Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster I: Treatment Patterns and Response
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients (pts) tend to have higher absolute neutrophil count (ANC) values compared to healthy individuals.1 Baricitinib (BARI), an oral, selective Janus kinase (JAK)1/JAK2 inhibitor,2 reduced disease activity levels in RA pts with an inadequate response (IR) to methotrexate (MTX).3 BARI also reduced neutrophil counts in these pts.3 Herein we assessed the association between changes in ANC and the reduction in inflammation, as determined by high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) levels, and by inference clinical responses in pts receiving BARI 4-mg in the RA-BEAM trial.
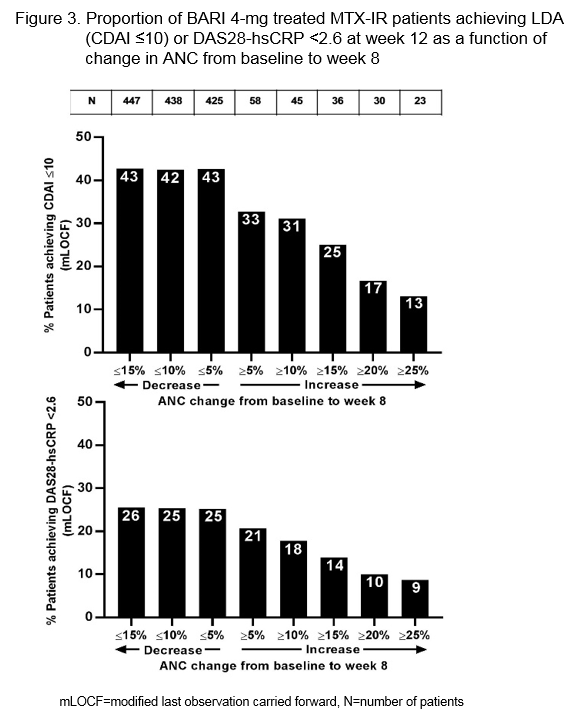
Methods: RA-BEAM was a 52 week (wk) Phase 3 trial with RA pts randomized to placebo, BARI 4-mg once daily, or adalimumab 40-mg biweekly. Primary end-point of the trial was the proportion of pts achieving ACR20 at wk 12. This post hoc analysis evaluated the changes in observed ANC in BARI 4-mg treated pts with either ≤15% or ≥70% reduction in hsCRP from baseline to wk 12. Proportion of pts achieving low disease activity (LDA), as determined by Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) ≤10, or DAS28-hsCRP <2.6 at 12 wks was evaluated as a function of percent change in ANC from baseline to wk 8, at which time a peak decline in ANC was observed (Figure 1).
Results: Of the 487 pts in the BARI 4-mg treatment arm of the RA-BEAM study, 78 pts demonstrated ≤15% reduction in hsCRP and 298 pts had ≥70% reduction in hsCRP at 12 wks. The mean neutrophil count at wk 8 in pts with ≤15% reduction in hsCRP was higher when compared to pts with ≥70% reduction (Figure 2), suggesting that the decline in ANC was associated with reduction in the inflammatory process. The reduction in ANC was associated with an improved clinical response as demonstrated by the proportion of pts achieving LDA (CDAI ≤10) or DAS28-hsCRP <2.6 at 12 wks. In contrast, a smaller proportion of pts achieved LDA when an increase in ANC was observed (Figure 3). These observations were similar regardless of the use of concomitant oral corticosteroids.
Conclusion: The decline in ANC is associated with a reduction in the overall inflammatory process and may also be associated with disease activity.
References: 1.Syed KM J Clin Rheumatol (1996) 2. Fridman JS J Immunol (2010) 3.Taylor PC et al N Engl J Med (2017)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McInnes IB, Simon LS, Moots RJ, Arora VK, Bradley JD, Muram D. An Evaluation of Absolute Neutrophil Count As a Biomarker of Inflammatory and Clinical Disease Activity in Baricitinib-Treated Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-evaluation-of-absolute-neutrophil-count-as-a-biomarker-of-inflammatory-and-clinical-disease-activity-in-baricitinib-treated-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-evaluation-of-absolute-neutrophil-count-as-a-biomarker-of-inflammatory-and-clinical-disease-activity-in-baricitinib-treated-patients/