Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The efficacy and safety of certolizumab pegol (CZP) treatment in combination with dose-optimized MTX in Japanese MTX-naïve early RA patients (pts) with poor prognostic factors have previously been reported.1 Here, we report the factors at Week (Wk) 52 associated with the maintenance of clinical remission and radiographic non-progression after discontinuation of CZP treatment to Wk 104.
Methods: MTX-naïve early RA pts entered C-OPERA (NCT01451203)1 and were randomized to CZP+MTX (n=159) or placebo (PBO)+MTX (n=157); oral MTX was escalated to 16 mg/wk by Wk 8, if tolerated (optimized MTX). After completing the 52-wk double-blind period, CZP or PBO was discontinued and MTX therapy continued up to Wk 104 (post-treatment [PT] period; CZP+MTX→MTX). All pts (n=108) who were initially randomized to CZP+MTX and entered the PT period were included in these analyses. Clinical disease activity, remission (SDAI, DAS28[ESR], Boolean, at Wks 52 and 104), and radiographic non-progression rates (change from baseline [BL] or Wk 52 ≤0.5 in van der Heijde modified Total Sharp Score [mTSS], joint erosion score, and joint space narrowing score) were calculated. Missing values used last observation carried forward (LOCF) for remission and linear extrapolation for radiographic outcomes. Post-hoc logistic regression analyses were used to investigate the Wk 52 factors (DAS28[ESR], HAQ-DI, mTSS, rheumatoid factor [RF], anti-CCP antibody, and MMP-3) associated with remission and radiographic non-progression. Factors with p<0.1 in univariate analyses were included in multivariate analyses.
Results: At Wk 52, 77.8%, 79.6%, and 61.1% pts were in DAS28(ESR), SDAI, and Boolean remission, respectively. Remission rates decreased from Wk 52 to Wk 104 after stopping CZP, although most pts maintained remission (Figure A). Over 90% pts who entered the PT period achieved radiographic non-progression during CZP+MTX treatment; the non-progression rate was maintained after stopping CZP from Wks 52–104 (Figure B). In sensitivity analyses, DAS28(ESR) at Wk 52 was associated with DAS28(ESR), SDAI, and Boolean remission at Wk 104 (odds ratio: 0.23, 0.29, 0.36); Wk 52 RF was associated with SDAI and Boolean remission at Wk 104 (odds ratio: 0.67 and 0.69) (Table).
Conclusion: Clinical remission can be maintained up to an additional 52 wks after CZP discontinuation in early RA pts with poor prognostic factors. Both low disease activity and low RF at CZP discontinuation (Wk 52) were associated with the maintenance of clinical remission. Radiographic non-progression was observed even after CZP discontinuation at Wk 52. References: 1. Atsumi T. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75(1):75–83 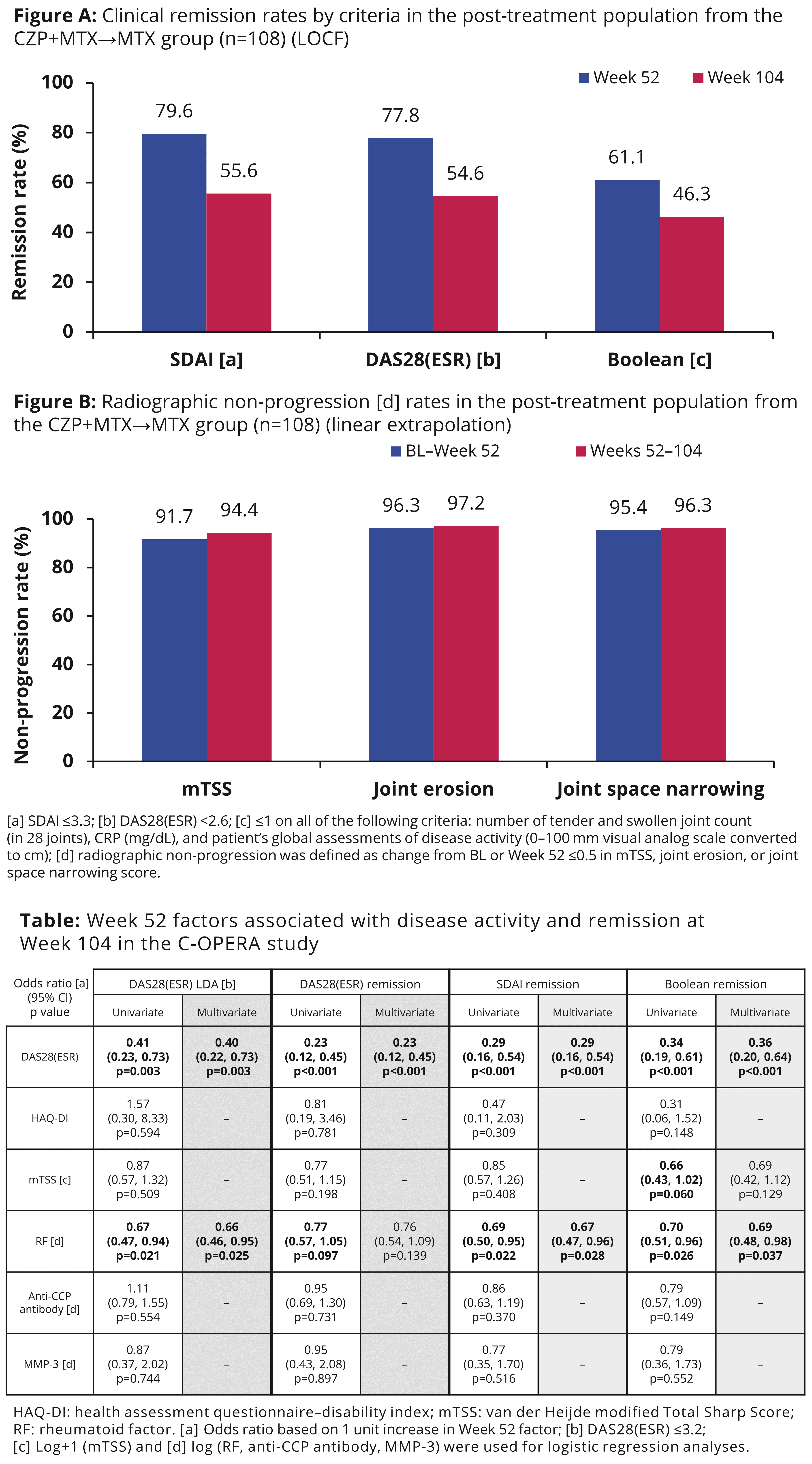
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tanaka Y, Atsumi T, Yamamoto K, Takeuchi T, Yamanaka H, Ishiguro N, Eguchi K, Watanabe A, Origasa H, Shoji T, Ralston P, van der Heijde D, Miyasaka N, Koike T. Maintenance of Clinical Remission and Radiographic Non-Progression with MTX after Completion of 1 Year Initial Treatment with Certolizumab Pegol in Japanese Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/maintenance-of-clinical-remission-and-radiographic-non-progression-with-mtx-after-completion-of-1-year-initial-treatment-with-certolizumab-pegol-in-japanese-patients-with-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/maintenance-of-clinical-remission-and-radiographic-non-progression-with-mtx-after-completion-of-1-year-initial-treatment-with-certolizumab-pegol-in-japanese-patients-with-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/
