Session Information
Session Type: ACR Plenary Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor under investigation for treatment of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). This study evaluated tofacitinib efficacy and safety vs placebo (PBO) in patients (pts) with active PsA.
Methods: This was a randomized, PBO- and active-controlled, double-blind, multicenter, Phase 3 study. Eligible pts had a diagnosis of PsA for ≥6 months, fulfilled ClASsification criteria for Psoriatic ARthritis (CASPAR), had active arthritis (≥3 tender/painful and ≥3 swollen joints) and active plaque psoriasis, inadequate response to ≥1 csDMARD, and were tumor necrosis factor-inhibitor-naïve. Pts were randomized 2:2:2:1:1 to tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID; n=107), tofacitinib 10 mg BID (n=104), adalimumab 40 mg subcutaneous injection once every 2 weeks (n=106), PBO→tofacitinib 5 mg BID (n=52) or PBO→tofacitinib 10 mg BID (n=53). Pts who initially received PBO advanced to tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID in a blinded manner at Month (M) 3. Ongoing treatment with a stable dose of 1 csDMARD was mandatory. Pts were followed through M12. The primary endpoints were ACR20 response rate and change from baseline in Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (ΔHAQ-DI) at M3.
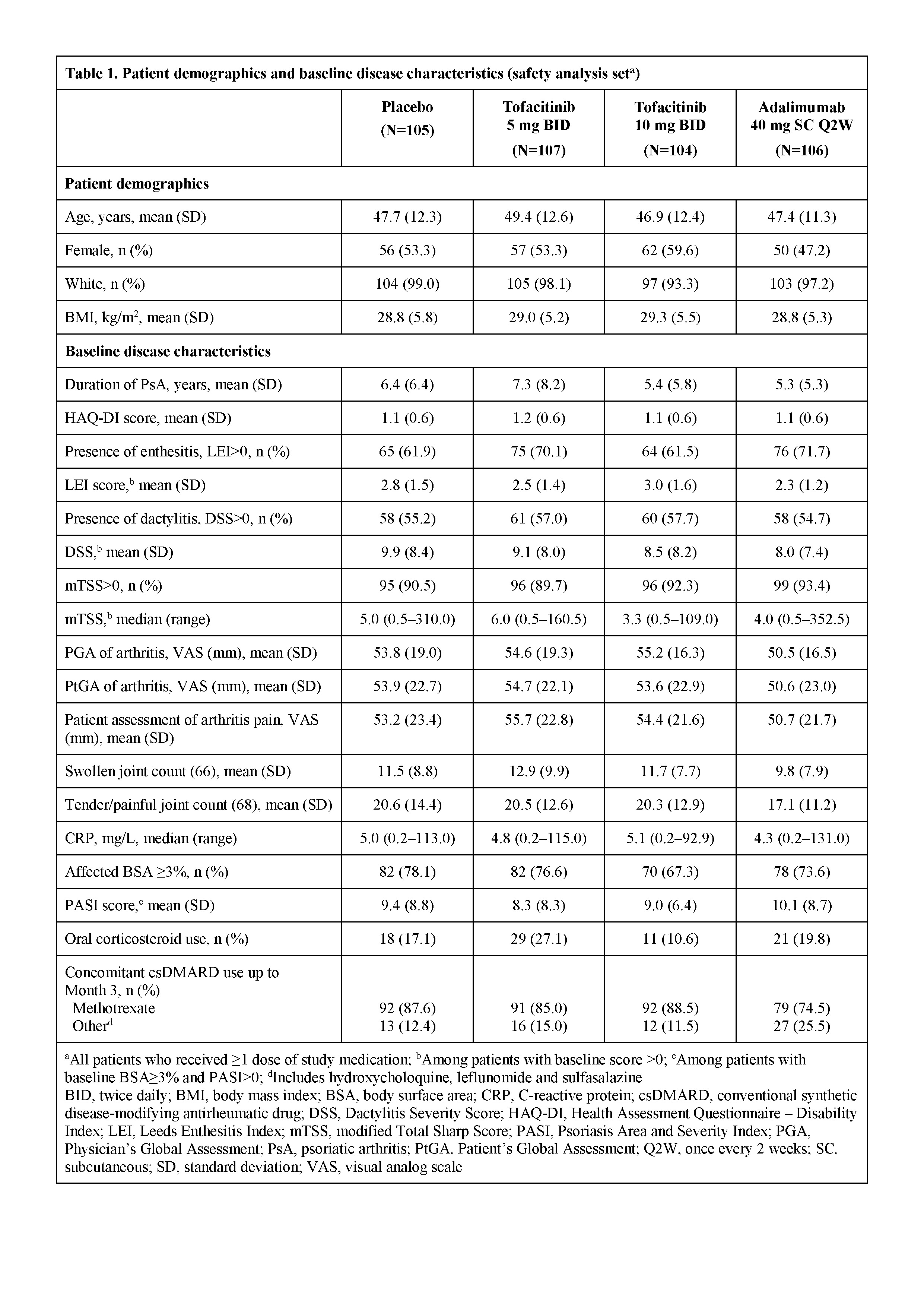
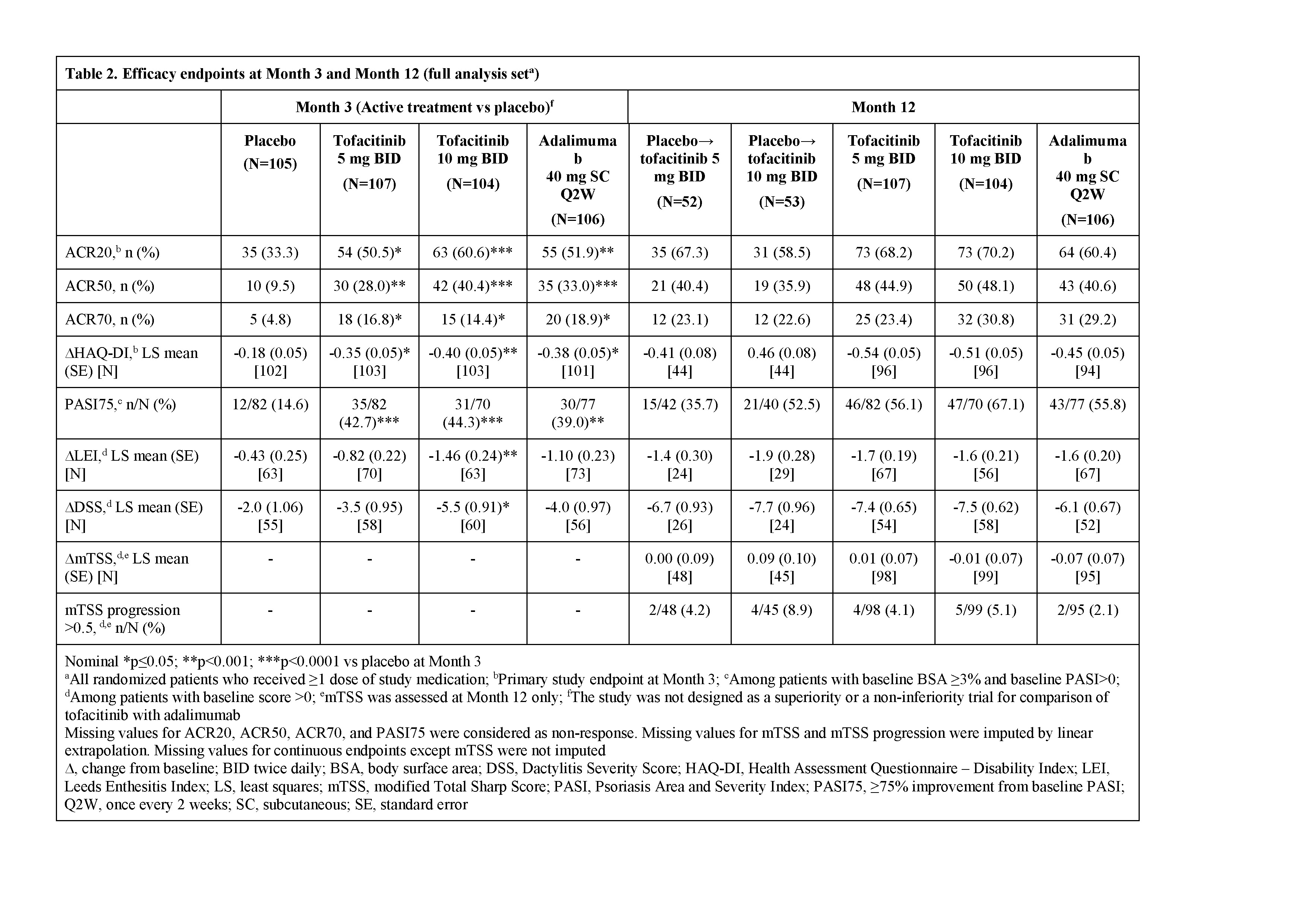
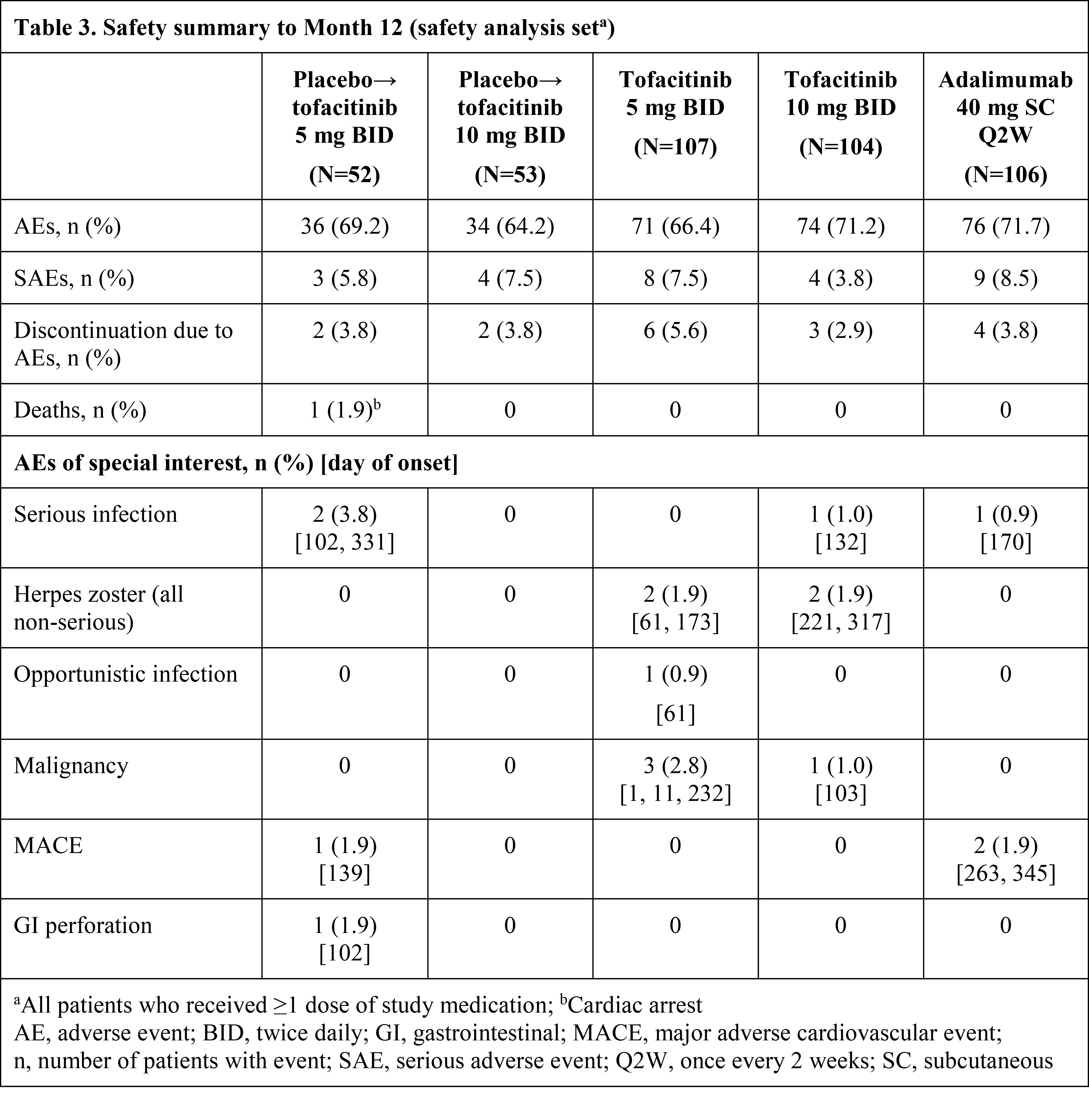
Results: Pt demographics and baseline disease characteristics were similar across groups (Table 1). Of the 422 randomized pts, 405 (96.0%) completed M3 and 373 (88.4%) completed M12. Significantly greater improvements in ACR20 response rates and ΔHAQ-DI were observed for both tofacitinib doses vs PBO at M3 and were maintained to M12 (Table 2); greater improvements were also observed for adalimumab vs PBO. Tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg BID demonstrated superiority vs PBO for ACR20 response rate as early as Week 2 (22.4% and 31.7% vs 5.7%; p<0.001). Secondary efficacy endpoints supported the primary findings (Table 2). Safety findings through M12 were similar between groups (Table 3). The most common adverse events over 12 months were upper respiratory tract infection (7.5–10.6% of pts across groups), nasopharyngitis (7.5–11.5%), and headache (3.8–10.6%).
Conclusion: Tofacitinib was superior to PBO in ACR20 response rate and ΔHAQ-DI at M3, with superiority vs PBO as early as Week 2 (first assessment) for ACR20, which was maintained to M12. Secondary endpoints supported the primary analyses. No new safety risks were identified vs previous studies in RA or psoriasis pts.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease PJ, Hall S, FitzGerald O, van der Heijde D, Merola JF, Avila-Zapata F, Cieślak D, Graham D, Wang C, Menon S, Hendrikx T, Kanik K. Efficacy and Safety of Tofacitinib, an Oral Janus Kinase Inhibitor, or Adalimumab in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis and an Inadequate Response to Conventional Synthetic Dmards: A Randomized, Placebo‑Controlled, Phase 3 Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-tofacitinib-an-oral-janus-kinase-inhibitor-or-adalimumab-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-and-an-inadequate-response-to-conventional-synthetic-dmards-a-randomized/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-tofacitinib-an-oral-janus-kinase-inhibitor-or-adalimumab-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-and-an-inadequate-response-to-conventional-synthetic-dmards-a-randomized/