Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster I: Treatment Patterns and Response
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (bari) is an oral selective inhibitor of Janus kinase (JAK) 1/JAK2.1 In the European Union, bari is approved for the treatment of moderate to severe RA in adults. GlycA, a measure of glycosylated acute phase proteins, is an emerging inflammatory marker that may be useful for assessment of disease activity and is associated with subclinical cardiovascular (CV) disease in patients with RA.2,3 The objective of this analysis was to assess GlycA levels in a Phase 2 and 3 (RA-BEAM) study in patients (pts) with RA treated with bari.
Methods: In the Phase 2 study, 301 pts were randomized 2:1:1:1:1 to placebo (PBO) or bari (1, 2, 4, or 8 mg) once daily (QD) for 12 weeks (wks). At Wk 12, pts initially assigned to PBO or bari 1 mg were rerandomized 1:1 to bari 2 mg twice daily or bari 4 mg QD; pts initially assigned to bari 2, 4, or 8 mg QD continued that treatment. In RA-BEAM, 1305 pts were randomized 3:3:2 to PBO, bari 4 mg QD, or adalimumab (ADA) 40 mg every 2 wks. GlycA levels were evaluated with nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy at baseline and Wks 12 and 24. In these post hoc analyses, change from baseline to week 12 in GlycA levels were compared between treatment groups without adjustment for multiple comparisons.
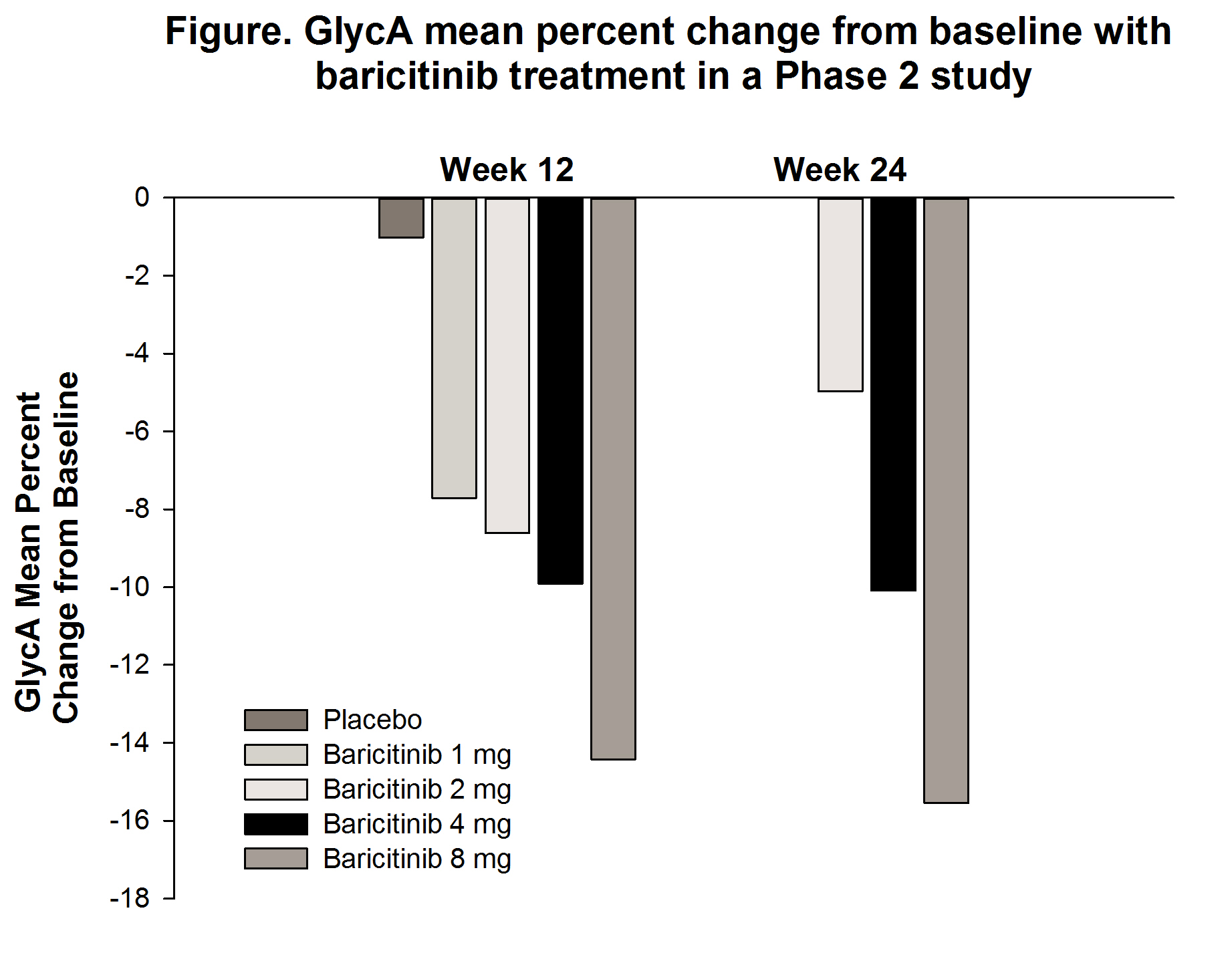
Results: Treatment with bari resulted in dose-dependent decreases in GlycA levels from baseline to Wk 12 in the Phase 2 study (-7.7% to -14.4% in the 1- and 8-mg treatment groups, respectively), with similar results at Wk 24 (Figure). In RA-BEAM at Wk 12, GlycA levels in pts treated with bari decreased significantly compared to PBO or ADA (Table 1). There were similar reductions in GlycA with bari regardless of baseline statin use (Table 2).
Conclusion: Bari decreases GlycA in a dose-dependent manner; reductions were seen regardless of baseline statin treatment. With recent studies suggesting GlycA as a marker for CV risk, these reductions in Phase 2 and 3 studies in an RA population may portend a reduction in overall CV risk. Further long-term data will be required to assess the possibility.
References: 1Fridman JS et al. J Immunol 2010;184:5298-307; 2Ormseth MJ et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2015;17:117; 3Joshi AA et al. Circulation Research 2016;119:1242-53
|
Table 1. GlycA levels in the Phase 3 RA-BEAM study |
|||
|
|
Placebo (N=488) |
Baricitinib 4 mg (N=487) |
Adalimumab (N=330) |
|
Baseline, µmol/L |
508.9 (104.6) |
517.2 (114.4) |
513.9 (106.4) |
|
Week 12, µmol/L |
496.9 (104.3) |
404.3 (91.9) |
416.3 (105.0) |
|
Change from baseline to Week 12 |
-13.6 (3.8) |
-110.9 (3.8)***† |
-98.7 (4.7)*** |
| |
|||
|
Table 2. Change in lipid and GlycA levels from baseline to Week 12 according to baseline statin use in the Phase 3 RA-BEAM study |
|||||
|
Baseline Statin Use |
Placebo (N=488) |
Baricitinib 4 mg (N=487) |
Adalimumab (N=330) |
Baricitinib 4 mg vs Placebo |
Adalimumab vs Placebo |
|
|
LSM (SE) |
LSMD (95% CI) |
|||
|
GlycA, µmol/L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
No (n=389) |
-13.5 (4.0) |
-109.5 (4.0) |
-99.5 (4.9) |
-96.0 (-107, -85)*** |
-86.0 (-98, -74)*** |
|
Yes (n=37) |
-14.3 (14.1) |
-131.0 (14.3) |
-94.2 (16.3) |
-116.7 (-157, -77)*** |
-79.9 (-123, -37)*** |
|
Total cholesterol, mg/dL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
No (n=412) |
-1.3 (1.3) |
25.5 (1.2) |
11.6 (1.5) |
26.8 (23.4, 30.3)*** |
12.9 (9.0, 16.8)*** |
|
Yes (n=37) |
-5.7 (6.7) |
34.7 (6.4) |
10.5 (7.6) |
40.4 (22.0, 58.7)*** |
16.2 (-3.9, 36.3) |
|
LDL cholesterol, mg/dL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
No (n=404) |
-2.2 (1.1) |
15.5 (1.0) |
7.6 (1.3) |
17.7 (14.8, 20.6)*** |
9.8 (6.5, 13.0)*** |
|
Yes (n=37) |
-4.6 (5.4) |
20.5 (5.2) |
6.7 (6.2) |
25.0 (10.1, 40.0)** |
11.2 (-5.1, 27.6) |
| |
|||||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kremer J, Emery P, Connelly MA, Otvos JD, Zuckerman SH, Ruotolo G, Chen L, Issa M, Macias WL, McInnes IB. Baricitinib Reduces GlycA Levels in Phase 2 and Phase 3 Clinical Trials in Patients with Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baricitinib-reduces-glyca-levels-in-phase-2-and-phase-3-clinical-trials-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baricitinib-reduces-glyca-levels-in-phase-2-and-phase-3-clinical-trials-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis/