Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: GPA (Wegener’s) and MPA are organ- and life-threatening systemic vasculitides characterized by the presence of ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV), implicating B cells in disease pathogenesis. This study investigated the efficacy and safety of belimumab (BEL), a monoclonal antibody that inhibits B lymphocyte stimulator, in addition to standard of care, for the maintenance of remission in AAV following a standard induction regimen.
Methods: This multicenter, double-blind study (BEL115466/NCT01663623) randomized (1:1) patients (≥18 years) with GPA or MPA in remission (Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score [BVASv3] = 0 plus prednisolone ≤10 mg/day or equivalent) following prior induction with CYC or RTX for new or relapsing disease. Patients received azathioprine (AZA) 2 mg/kg/day, and oral glucocorticoids, plus either intravenous BEL 10 mg/kg or placebo (PBO) (Days 0, 14, 28, and every 28 days thereafter until study completion [12 months after last patient randomized]). The primary endpoint was time to first relapse, defined as ≥1 major BVAS item, total BVAS score ≥6, or receipt of prohibited medications resulting in treatment failure. Adverse events (AE) were monitored. The study was truncated from 300 to 105 patients due to changes in conventional treatment practice.
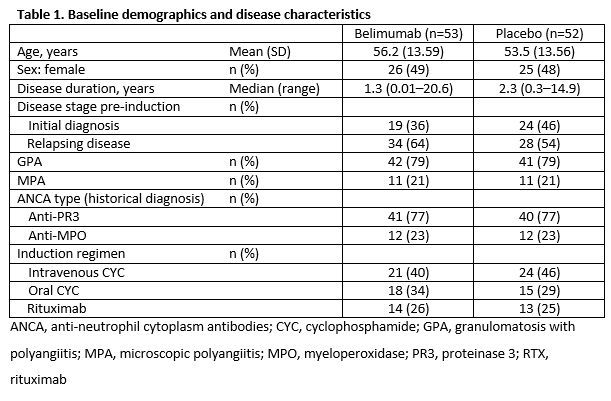
Results: When the study stopped, of 105 patients in the intent-to-treat population, 76 continued for ≥1 year, 21 for ≥2 years, and 2 for ≥3 years. Baseline data:
There was no significant difference in time to first relapse between treatment groups: adjusted hazard ratio (95% confidence interval), 1.07 [0.44, 2.59]; p=0.884. Among patients who relapsed (BEL, 10 [19%]; PBO, 11 [21%]), median (range) time to first relapse was 162 (1–371) days for BEL and 95 (15–789) days for PBO. For patients induced with RTX there were 0/1 relapses classified as vasculitis related in the BEL group versus 3/4 in the PBO group. In CYC-induced patients there were 6/9 versus 5/7 vasculitis relapses, respectively. At the final visit (double-blind) most patients were in remission (BEL, 40 [82%]; PBO, 40 [87%]).
AEs were reported in 49 (93%) BEL and 43 (83%) PBO patients post baseline. The most common AE category was infection (BEL, 30 [57%]; PBO, 30 [58%]). Serious AEs (SAEs) occurred in 18 (34%) BEL and 16 (31%) PBO patients; the most common category was infection (BEL, 4 [8%]; PBO, 4 [8%]).
Conclusion: In patients with AAV who were in remission, the addition of BEL to maintenance therapy with AZA and oral glucocorticoids did not reduce risk of relapse. RTX-induced patients exhibited numerically fewer relapses of vasculitis with treatment with belimumab compared with placebo, warranting further investigation. Overall relapse rate was low (21/105 [20%]). No new safety signals were identified for BEL in the overall population.
Study funded/conducted by GSK. Editorial assistance: Sam Halliwell, PhD, Fishawack Indicia Ltd, funded by GSK
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jayne D, Blockmans D, Luqmani R, Ji B, Green Y, Hall L, Roth D, Merkel PA. Efficacy and Safety of Belimumab in Combination with Azathioprine for Remission Maintenance in Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis and Microscopic Polyangiitis: A Multicenter Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-belimumab-in-combination-with-azathioprine-for-remission-maintenance-in-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis-and-microscopic-polyangiitis-a-multicenter-randomized-placebo-controll/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-belimumab-in-combination-with-azathioprine-for-remission-maintenance-in-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis-and-microscopic-polyangiitis-a-multicenter-randomized-placebo-controll/