Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster I: Treatment Patterns and Response
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To date, no clinically useful baseline biomarkers have been found to predict response to TNF inhibitor (TNFi) treatment .1 Calprotectin was shown to be predictive for treatment response to adalimumab (ADA) while no difference in calprotectin levels was found between responders and non-responders in RA patients treated with etanercept (ETN) and methotrexate.2,3
Objectives: To assess the added predictive value of serum calprotectin for clinical response after 6 months treatment with ADA or ETN in RA patients.
Methods: RA patients starting treatment with ADA or ETN in the BIO-TOP study (a prospective cohort study) were included. Patients who discontinued TNFi treatment within 2 months were excluded from analysis. Serum calprotectin was measured at baseline using ELISA. EULAR response was measured at 6 months (good versus moderate/no response). Discontinuation of TNFi before 6 months was regarded as non-response (in case of lack of effect) and clinical response at 3 months was carried forward (when stopped for other reasons). First calprotectin levels were correlated cross-sectionally with several clinical baseline markers. Thereafter, receiver-operator-characteristic (ROC) curves were created for ADA and ETN separately. Finally logistic prediction models were created using backward selection, including baseline characteristics and calprotectin levels to examine the added predictive value of calprotectin.
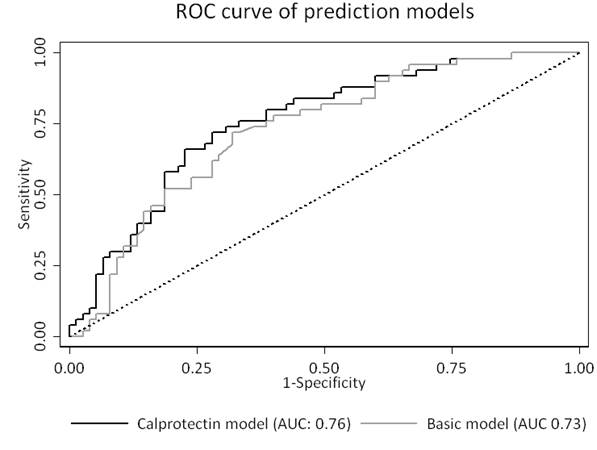
Results: Calprotectin levels and EULAR response were available for 125 patients (ADA (n=50), ETN (n=75)), with 40% of patients achieving EULAR good response. Responders showed significantly higher baseline calprotectin levels: 985 ng/mL (p25-p75: 558-1417) versus 645 ng/mL (p25-p75: 415-973) (p=0.04). Calprotectin levels were significantly correlated to DAS28-CRP (Spearman ρ=0.32, p<0.01) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels (Spearman ρ=0.57, p<0.01) and significantly higher in rheumatoid factor positive patients (p=0.03). No significant correlation was found between calprotectin and age, gender or ACPA positivity. The area under the curve (AUC) for calprotectin in the ADA and ETN group were 0.68 (95% CI: 0.49-0.88) and 0.49 (95% CI: 0.35-0.63), respectively. The basic model (selected variables: baseline DAS28-CRP and medication used (ADA vs ETN)) showed an AUC of 0.73 (95% CI: 0.64-0.82). The calprotectin added model performed similarly with an AUC of 0.76 (95% CI: 0.67-0.84) (p=0.27).
Conclusion: Serum calprotectin is modestly predictive for EULAR good response to ADA but not ETN treatment after 6 months in RA patients. However, calprotectin does not provide additional predictive value over a basic clinical prediction model.
References
1 Cuppen et al. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2016;55(5):826-39
2 Choi IY et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74(3):499-505
3 Obry A et al. PLoS One 2014;9(12):e115800
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tweehuysen L, den Broeder N, Joosten LAB, Vogl T, van den Hoogen FHJ, Thurlings R, Den Broeder AA. No Added Predictive Value of Serum Calprotectin for Treatment Response to Adalimumab or Etanercept in RA Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/no-added-predictive-value-of-serum-calprotectin-for-treatment-response-to-adalimumab-or-etanercept-in-ra-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/no-added-predictive-value-of-serum-calprotectin-for-treatment-response-to-adalimumab-or-etanercept-in-ra-patients/