Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To inform the task force for the 2016 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of RA on the evidence regarding the efficacy and safety of glucocorticoids (GCs), conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) and targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs) in RA by performing a systematic literature review (SLR). <>
Methods: A SLR update using PubMed, Embase and the Cochrane library was performed (2013 – 2016) to assess the efficacy and safety of GCs, csDMARDs (as monotherapy or combination therapy) and tsDMARDs (tofacitinib and baricitinib) in randomized clinical trials. Meta-analysis was performed when possible. Risk of bias (RoB) was assessed using the Cochrane Collaboration tool.
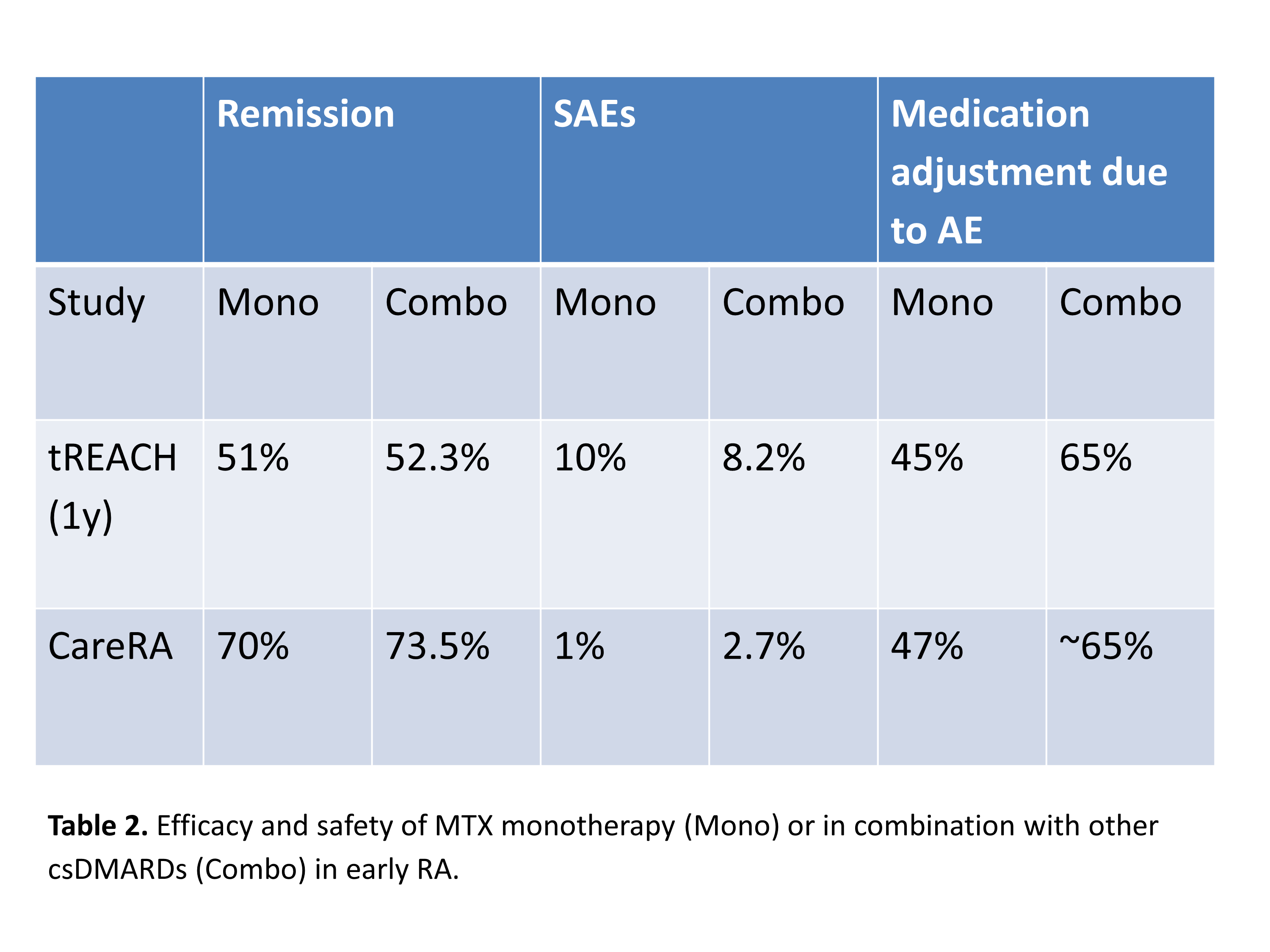
Results: With regard to GCs, among 348 hits 5 studies were included in the analysis (table 1). Even patients without poor prognostic factors benefit from the addition of GCs to methotrexate (MTX). Lower doses of GCs seem to be as effective as higher doses. Long-term results of the CAMERA II trial showed increased cardiovascular risk for the early RA patients treated for at least 2 years with 10mg/d prednisone (not included in the table). With regard to csDMARDs, among 518 hits 2 new studies comparing MTX monotherapy with MTX in combination with another csDMARD without differences in GCs usage were identified. The tREACH trial, which used tight-control principles, reported a statistically significant benefit of combination therapy over monotherapy at 3 months that had disappeared at 12 months (disease activity, functional ability and radiographic progression) (table 2). In addition, more medication adjustments were needed in the combination group. In the CareRA trial combination with other csDMARDs was not superior to methotrexate monotherapy in early RA and monotherapy was better tolerated. With regard to tofacitinib (n=7) and baricitinib (n=9) RCTs had been meta-analysed showing that both are more effective than placebo on background MTX or de novo MTX (MTX-naïve) in different patient populations (MTX-naïve, csDMARD and bDMARD inadequate responders) with a pooled OR (95% CI) for ACR20 response for tofa and bari vs placebo of 3.1 (2.0-4.7) and 3.6 (2.4-5.5), respectively.
Conclusion: New evidence on the efficacy and safety of DMARDs in RA confirmed the benefit of the addition of GCs to csDMARDs in early RA but pointed to long-term cardiovascular risk. MTX monotherapy is as effective as MTX in combination with csDMARDs but better tolerated. Tofacitinib and baricitinib are effective tsDMARDs in various RA populations.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chatzidionysiou K, Emamikia S, Nam JL, Ramiro S, Smolen J, van der Heijde D, Dougados M, Bijlsma JW, Burmester G, Scholte-Voshaar M, van Vollenhoven R, Landewé R. Efficacy and Safety of Conventional and Targeted Synthetic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs As Well As Glucocorticoids: A Systematic Literature Review Informing the 2016 Update of the Eular Recommendations for the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-conventional-and-targeted-synthetic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-as-well-as-glucocorticoids-a-systematic-literature-review-informing-the-2016-update-of-the-eular/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-conventional-and-targeted-synthetic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-as-well-as-glucocorticoids-a-systematic-literature-review-informing-the-2016-update-of-the-eular/