Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Aspects and Treatment - Poster III: Biomarkers and Nephritis
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: An aptamer-based screening assay was used to analyze the levels of 1129 different proteins in 24 human urine samples (8 active lupus nephritis (LN), 8 inactive LN, and 8 healthy controls).
Methods: The assay revealed 281 proteins to be significantly elevated in both SLE patients relative to healthy controls and in active LN relative to inactive LN. These proteins were then analyzed to determine their effectiveness as urinary biomarkers for lupus nephritis.
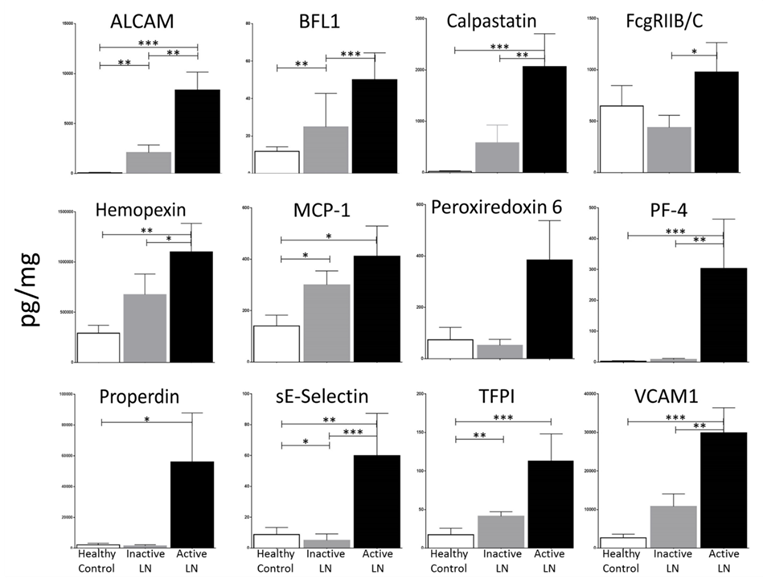
Results: Ingenuity Pathway Analysis revealed that the upregulated proteins belong to known inflammatory, fibrosis, and chemokine/cytokine networks. In an independent cohort of 93 subjects (16 active LN, 52 inactive LN, 25 healthy controls), urine ALCAM, BFL1, calpastatin, hemopexin, PRX6, PF4, properdin, sE-selectin, TFPI and VCAM1 were ELISA-validated and shown to be once again significantly elevated in active LN compared to disease/healthy controls (Fig 1); they also correlated strongly with various clinical or laboratory parameters, including renal-SLEDAI, PGA, eGFR, ESR and C3/C4. In ROC curve analysis, many proteins showed significant AUC in classifying active LN: ALCAM [0.89], calpastatin [0.82], FcgRIIBC [0.70], hemopexin [0.76], PRX6 [0.67], PF4 [0.77], properdin [0.71], TFPI [0.77] and VCAM1 [0.81]. Lasso logistic regression analysis identified a 4-marker-panel (PF4, TFPI, PRX6 and VCAM1) as the best discriminator of active LN, with an ROC AUC value of 0.93. A longitudinal cohort study of 18 LN patients with an average of 3 visits per patient revealed these urine markers to vary considerably in their ability to track with standard disease indices.
Conclusion: Urine ALCAM, BFL1, calpastatin, FcgRIIBC, hemopexin, MCP1, NAP2, PRX6, PF4, properdin, sE-selectin, TFPI and VCAM1 emerge as potential urinary biomarkers of lupus nephritis; further studies are warranted to establish their biomarker potential and pathogenic relevance. 
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Stanley S, Ding H, Pedroza C, Saxena R, Petri M, Mohan C. Comprehensive Aptamer-Based Screening of 1129 Proteins Reveals Novel Urinary Biomarkers of Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comprehensive-aptamer-based-screening-of-1129-proteins-reveals-novel-urinary-biomarkers-of-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comprehensive-aptamer-based-screening-of-1129-proteins-reveals-novel-urinary-biomarkers-of-lupus-nephritis/
