Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster I: Treatment Patterns and Response
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Biologic therapy for the treatment of RA has increased dramatically and has substantially increased costs of care. This study aimed to identify factors associated with initiation of biologic use, including previous methotrexate (MTX) adherence and dose.
Methods: We used U.S. Veteran’s Affairs administrative databases to identify RA patients receiving a first-ever prescription of MTX between 2005 and 2014 with at least 6 months of prior baseline data. Patients with prior biologic therapy use or those initiating biologic therapy within 30 days of starting MTX were excluded. Multivariable Cox analysis assessed factors associated with biologic therapy initiation within 2 years of MTX start, censoring at death. To assess impact of MTX adherence and dose on biologic use, we examined a subset of patients who received MTX continuously for at least 6 months with no biologic initiation during this time. In this population we evaluated associations between PDC (proportion of days covered) in the first 6 months and MTX dose at 6 months with subsequent biologic initiation.
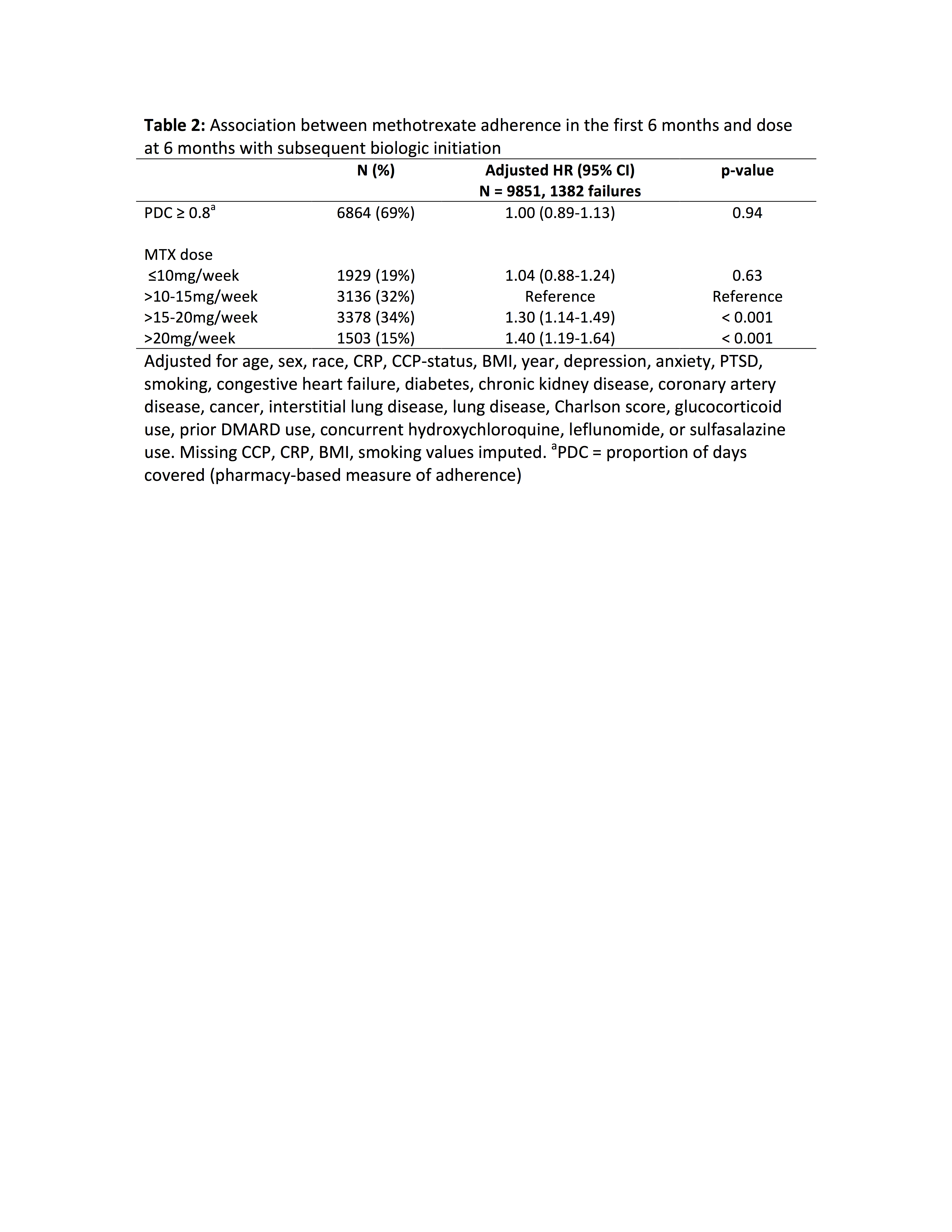
Results: 17,634 patients met inclusion criteria contributing 29,350 person years of follow-up. 3,263 initiated biologic therapy within 2 years (incidence 11.1%/year). CCP positivity, later calendar year, and concurrent use of glucocorticoids, leflunomide, or sulfasalazine were associated with a greater likelihood of biologic initiation (Table 1). Factors associated with a lower rate of biologic initiation included advancing age, non-white race, greater comorbidity (Charlson score), congestive heart failure, and malignancy (Table 1, Figure 1). Among the smaller cohort of 9,851 patients remaining on methotrexate continuously for 6 months, methotrexate adherence (PDC ≥ 0.8) was not associated with likelihood of subsequent biologic initiation [aHR 1.00 (0.89-1.13), p = 0.94]. Higher methotrexate dose was associated with greater likelihood of initiating biologic therapy (Table 2).
Conclusion: Biologic therapy is initiated less frequently in elderly patients and those with comorbidities, possibly reflecting safety concerns. Future studies should evaluate whether these concerns lead to under-treatment of these populations. Surprisingly, low methotrexate adherence and dose were not associated with increased biologic use; the impact of reduced methotrexate effectiveness could be masked by differences in disease severity, follow-up, or medication preferences in these patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
George MD, Sauer B, Teng MS CC, Cannon G, England BR, Kerr GS, Mikuls TR, Baker J. Predictors of Earlier Biologic Initiation Among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Starting Methotrexate [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-earlier-biologic-initiation-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-starting-methotrexate/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-earlier-biologic-initiation-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-starting-methotrexate/