Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The objective of this study was to determine whether extended versus flexed knee position is superior for arthrocentesis.
Methods: 55 clinically effusive knees with osteoarthritis underwent arthrocentesis: 20 knees in the extended knee position using the lateral superior approach, and 35 knees in the flexed knee position using the inferiolateral approach. Conventional arthrocentesis maneuvers including manual compression were used and fluid yield in milliliters measured. After fluid return ceased in the flexed knee, constant compression was applied using an elastomeric knee brace on the superior knee and additional fluid yield recorded. The measurement data were compared using the Student test.
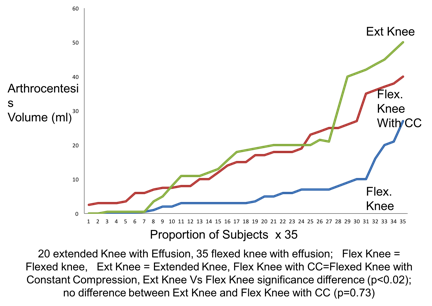
Results: Fluid yield for arthrocentesis with the extended knee was greater (191% greater) than the flexed knee: extended knee: 16.9±15.7 ml, flexed knee 5.8±6.3 ml (difference 11.1 ml, CI 0.91 <8.8< 16.7, p<0.02). After constant compression to the flexed knee fluid yields were identical (1% different): extended knee: 16.9±15.7 ml, flexed knee 16.7±11.3ml (difference -0.2 ml, 95% CI 11.09 <-2.7< 5.6, p=0.73).
Conclusion: The extended knee lateral approach is superior to the flexed knee approach for conventional arthrocentesis. However, when constant compression is applied, the two approaches have identical fluid yields. This new flexed knee constant compression technique is particularly useful for patients who cannot get onto the examining table, who are in wheelchairs, have flexion contractures, or who cannot otherwise extend their knee.
Figure 1: Fluid yields in extended and flexed knee positions
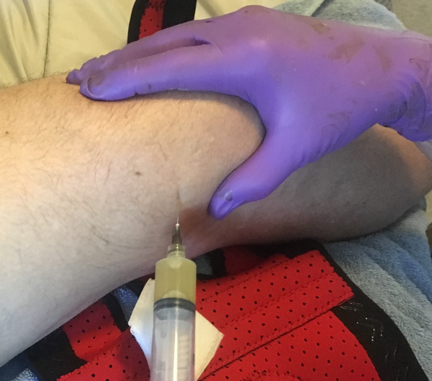
Figure 2: Arthrocentesis in Extended Knee Position
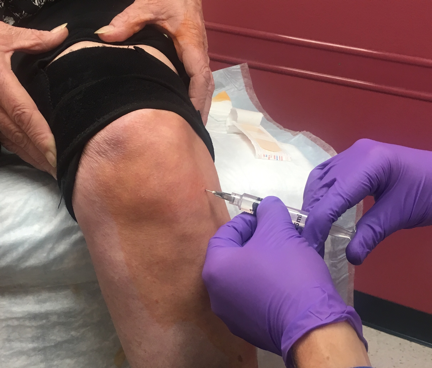
Figure 3: Arthrocentesis in Flexed Knee Position
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yaqub S, Bhavsar T, Cabacungan R, Bennett J, Fangtham M, Emil NS, Fields R, Konstantinov K, Bankhurst A, Haseler L, Sibbitt W Jr.. Comparison of Flexed and Extended Knee Arthrocentesis and the Role of Constant Compression [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-flexed-and-extended-knee-arthrocentesis-and-the-role-of-constant-compression/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-flexed-and-extended-knee-arthrocentesis-and-the-role-of-constant-compression/