Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: CR6086 is a selective EP4 receptor antagonist immunomodulator in clinical development for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In animal models of RA, it demonstrated a superior efficacy vs. conventional, biologic, or targeted synthetic DMARDs in both early and late disease paradigms. In vitro on human immunocompetent cells, we previously showed that CR6086 counteracts the immunological unbalance characteristic of RA. This partly explains its efficacy in vivo, but does not completely account for its superior efficacy vs. DMARDs. Bone erosion contributes even to very early phases of RA and EP4 receptors have a key role in bone resorption. Acting on this receptor, PGE2 stimulates different cell types (including macrophages, chondrocytes, and osteoblasts) to release mediators causing bone erosion. Among them, IL-6, RANK ligand (RANKL), the major inducer of osteoclastogenesis, and VEGF that has angiogenic, pro-inflammatory and bone destructive roles in RA. Aim of this study was to assess the effects of CR6086 on the expression and release of these mediators by human macrophagic cells, chondrocytes and osteoblasts.
Methods: Human THP-1 cells were differentiated to macrophages with PMA. Chondrocytes and osteoblasts were purified from material obtained from patients undergoing knee replacement. Gene expression and release of IL-6, RANKL with its endogenous inhibitor osteoprotegerin (OPG), and VEGF were analysed by Real Time PCR and ELISA assay.
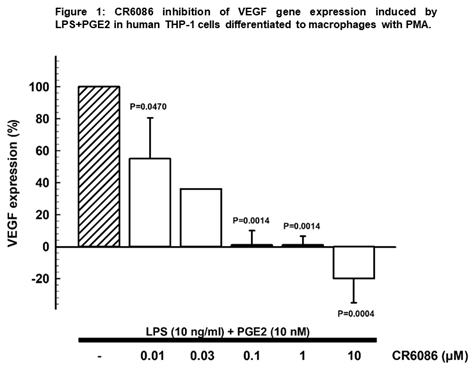
Results: CR6086 dose-dependently inhibited gene expression of IL-6, RANKL and VEGF in human macrophages and/or chondrocytes. Conversely, it had no effect on gene expression of OPG, maintaining the balance RANKL/OPG in favor of a reduction of bone erosion. In particular, in macrophages stimulated with LPS 10ng/ml + PGE2 10nM, CR6086 dose dependently inhibited gene expression of VEGF (fig. 1), reduced IL-6 gene expression (up to 44%) and IL-6 release (up to 53%).
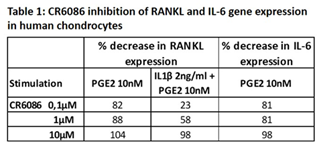
In chondrocytes stimulated with PGE2 or IL-1β + PGE2, CR6086 dose-dependently suppressed RANKL and IL-6 gene expression (Table 1). Similar results were obtained in osteoblasts.
Conclusion: The new potent EP4 receptor antagonist immunomodulator CR6086 directly affects bone resorption by inhibiting the expression of different mediators that induce bone erosions in RA (RANKL, IL-6 and VEGF). These results support the in vivo findings and confirm that CR6086 may potentially act as a novel DMARD. CR6086 is in Phase II clinical development in DMARD-naïve early RA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Piepoli T, Montagna M, Maggioni D, Zerbi S, Mennuni L, Lanza M, Caselli G, Rovati LC. In Vitro Effects of CR6086, a Potent ProstaglandinE2 Subtype 4 Receptor Antagonist, on Bone Erosive Pathways [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-vitro-effects-of-cr6086-a-potent-prostaglandine2-subtype-4-receptor-antagonist-on-bone-erosive-pathways/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-vitro-effects-of-cr6086-a-potent-prostaglandine2-subtype-4-receptor-antagonist-on-bone-erosive-pathways/