Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
The purpose of this analysis was to assess whether early improvement in ACR components could act as predictors of low disease activity (LDA) or remission (REM) at Week 12 in Phase 3 trials of baricitinib (BARI). The patient’s assessment of pain, a patient-reported outcome measured by a 0-100 mm visual analog scale (VAS), was a focus for this analysis.
Methods:
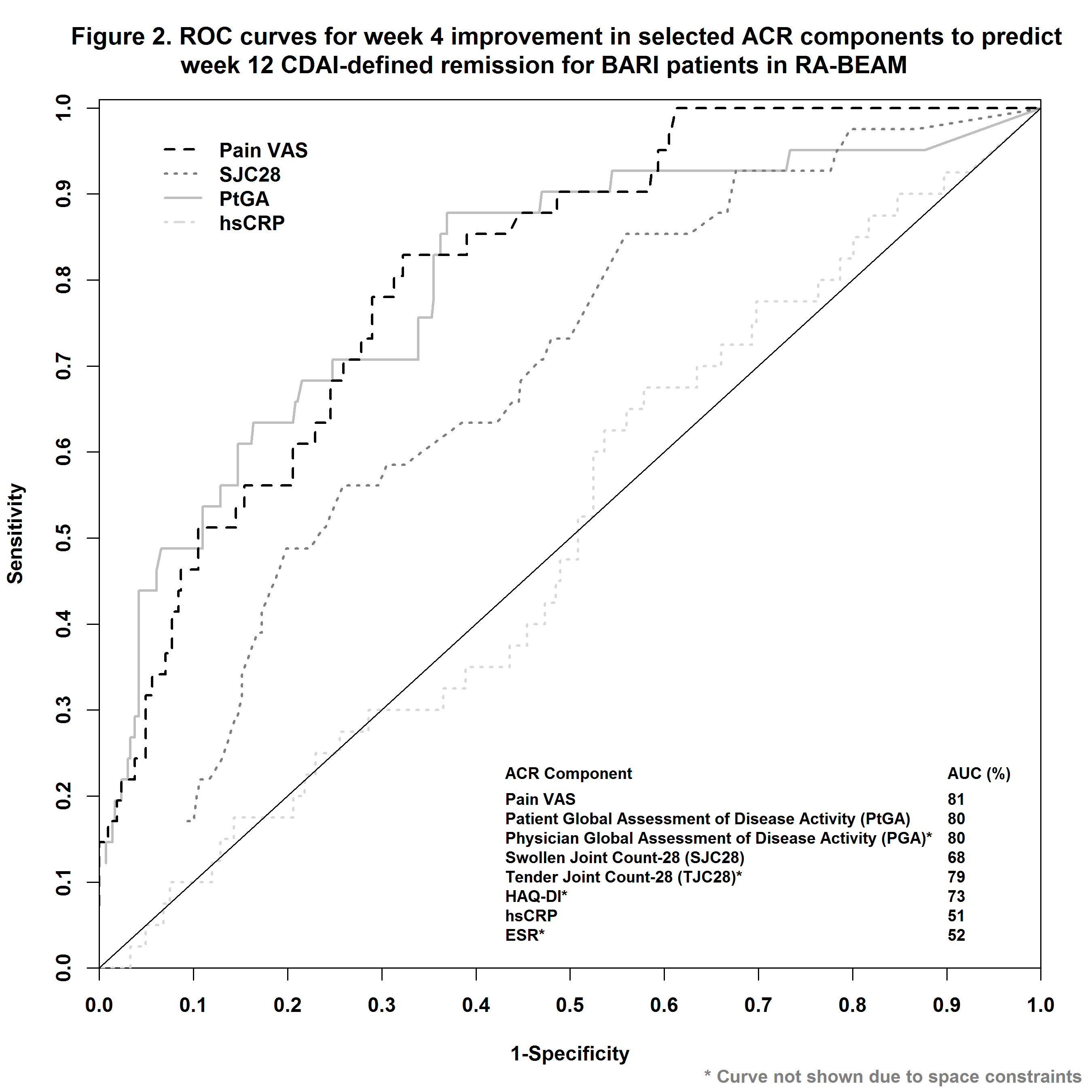
In RA-BEAM1, 487 patients with inadequate response (IR) to methotrexate (MTX) were randomized to BARI 4 mg once daily. In RA-BEACON2, a trial of bDMARD-IR patients, 174 patients were randomized to BARI 2 mg and 177 to BARI 4 mg once daily. In RA-BUILD3, a trial with csDMARDs-IR patients, 229 patients were randomized to BARI 2 mg and 227 to BARI 4 mg once daily. LDA was defined as CDAI ≤10 or DAS28-ESR ≤3.2 and REM as CDAI ≤ 2.8 or DAS28-ESR<2.6 at Week 12. Early improvement, changes from baseline to Week 4, for each of the ACR components (pain VAS, patient global assessment of disease activity [PtGA], physician global assessment of disease activity [PGA], swollen joint count, tender joint count [TJC], HAQ-DI, hsCRP, and ESR) was evaluated on their respective predictability for LDA or REM at Week 12 using area under the curve (AUC) of receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. The optimum cutoff-point in percent improvement at Week 4 was evaluated based the Youden index and the negative predictive value (NPV).
Results:
Early improvement in pain VAS, TJC, PtGA, and PGA had among the highest predictability, whereas hsCRP and ESR had among the lowest, as measured by AUC of ROC (Figs. 1 and 2 for RA-BEAM data), for achieving both LDA and REM at Week 12. A threshold of 30-50% improvement in pain from baseline to Week 4 had the optimum range for predicting LDA and REM at Week 12 (Table). Consistent results were observed for csDMARD-IR and bDMARD-IR patients, and these results were similar for both BARI 2 mg and BARI 4 mg doses.
Conclusion:
In these trials, patients with a lack of early response to BARI, as assessed by improvement in pain VAS at Week 4, tended to be less likely to achieve LDA or REM at Week 12 vs. patients with an early response. A minimum of 30% improvement in pain resulted in optimum NPV in this analysis.
References:
- Taylor et al. N Engl J Med 2017; 376:652-662
- Genovese et al. N Engl J Med 2016; 374:1243-1252
- Dougados et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:88-95
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Weinblatt M, Genovese MC, Kremer J, Sun L, Patel H, Koch A, Muram D, Curtis JR, Larmore CJ, Zhu B. Assessment of Early Improvement in Pain and Other ACR Components As Predictors for Achieving Low Disease Activity or Remission in Three Phase 3 Trials of RA Patients Treated with Baricitinib [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-early-improvement-in-pain-and-other-acr-components-as-predictors-for-achieving-low-disease-activity-or-remission-in-three-phase-3-trials-of-ra-patients-treated-with-baricitinib/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-early-improvement-in-pain-and-other-acr-components-as-predictors-for-achieving-low-disease-activity-or-remission-in-three-phase-3-trials-of-ra-patients-treated-with-baricitinib/