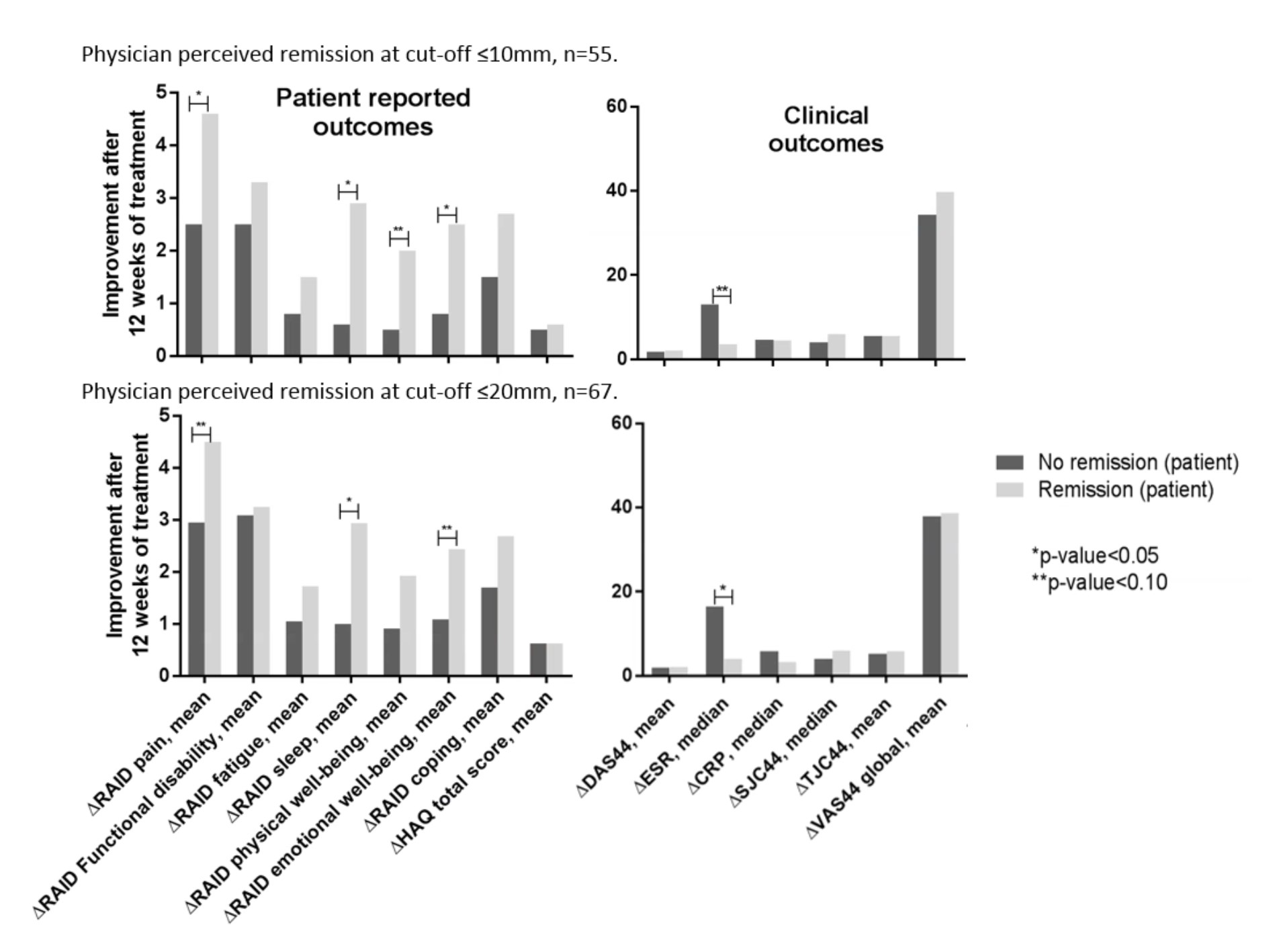
Eighty-four consecutive patients were included (mean age 50 years, 67% female). Agreement between the assessed outcome measures differed enormously. The agreement between physician-perceived and patient-perceived remission was 64% (kappa 0.25, p<0.01). Physician-perceived remission (cut-off VAS ≤20 mm) had the best agreement with EULAR good response (86%, kappa 0.58, p<0.01). Agreement between patient-perceived remission was 69% for EULAR good and ACR70 response (kappa 0.36, p<0.01; kappa 0.40, p<0.01, respectively). Patients not in self-perceived remission improved less on components of the RAID, especially on pain, sleep and emotional well-being.
Conclusion:
One-third of the early RA patients disagreed with the physician on being in remission. Those patients had less improvement on components of the RAID, especially on pain, sleep and emotional well-being. Together with the variability in clinical response and remission definitions, these results highlight the need to increase patient involvement in their own health care decisions.
Table. Agreement between different definitions of response and remission.
|
|
Physician- perceived remission (≤10 mm)
|
Physician- perceived remission (≤20 mm)
|
Patient- perceived remission
|
DAS44 remission |
EULAR good response |
ACR70 response |
Boolean remission |
|
Physician- perceived remission (≤10 mm)
|
x |
86% Ƙ=0.650 P=0.000 |
67% Ƙ=0.318 P=0.003 |
74% Ƙ=0.439 P=0.000 |
79% Ƙ=0.484 P=0.000 |
60% Ƙ=0.281 P=0.001 |
57% Ƙ=0.248 P=0.002 |
|
Physician- perceived remission (≤20 mm)
|
86% Ƙ=0.650 P=0.000 |
x |
64% Ƙ=0.254 P=0.005 |
64% Ƙ=0.454 P=0.000 |
86% Ƙ=0.576 P=0.000 |
45% Ƙ=0.117 P=0.069 |
48% Ƙ=0.175 P=0.005 |
|
Patient-perceived remission |
67% Ƙ=0.318 P=0.003 |
64% Ƙ=0.254 P=0.005 |
x |
46% Ƙ=0.516 P=0.000 |
69% Ƙ=0.356 P=0.000 |
69% Ƙ=0.398 P=0.000 |
67% Ƙ=0.354 P=0.000 |
|
DAS44 remission |
74% Ƙ=0.439 P=0.000 |
64% Ƙ=0.454 P=0.000 |
46% Ƙ=0.516 P=0.000 |
x |
83% Ƙ=0.622 P=0.000 |
64% Ƙ=0.343 P=0.000 |
67% Ƙ=0.392 P=0.000 |
|
EULAR good response |
79% Ƙ=0.484 P=0.000 |
86% Ƙ=0.576 P=0.000 |
69% Ƙ=0.356 P=0.000 |
83% Ƙ=0.622 P=0.000 |
x |
52% Ƙ=0.220 P=0.001 |
50% Ƙ=0.199 P=0.002 |
|
ACR70 response |
60% Ƙ=0.281 P=0.001 |
45% Ƙ=0.117 P=0.069 |
69% Ƙ=0.398 P=0.000 |
64% Ƙ=0.343 P=0.000 |
52% Ƙ=0.220 P=0.001 |
x |
74% Ƙ=0.359 P=0.001 |
|
Boolean remission |
57% Ƙ=0.248 P=0.002 |
48% Ƙ=0.175 P=0.005 |
67% Ƙ=0.354 P=0.000 |
67% Ƙ=0.392 P=0.000 |
50% Ƙ=0.199 P=0.002 |
74% Ƙ=0.359 P=0.001 |
x |
Numbers are presented as level of agreement (%), kappa value (K) and p-value (P).
Figure.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Turk SA, Rasch LA, Lems WF, van Tuyl L, van Schaardenburg D, Ter Wee MM. Patient Reported Outcomes Explain the Lack of Agreement between Physician and Patient Perceived Remission in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-outcomes-explain-the-lack-of-agreement-between-physician-and-patient-perceived-remission-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-reported-outcomes-explain-the-lack-of-agreement-between-physician-and-patient-perceived-remission-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/