Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
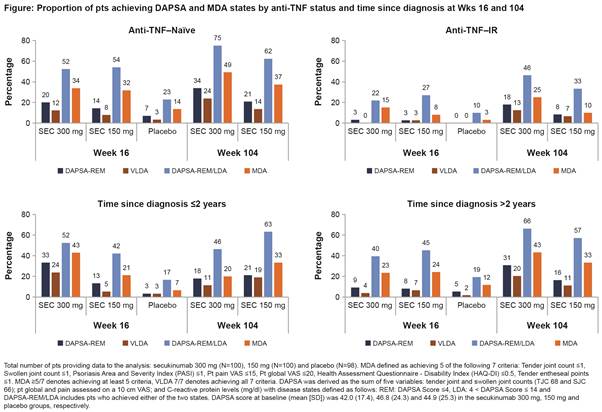
Background/Purpose: Very low disease activity (VLDA) or remission (REM) and alternatively, minimal disease activity (MDA) or low disease activity (LDA) are optimal targets to be achieved by psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients (pts).1,2 DAPSA and MDA are validated composite indices used in PsA to measure disease activity states.3 This exploratory analysis assessed the proportion of pts treated with secukinumab reaching DAPSA REM or LDA and those who reached either MDA or VLDA at Weeks (wks) 16 and 104 in the FUTURE 2 study.
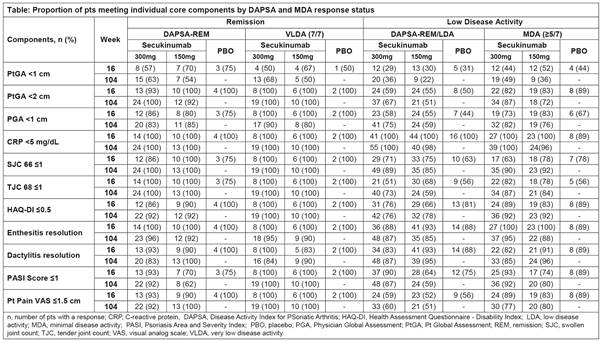
Methods: Data through 2 years for the FUTURE 2 study have been reported.4 DAPSA cut-offs included: REM (≤4) and LDA (>4 and ≤14).5 MDA and VLDA are defined as having achieved at least 5 (≥5/7) or all (7/7) of the 7 pre-specified criteria, respectively.6 DAPSA-REM, DAPSA-REM/LDA, MDA, and VLDA and their core components were assessed in the overall population and in pts stratified by prior anti-tumor necrosis factor use and time since first PsA diagnosis using as observed data. Only data for secukinumab 300 and 150 mg (approved doses) and placebo are reported.
Results: Baseline characteristics were similar across treatment groups.4 At Wk 16, in the overall population, the proportion of pts treated with secukinumab 300/150 mg achieving remission was 14%/10% (DAPSA-REM) and 8%/6% (VLDA) and achieving low disease activity was 42%/44% (DAPSA-REM/LDA) and 28%/23% (MDA). DAPSA and MDA responses by prior TNF-inhibitor status and time since diagnosis are presented in figure. DAPSA and MDA responses with secukinumab were sustained through Wk 104. Secukinumab treated pts who achieved either DAPSA-REM or VLDA at Wk 16 had complete resolution of TJC, SJC, enthesitis and PtGA. Numerically somewhat higher proportion of pts achieved skin clearance, HAQ-DI and PGA with VLDA than DAPSA-REM at Wk 16 and sustained to Wk 104 (Table).
Conclusion: In the overall population, a higher proportion of secukinumab treated pts at Wk 16 achieved DAPSA-REM, VLDA, DAPSA-REM/LDA, and MDA than those treated with placebo with a greater number of pts achieving DAPSA-REM or LDA than VLDA or MDA, respectively. These responses were sustained through Wk 104. At Wk 16, a higher proportion of anti–TNF-naïve pts and pts with early diagnosis (≤2 years) treated with secukinumab achieved and sustained DAPSA-REM, MDA and VLDA than in the overall population.
References: 1. Coates LC, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016;68:1060–71 ; 2. Gossec L, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:499–510 ; 3. Coates LC, Helliwell PS. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:640-43; 4. McInnes IB, et al. Rheumatol. In press; 5. Schoels MM, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:811–8 ; 6. Coates LC, Helliwell PS. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010; 62(7):965-969.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Coates LC, Nash P, Kvien T, Gossec L, Mease PJ, Rasouliyan L, Pricop L, Jugl S, Gandhi K, Gaillez C, Smolen JS. Secukinumab Provides Sustained Minimal Disease Activity (MDA) and Remission Related to Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis (DAPSA): 2-Year Results from a Phase 3 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-provides-sustained-minimal-disease-activity-mda-and-remission-related-to-disease-activity-index-for-psoriatic-arthritis-dapsa-2-year-results-from-a-phase-3-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-provides-sustained-minimal-disease-activity-mda-and-remission-related-to-disease-activity-index-for-psoriatic-arthritis-dapsa-2-year-results-from-a-phase-3-study/