Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
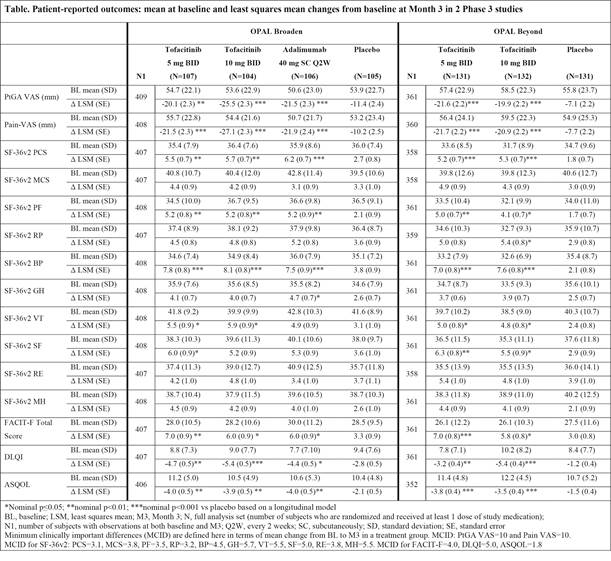
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor under investigation for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Safety and efficacy were investigated in 2 Phase 3 randomized controlled trials (RCTs: OPAL Broaden [12 months; NCT01877668]; OPAL Beyond [6 months; NCT01882439]). This analysis evaluated patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in patients with active PsA in OPAL Broaden (N=422), with inadequate responses (IR) to ≥1 conventional synthetic DMARD, naïve to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi); and in OPAL Beyond (N=394), IR to ≥1 TNFi.
Methods: Patients were randomized to tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg twice daily (BID) or placebo (PBO) advanced to either tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID at Month 3, and, in OPAL Broaden, to adalimumab 40 mg subcutaneously every 2 weeks. Based on a longitudinal model, least squares mean (LSM) changes from baseline were reported for the following: Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity Visual Analog Scale (PtGA VAS), Pain VAS, Short Form-36 Health Survey Version 2 (SF-36v2), Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F), Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), and Ankylosing Spondylitis Quality of Life (ASQOL). Findings were reported using nominal p values without adjustments for multiple comparisons.
Results: Improvements in PtGA and Pain were observed as early as Week 2 (first assessment), and exceeded PBO at Month 3 with both tofacitinib doses in both RCTs (p≤0.05 vs PBO) (Table). At Month 3, SF-36v2 Physical Component Summary (PCS), physical functioning (PF), bodily pain (BP), and vitality (VT) domains, and FACIT-F scores, exceeded PBO with both doses (p≤0.05) in both trials; improvements in PCS, PF, BP, and FACIT-F exceeded minimum clinically important differences (MCID). DLQI and ASQOL scores at Month 3 exceeded PBO with both doses in both RCTs (p≤0.05), and social functioning (SF) domain with both doses in OPAL Beyond and 5 mg BID in OPAL Broaden (p≤0.05). PRO improvements reported in OPAL Broaden with tofacitinib were similar to adalimumab. The percentages of patients receiving both tofacitinib doses reporting changes ≥MCID at Month 3 in SF-36v2 PCS, PF, and BP domains were statistically significant in both RCTs, as were general health (GH) and mental health (MH) domains with 10 mg BID and FACIT-F with both doses in OPAL Broaden, and SF domains with both doses in OPAL Beyond and role physical (RP) with 10 mg BID.
Conclusion: Patients with active PsA receiving tofacitinib reported statistically greater and clinically meaningful improvements in PROs compared with PBO at Month 3 in both RCTs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, de Vlam K, Covarrubias-Cobos JA, Mease PJ, Gladman DD, Hendrikx T, Kudlacz E, Graham D, Wu J, Cappelleri JC, Hsu MA. Effect of Tofacitinib on Patient-Reported Outcomes in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from 2 Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-tofacitinib-on-patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-2-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-tofacitinib-on-patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-2-phase-3-studies/