Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and Osteoarthritis (OA) are two most common types of joint diseases with lots of similar symptoms, and their pathological mechanisms remain largely unknown. Although some key genes and diagnostic markers have been identified by microarray, these biomarkers still cannot reveal the complicated pathogenesis of RA and OA entirely. We conducted a novel integrative analysis of identification the key biomarkers of synovial tissue from RA and OA patients to better understand their difference.
Methods: After screening NCBI GEO database, 3 new expression profiling datasets (GSE 55235, GSE 55584, GSE 55457) met the eligibility criteria (from synovial tissue of RA and OA patients diagnosed according to American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria, detected by the same platform, and sample size >15). A global normalization was performed to minimize the data inconsistency and heterogeneity. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs, p<0.05, FDR<0.05, Fold Change >2) between RA and OA from the 3 datasets were explored by R v3.4.0 software. Gene Ontology and KEGG pathway analysis of the DEGs were conducted by Cytoscape 3.4.0. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of the DEGs was obtained from STRING database v9.05.
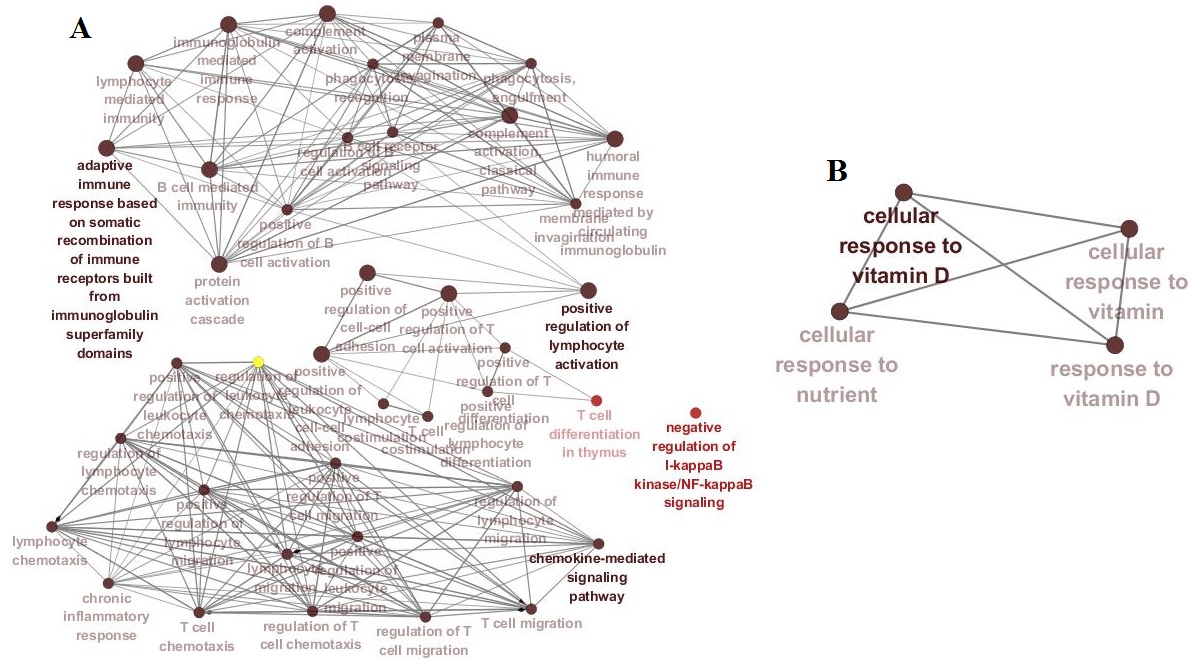
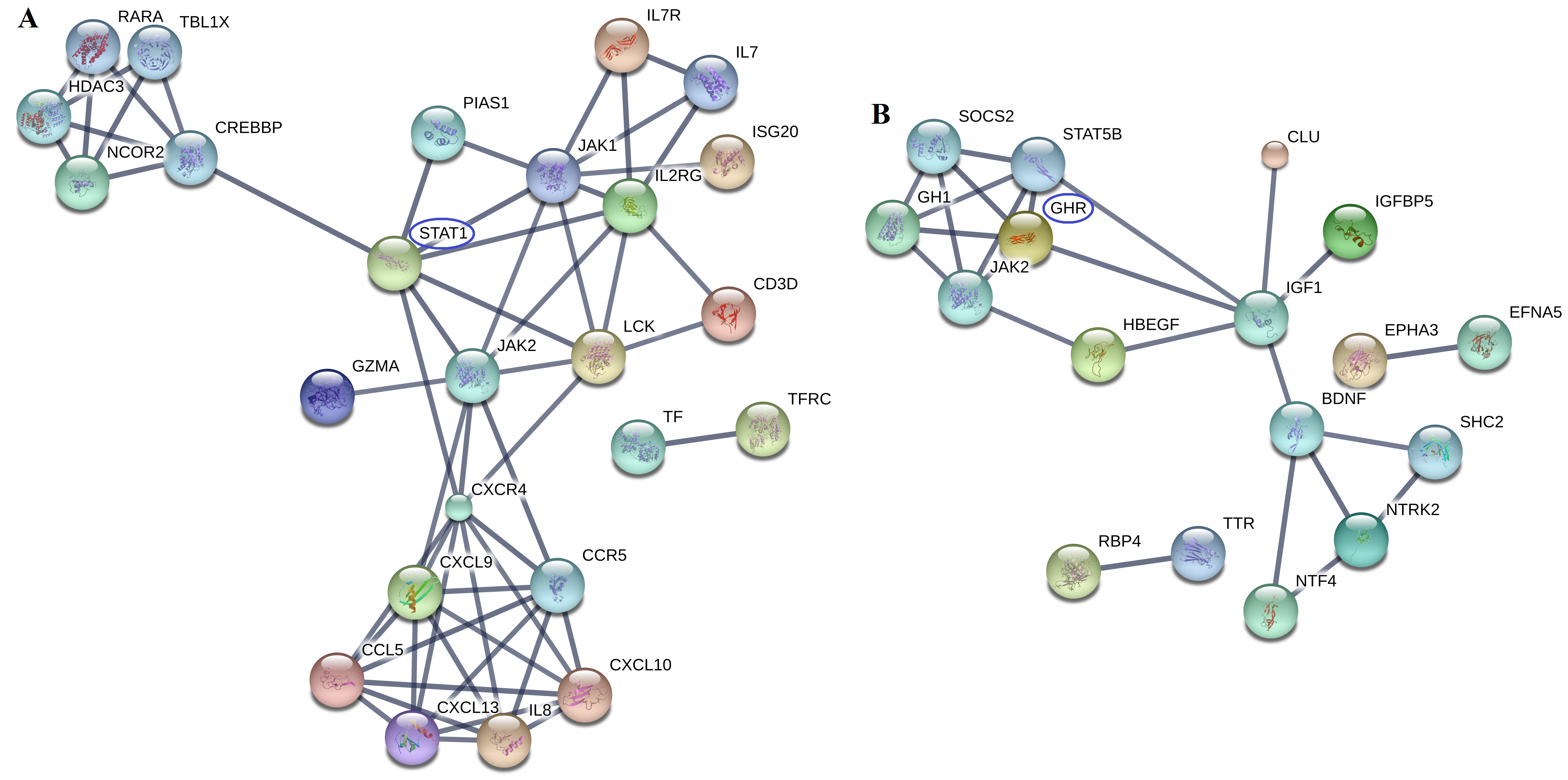
Results: 375, 242 and 264 DEGs from GSE 55235, GSE 55584 and GSE 55457 datasets were obtained, respectively. Among them, 81 DEGs presented identical expression trends in the 3 datasets, including 50 up-regulated genes (IGHG1, GUSBP11, STAT1, et al) and 31 down-regulated genes (SCRG1, MAB21L2, GHR, et al). The DEGs mainly involved in negative regulation of I-kappa B kinase/NF-kappa B signaling, cellular response to vitamin D pathway, et al(Fig. 1). STAT1 and GHR were the cores of PPI networks of 50 up-regulated proteins and 31 down-regulated proteins, respectively (Fig. 2).
Conclusion: Several apoptosis and vitamin D related pathways were more closely related to RA than OA, which suggested that anti-oxidative stress therapy and vitamin D might be more effective for RA. STAT1 and GHR (both relate to bone metabolism) are the key genes presenting statistical significant difference between RA and OA. This study provides novel insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying RA and OA, thereby aiding the diagnosis and treatment of the diseases. Well-designed, well-controlled and dependent experiments are needed in future to validate the findings of the present study.
Fig. 1. Networks of key pathways related to RA
(A: up-regulated DEGs; B: down-regulated DEGs; Names in dark color: P<0.05)
Fig. 2. PPI networks of up-regulated (A) and down-regulated DEGs (B)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang R, Yang A, Ren X, Zhang J, Yang X, Liu Q, Sun N, Yuan P, Xiong Y. Key Genes and Pathways between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis By Integrative Genome-Wide Gene Expression Profiling Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/key-genes-and-pathways-between-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-osteoarthritis-by-integrative-genome-wide-gene-expression-profiling-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/key-genes-and-pathways-between-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-osteoarthritis-by-integrative-genome-wide-gene-expression-profiling-analysis/